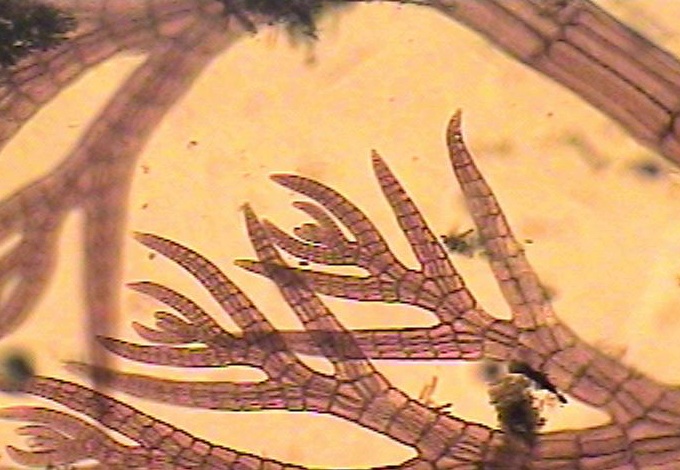
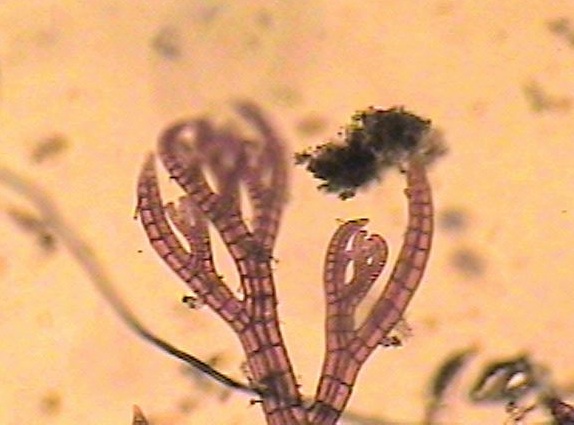
UPDATE 2023 Derek Sterling has taken some excellent photos and written about the return of barn Swallows to Race rocks
This video shows the barn swallow fledglings in their nest.
June, 2005: the adult birds were observed going in and out of the vents on the north side of the water desalinator building on Race Rocks.
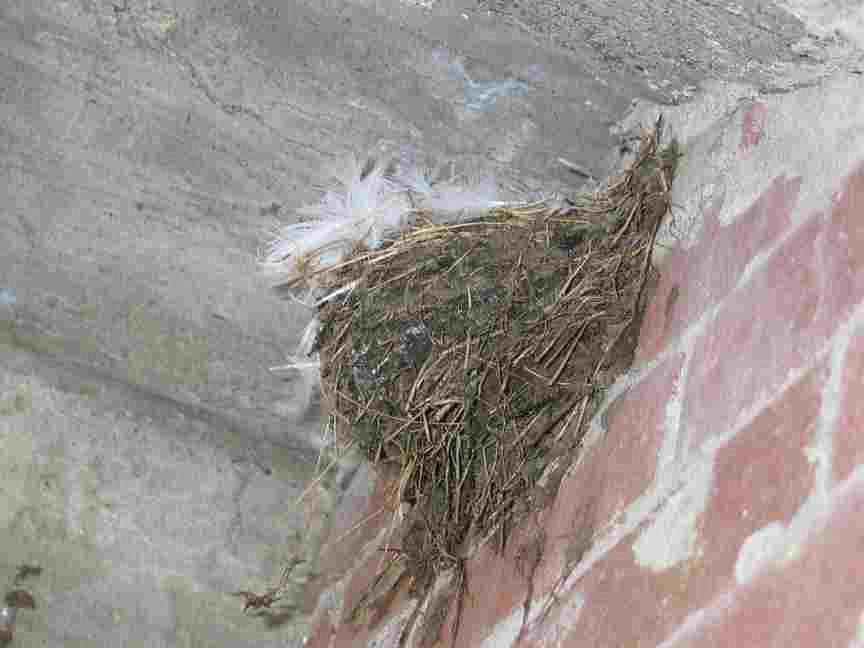 June-July 2006: This nest was built of mud, lined with goose and gull feathers under the concrete stairway of the Marine Science Centre. (Tis structure was replaced with a wooden staircase in 2020) On July 4, they were seen to be flying in and out of the opening frequently. Barn swallows are frequent nesters in rural areas all throughout western Canada. They choose a nesting site always located in an assured dry location.Frequently this is an out-building on a farm with an open door or window. They have excellent aerodynamic maneuvering control as they fly quickly over open areas catching insects with a wide opening mouth. They are valued for their voracious appetite for mosquitoes and flies. With their food being flying insects, the island certainly provides an abundant supply of the kelp fly Coelopa vanduzeei
June-July 2006: This nest was built of mud, lined with goose and gull feathers under the concrete stairway of the Marine Science Centre. (Tis structure was replaced with a wooden staircase in 2020) On July 4, they were seen to be flying in and out of the opening frequently. Barn swallows are frequent nesters in rural areas all throughout western Canada. They choose a nesting site always located in an assured dry location.Frequently this is an out-building on a farm with an open door or window. They have excellent aerodynamic maneuvering control as they fly quickly over open areas catching insects with a wide opening mouth. They are valued for their voracious appetite for mosquitoes and flies. With their food being flying insects, the island certainly provides an abundant supply of the kelp fly Coelopa vanduzeei
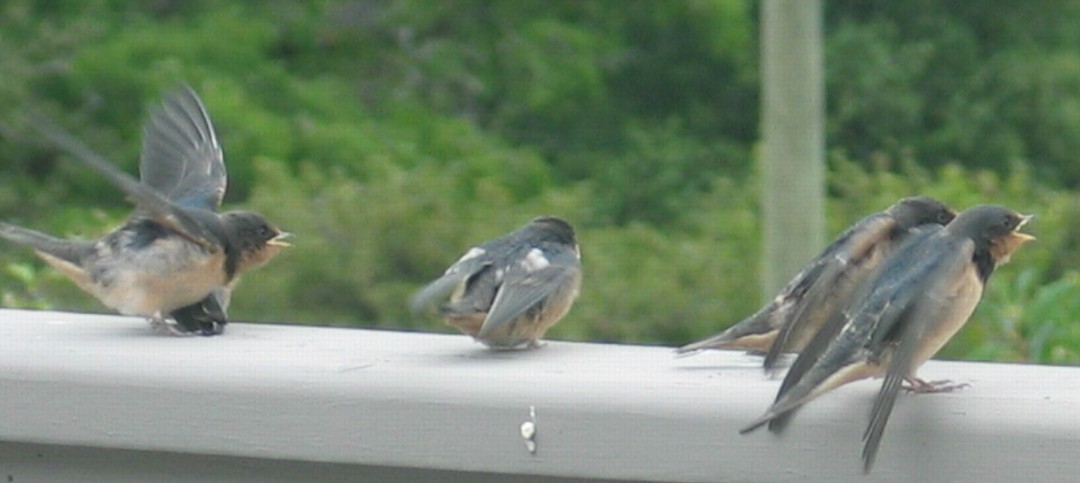



These pictures were taken of a newly-fledged family on a balcony in nearby Metchosin. The juvenile birds were waiting to be fed
An interesting question was posed by someone recently. Since swallows fly from the brightly lit outside rapidly into a dark building, do they have a specially evolved vision system for rapid dark adaptation? We know that bats do this with their echolocation system, but birds don’t have that ability.
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Sub-phylum: Vertebrata
Class: Aves
Order: Passeriformes
Family: Hirundinidae
Genus: Hirundo
Species: rustica
Common Name:Barn swallow
Physical Description:
The barn swallow is the only one of its family with a deeply forked tail. It can be identified by its rusty under parts and orange rump as well as a dark orange forehead and throat. Like all swallows, it is a strong and elegant flyer. Its legs and bill are short, but it has a wide mouth for capturing insects. These birds are generally around 15 cm in length.
Habitat:
True to its name, the barn swallow is common near farms. It builds a nest of mud on the timbers of barns and other such buildings. It commonly inhabits caves and areas
underneath bridges. Barn swallows are migratory birds, and fly south from North America to South America for the winter.
Reproduction:
The length of incubation for barn swallow eggs is 13 to 17 days. They lay in open-cup nests made of mud pellets and grass. The eggs are speckled and nesting begins in the second half of May. If the pair of swallows is successful, two broods are raised each year.
Feeding Habits:
This swallow feeds exclusively on insects. Hunting typically takes place on or close to ground level. However, on summer afternoons, they can be seen flying high in the air. The barn swallow simply follows the desired insects and catches them in flight.
Global Distribution:
The barn swallow can be found in almost all parts of Canada and the USA. It typically inhabits every continent except Australia. It is a resident of rural areas, and populations are most heavily concentrated in southern Texas and central USA.
Predators:
Predators are most commonly cats and raccoons. When a predator approaches, the entire colony will launch an attack in a display of aerial acrobatics.
Interesting Fact:
The barn swallow’s song is long and twittering. They are commonly known to perch on wires and are often seen in large, mixed flocks.
References:
. Brunn, B. C.S. Robbins, Singer and H.S. Zim. 1966. A Guide to Field Identification, Birds of North America. Golden Press. New York, NY.
. http://www.americanartifacts.com/smma/per/b4.htm
. http://www.museum.gov.ns.ca/mnh/nature/msbirds/bns0261.htm