The management Plan was produced many years ago and needs updating.
It can be found on the BC government website at:
https://nrs.objectstore.gov.bc.ca/kuwyyf/race_rocks_er_mp_20020515_502695e402.pdf
Author Archives: Garry Fletcher
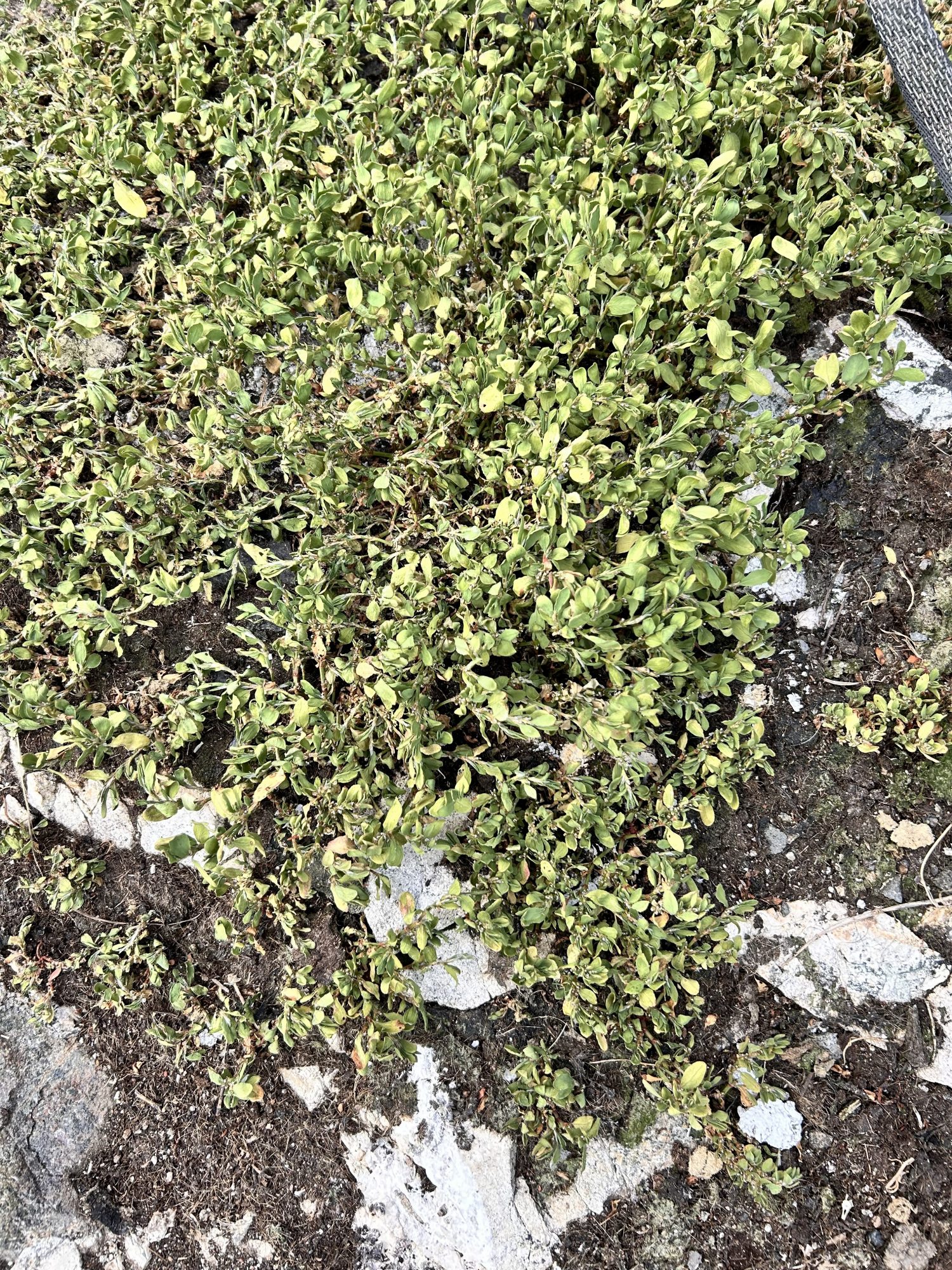
Polygonum aviculare : prostrate knotweed- The Race Rocks taxonomy
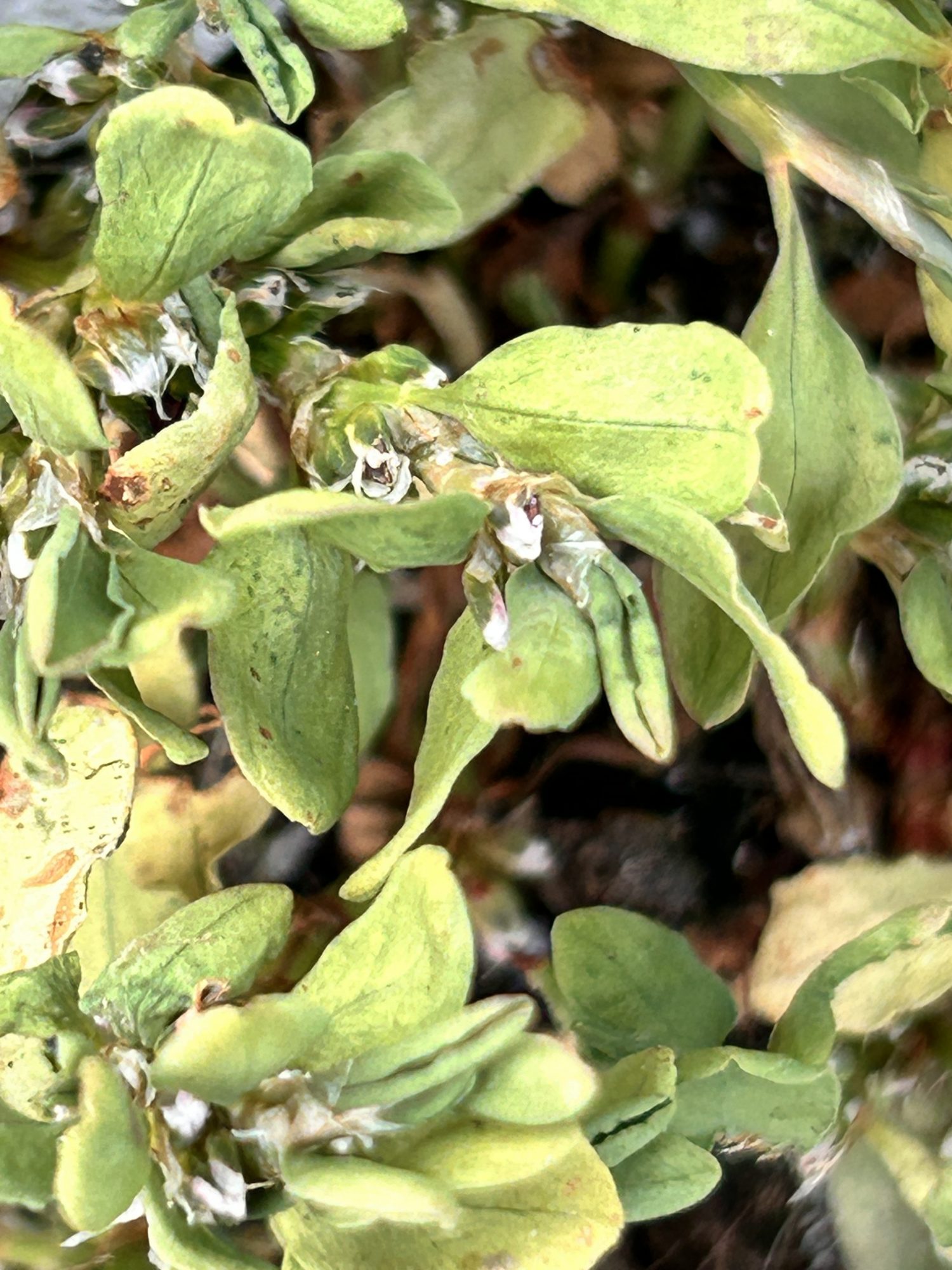
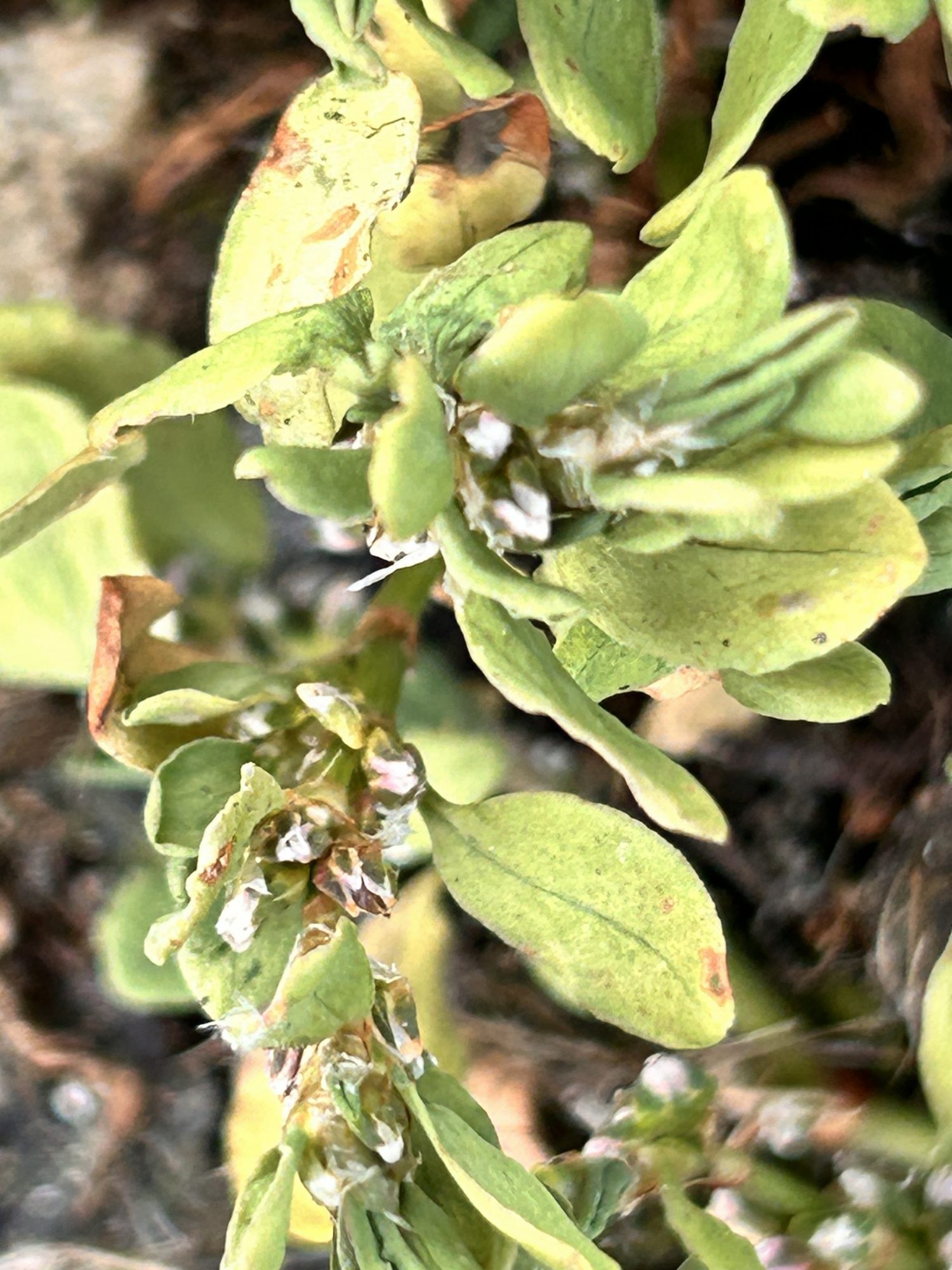
This summer there is a proliferation of knotweed in areas on Race Rocks in which it has not occurred before : also see: https://racerocks.ca/polygonum-aviculare-prostrate-knotweed-the-race-rocks-taxonomy/
- close up of flowers
The following Classification is from Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polygonum_aviculare
| Scientific classification |
|
|---|---|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Caryophyllales |
| Family: | Polygonaceae |
| Genus: | Polygonum |
| Species: |
P. aviculare
|
| Binomial name | |
| Polygonum aviculare
L. 1753
commonname : Common knotgrass or Prostrate knotweed
|
|
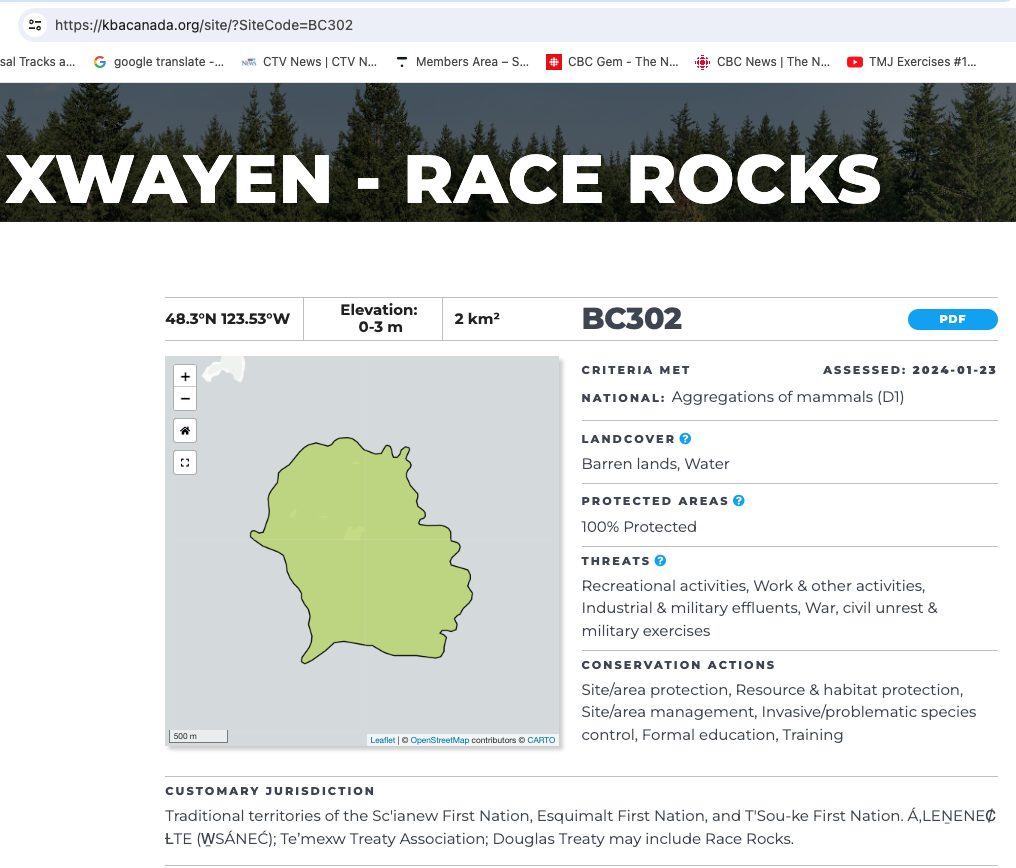
Race Rocks Key Biodiversity Area ( KBA)
Race Rocks has been designated as a Key Biodiversity Area, joining several other KBAs in the Victoria Area.
Ecoguardian Change-over day
FRIDAY 19 April CHANGE-OVER DAY
Sunny with brisk breeze. 7C NE 18/gusts33
6.30 AM Observed 9 Steller, 3 Cal plus two young (or females?) on Welcome Rock (near jetty).
Five Elephant seals. Gulls still at rest. Very odd to see no guillemots in sun from north window.
Early detonation on DND.
Housekeeping: The usual bath/floors/fridge. Wiped window casings and sills of new windows;
swept baseboards; cleaned light switches and cabinet pulls.
Flowers bloooming
Eco-guardians Allen and\ ilka Olsen
THURSDAY 18 April
Clear and sunny with brisk breeze. Numerous VHF warnings of CA warship conducting
ammunition firings. DND detonating explosives. Continued to view wildlife and vegetation.
Calendula beginning to bloom; flowering beach pea (Lathyrus japonica) on stump battered by
gale. Magnificent display of brodiaea along west house foundation. Found that the invasive
sedum is supported on sealion felt; beginning to invade grass.
Good recovery of grasses and other greens.
Chopped wood/filled stove box and cleaned area; filled batteries; finished with solar panel
wash.
Not a single wildlife tour boat.
Animal Census April 17, 2024
WEDNESDAY 17 April CENSUS DAY
Calm & sunny. Wind N6/18 gusts mid-morning.
Began count on tower at 6.30 to count especially gulls while still mostly at rest.
Vessel Traffic: At any time, 5-8 freighters including what looks to be super tankers. CA naval
patrol vessel. 8-10 fishers out at all time of day. May be after prawns as some floats visible. Not
a single tour vessel!
DND detonated explosives 4 times; one blast shook windows.
Facility Work: Cleaned solar panels; attached hose from student bldg.
Began sawing/splitting wood but again interrupted by E seals near by.
Cleaned/rearranged kitchen drawers; cleaned top of fridge
Cleaned out freezer
Census Count
Mammals: Sealion 43
Steller 12
California 31
Seal 77
Elephant seal 5
Birds: Gull 1531
Guillemot 150
Oystercatcher 8 (4 pair)
Bald eagle 2 (1 adult; 1 immature; 7 immature on 18 th )
Harlequin 27
Cormorant 100
Scoter white wing 7
Dunlin 4
Turnstone 6
Surfbird 5 (10 seen on 15 th )
Savanah sparrow 1
Golden-crowed kinglet 1 (seen 13-14th)
Junco 1 (seen on 15th)
Crow 1
Canada goose 8 (4 pair)
Moulting Elephant seals
Eco-guardians Allen and ilka Olsen
TUESDAY 16 April
Winds have lessened but still brisk and; cool out—West 14/gust 24—mid-afternoon.
Continue to go up tower to prepare for census day tomorrow. I’ll dispense with today’s count
as nothing extraordinary spotted except 4 dunlin and possibly 6 Cassin auklets (too swift for pic).
Birds are definitely pairing and prepping for nesting. Found a dead sealion on east shore well
along in decay.
Two additional moulting E seals came ashore; total now 5. Some vocalize frequently.
Of interest was the vessel traffic: HMCS frigate towed along south shore of Bentick to
Quarantine Cove. One likes to think that the two towing tugs have a lower carbon footprint
than the engine on frigate. Four detonations from DND. Spill Response vessel cruised by. Five-
7 freighters transversing at any time; several cruise ships. Number of wildlife tour boats
definitely correlate to number cruise ships in harbour.
Facility Work: Gathered, split and stacked wood, Washed windows.
Animal Census April14
by Eco-guardians Allen ilka Olsen MONDAY 15 April
Still windy. What a difference a day makes! At 7.15 only a single sealion on jetty (mature male
Cal); only 11 sealions on rocks near jetty/nine relocated to Middle Rocks. The ‘Two Sisters’
moulting Elephant seals separate but reunited and tucked into vegetation for wind protection.
Single moulting Elephant seal inactive most of day. The seal reported by Joan last week to Van
Aquarium not seen again.
Lots of freighter traffic—7 at once. Now watching for HMCS Max Bernays, new arctic patrol
vessel, to arrive at Esquimalt @1030. Failed to see its arrival, however a navy frigate was
observed. As well, US Coast Guard. Only one private vessel came in the turbulent seas.
Maximum flood today extremely dramatic with standing waves.
Cormorants and guillemots feeding in north water. Immature eagle on rocks next to jetty
keeping 50 guillemots from favourite, sunny east-facing perch. 20 Oystercatcher on seal rock
this morning; 10 surfbird; 6 Harlequin
Spent windy day (41 W/62 gusts) observing animal behaviour (and later in week):
1. Sealion— 18 mostly Cals have remained on rocks near jetty. 25 mostly Stellers have
relocated to Middle Rocks. On Saturday observed 18-20 sealions in water west & near
South Islands all day simply floating; occasionally one would swim staying nearby. They
remained there until dark but were gone Sunday morning. Observed this behaviour with
8 on Wed; group would occasionally go into herding mode.
2. Elephant seal—Moulting large females (?) very attached to each other; one observed
grooming/rubbing itself on the one less advanced in its moult. One quite vocal when
separated from the other. Youngster stays completely away from The Sisters (so
named by Joan).
3. Stellers roar; Cals bark; E seals honk/snore/growl/trumpet (played poorly).
4. Oystercatcher—single bathing in inter-tidal pool.
5. Surfbird—10 bathing in inter-tidal pool.
6. Eagles—three immature perched shoulder to shoulder on Turbine Rock; three more
immatures shoulder to shoulder on West Rock. Odd behaviour. A single elsewhere.
7. Cormorants leave the Rock each evening to roost (on DND land?) and return in droves in
early morning.
Animal census April 14/2024
SUNDAY 14 April
Internet restored by IT Dan by 1200.
1330 from tower:
Mammals: 51 seals on South Islands; 2 on Middle Rocks + 1 on West Rock. 27 sealions on Race
Rocks; 9 on Middle Rocks; 2 on West Rocks.
Young Elephant seal observed heading to water; not seen rest of day.
Birds:
22 cormorants
Weather: Sunny with lots of solar power generated. Lowered flag. Gale force winds by mid-
afternoon; big blow all night.
Census April 13/2024
Eco-guardians Allen & Ilka Olsen
SATURDAY 13 April
Weather: Warm; sunny; slight breeze
Birds: 100 guillemot,
52 cormorant (1 injured,)
4 harlequin,
4 oystercatcher,
6 Canada goose
6 turnstone,
6 surfbird,
1 Golden-crown kinglet
Mammals:
4 Elephant seal,
17 sealion
Maintenance: Internet down from 30 pm until noon Sunday; many trips to gen
building/eventually told to wait for IT help on Sunday morning.
Cleaned hand railing &molding in stairwell/some cabinet doors