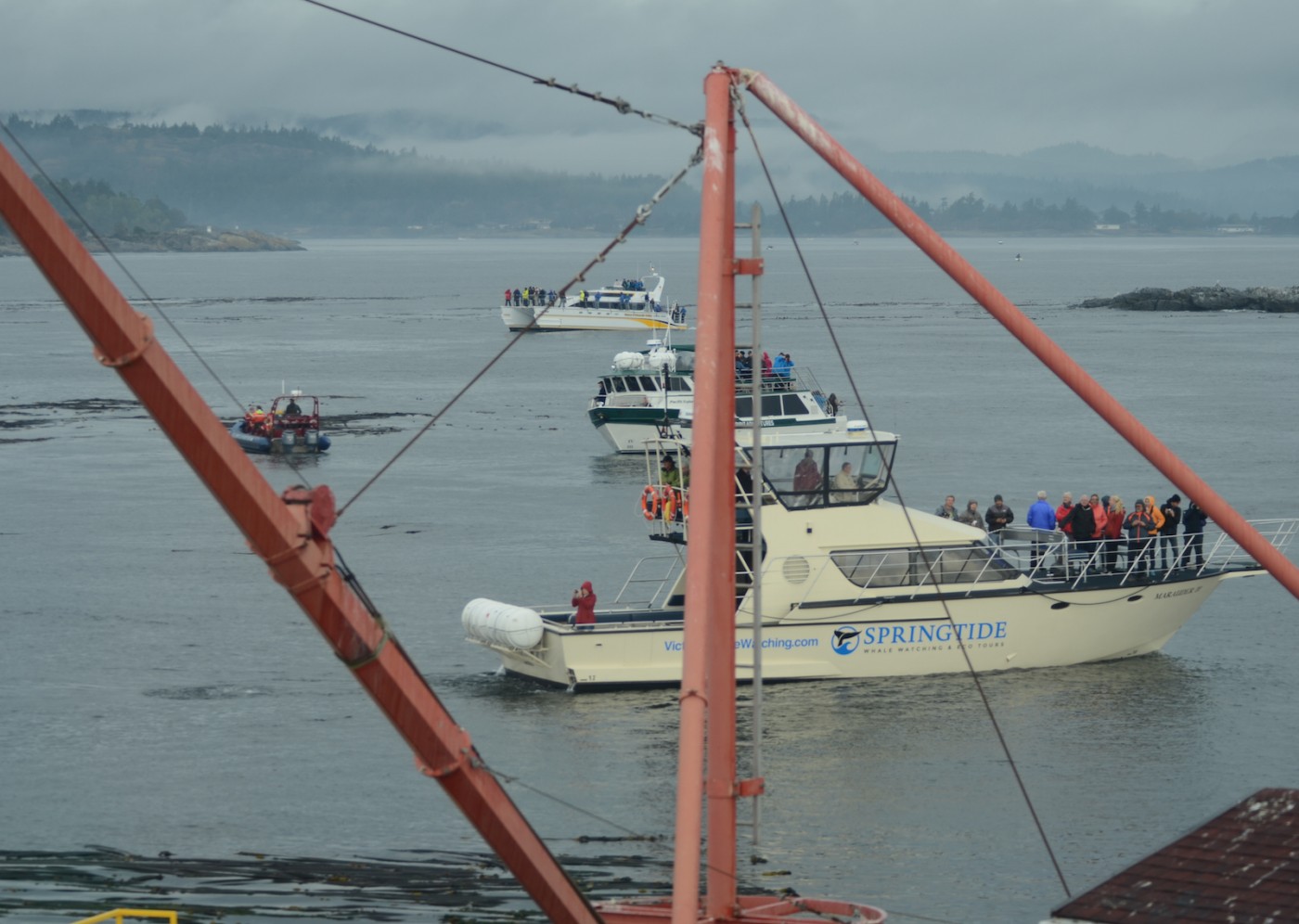
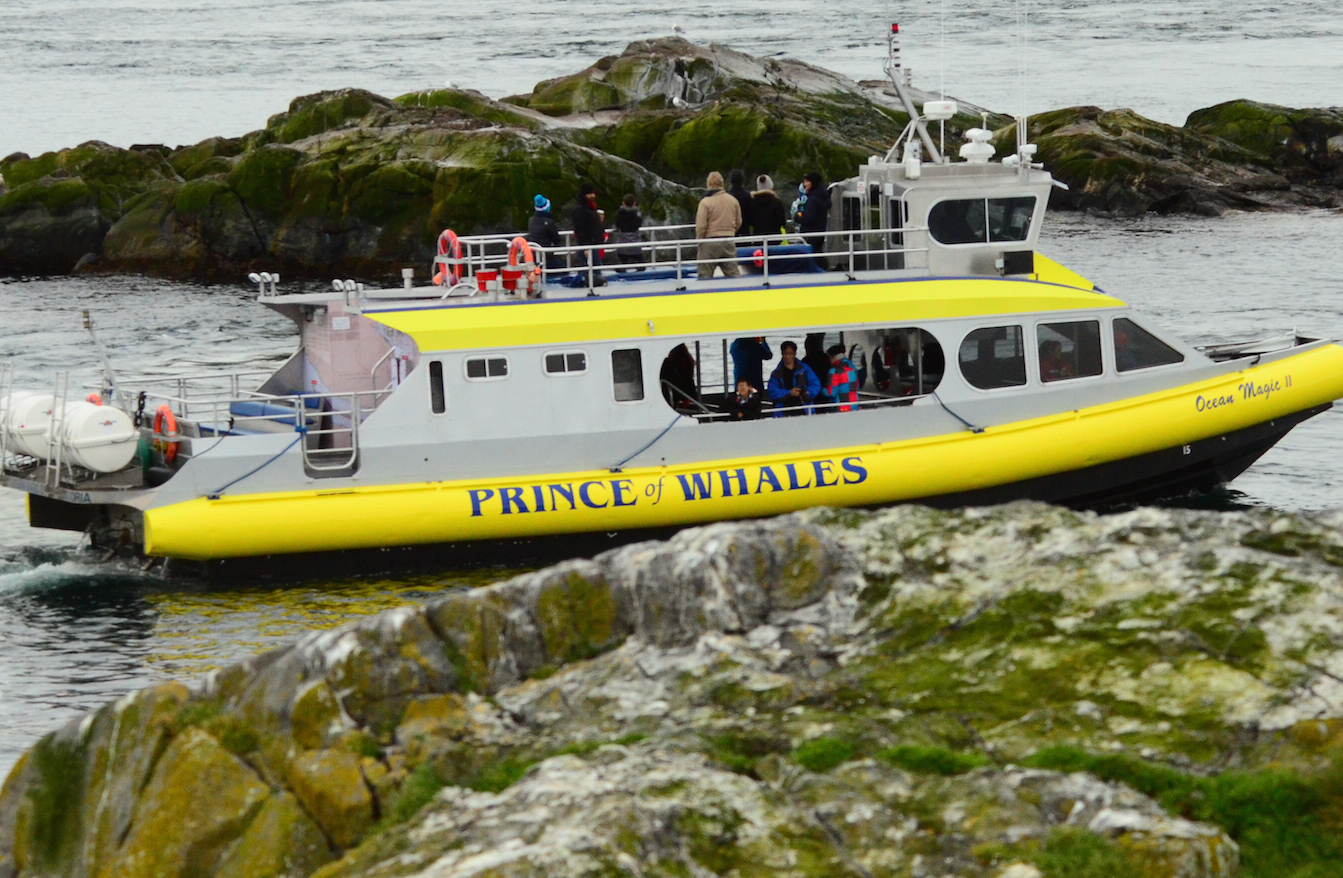
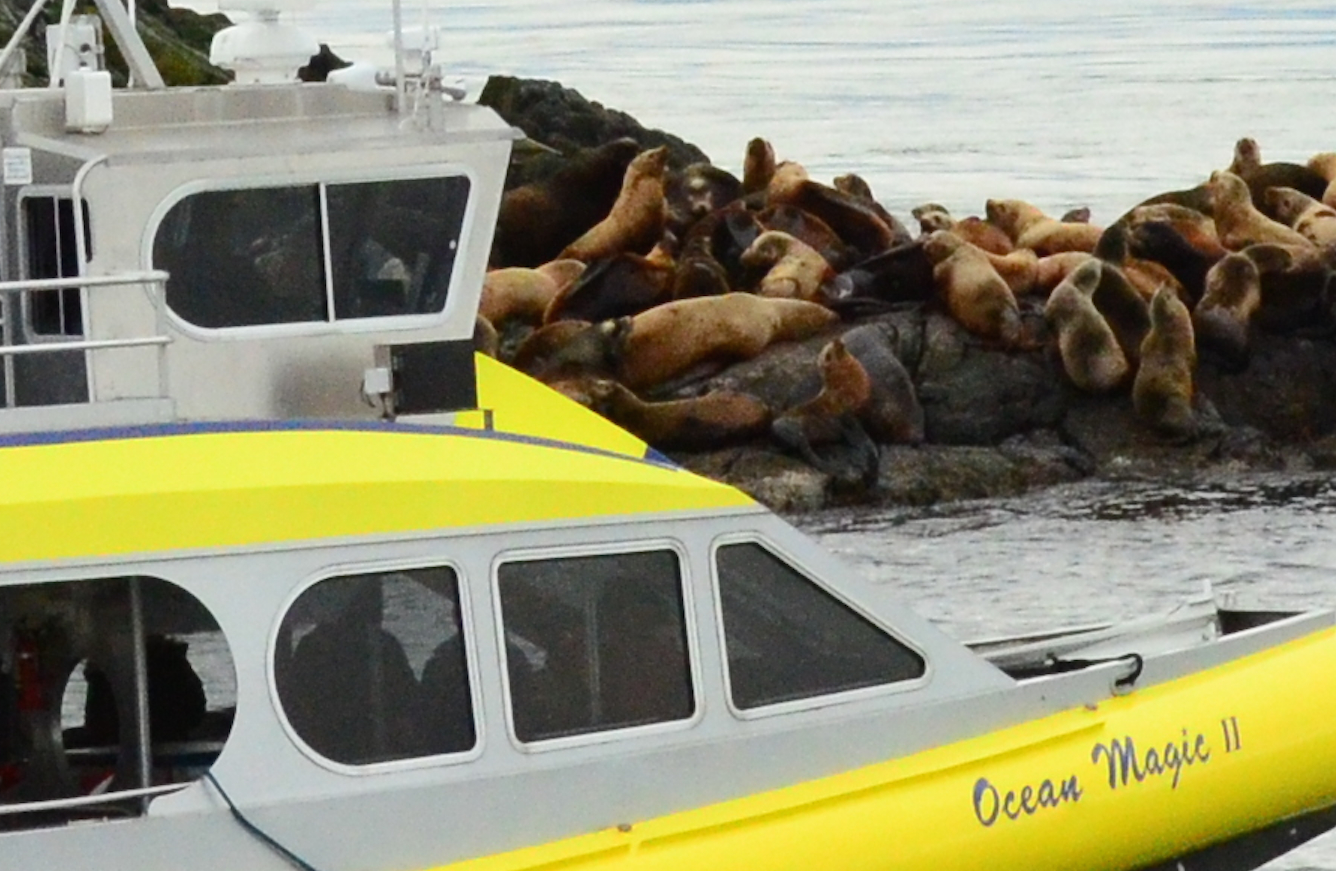
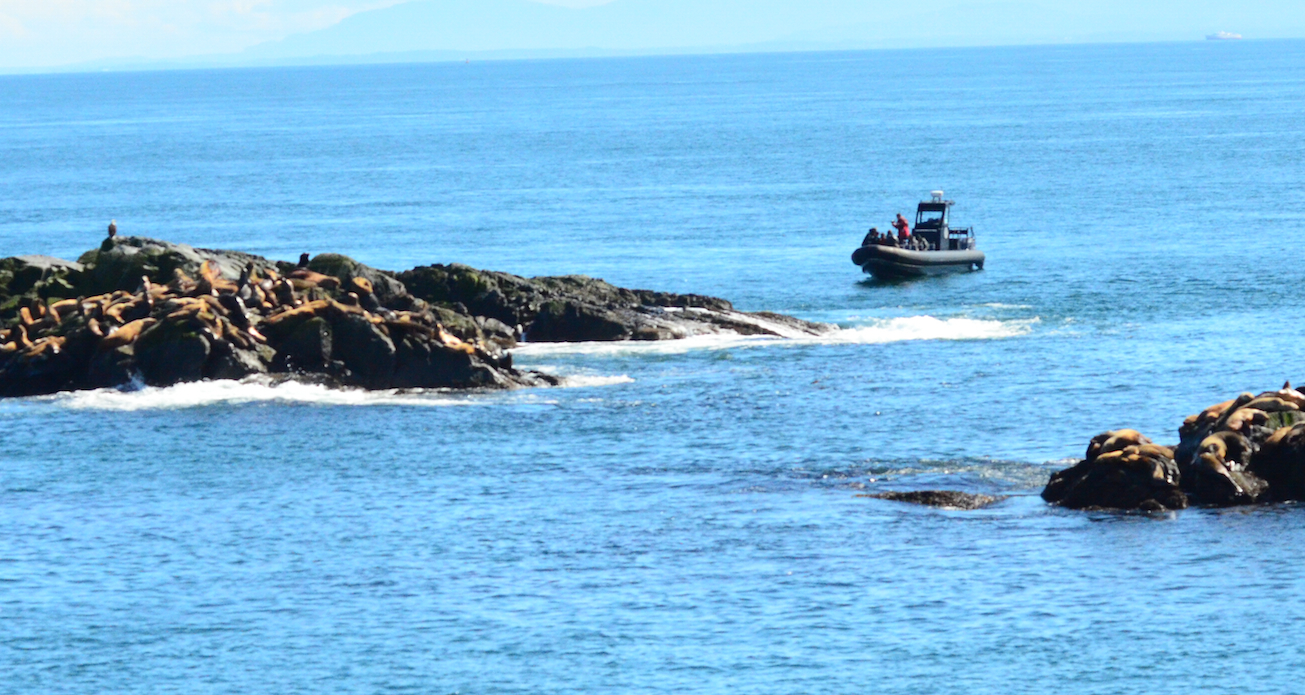
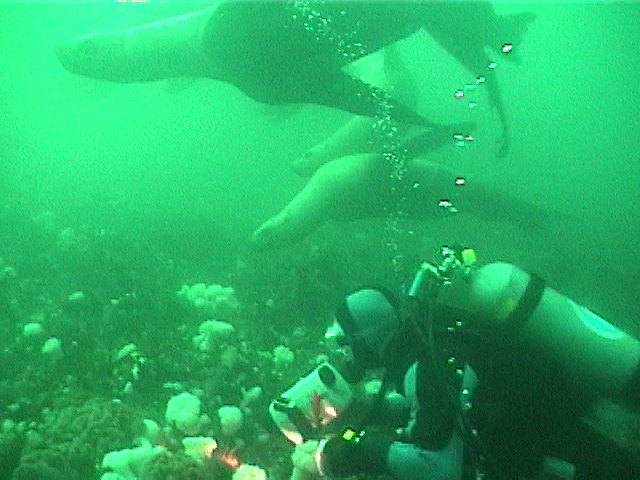
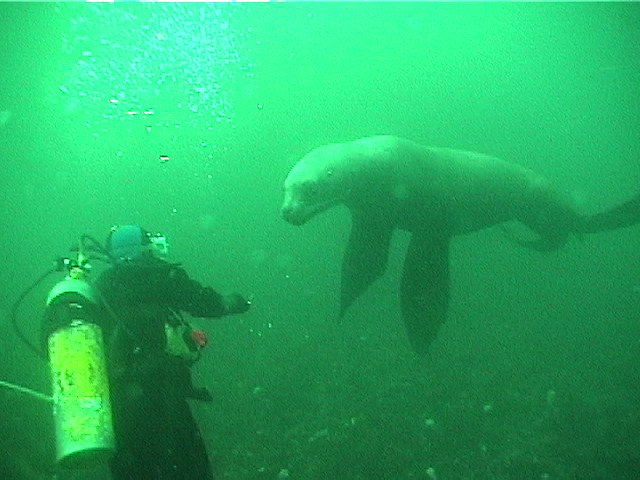
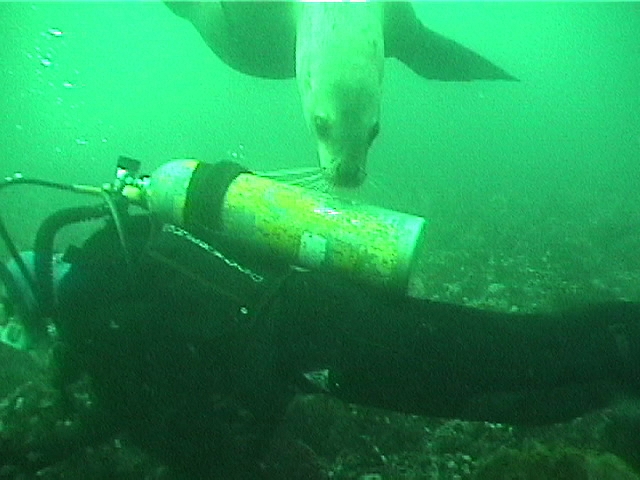
The Problem with Ecotourism boats:
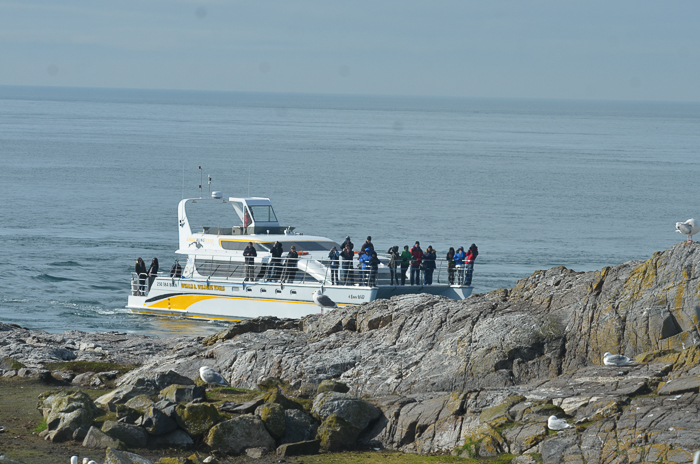
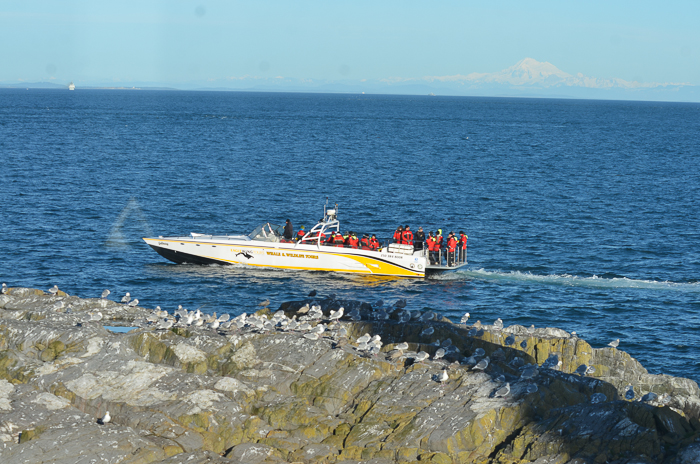
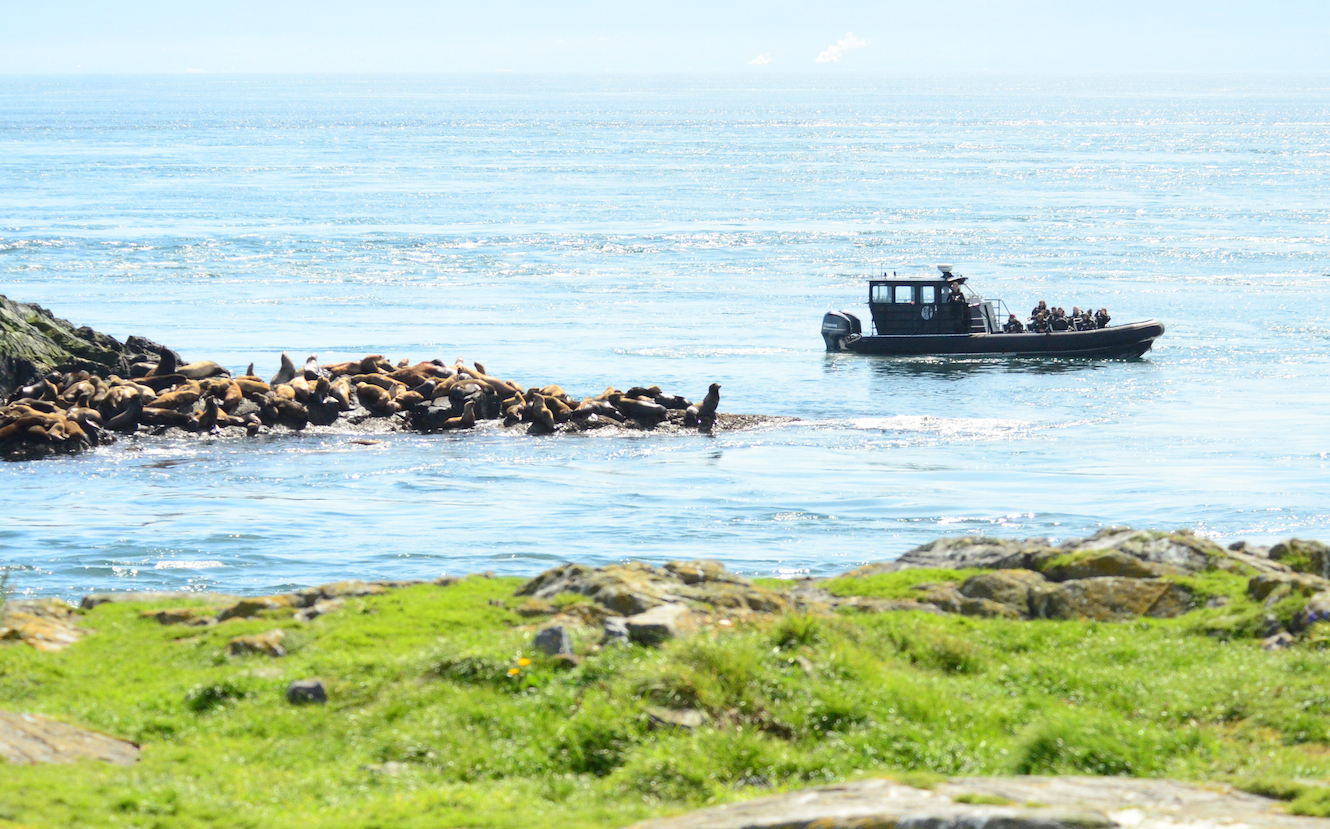
- April 5, 2016. An ecotour boat passes throught the narrow south channel.
- This is where the harbour seals have pups coming up at this time of year
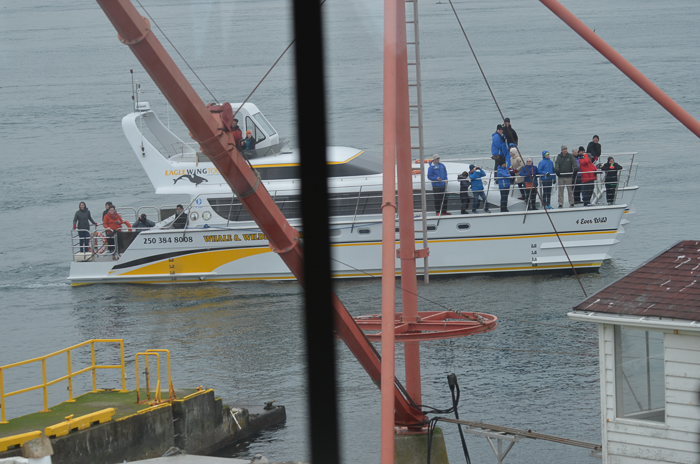
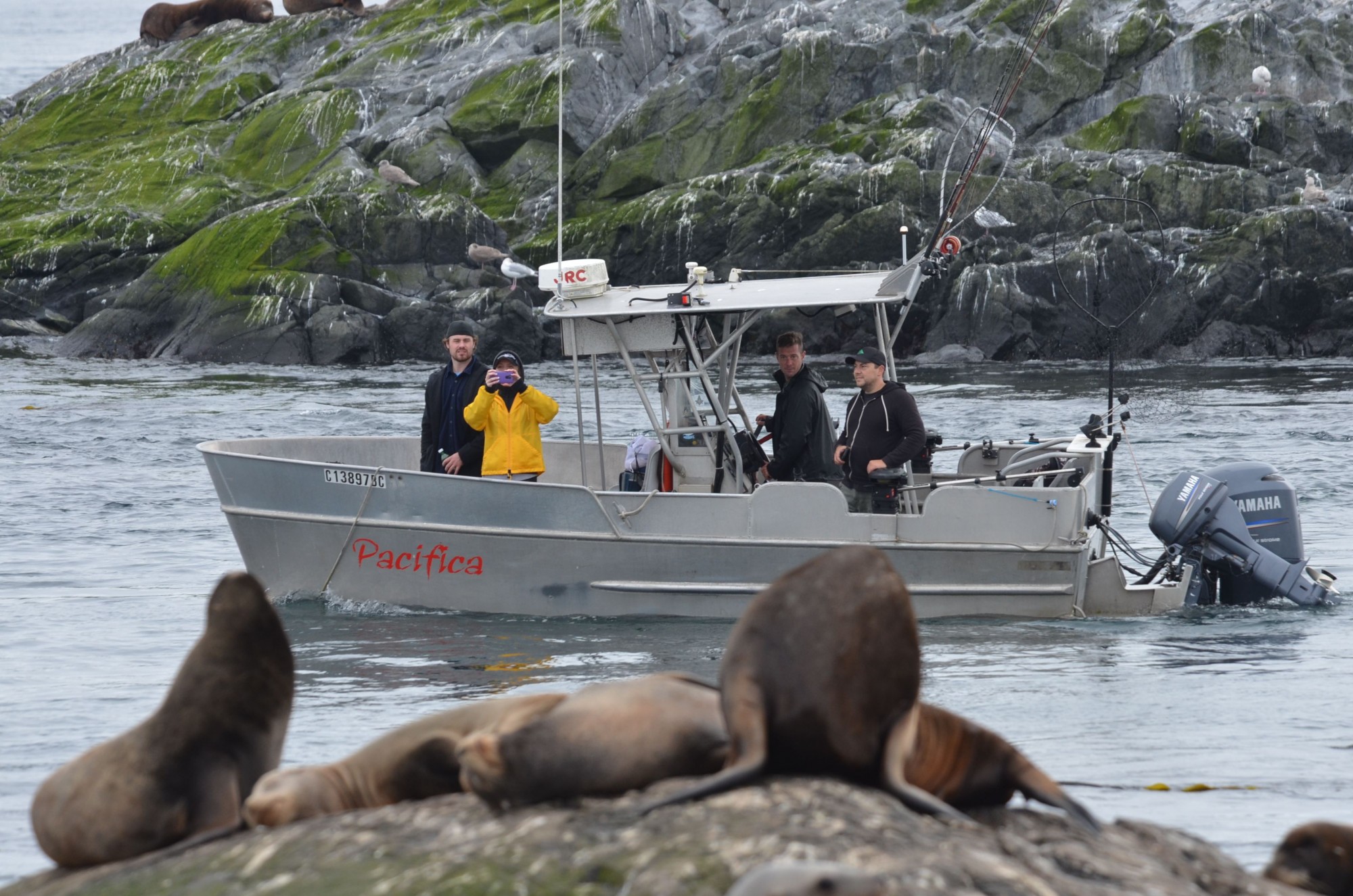
- March 25, 2016 Skipper taking photos
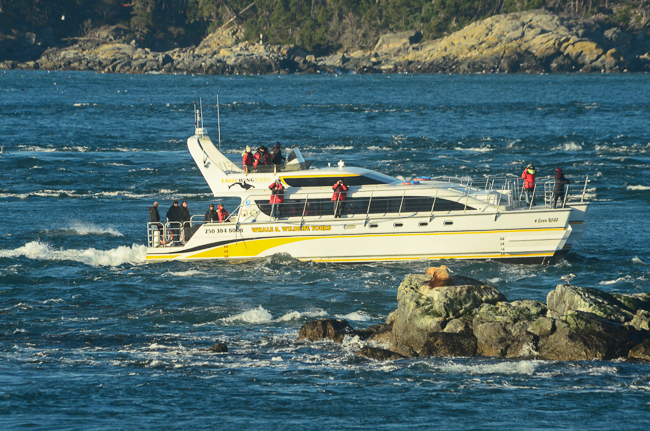
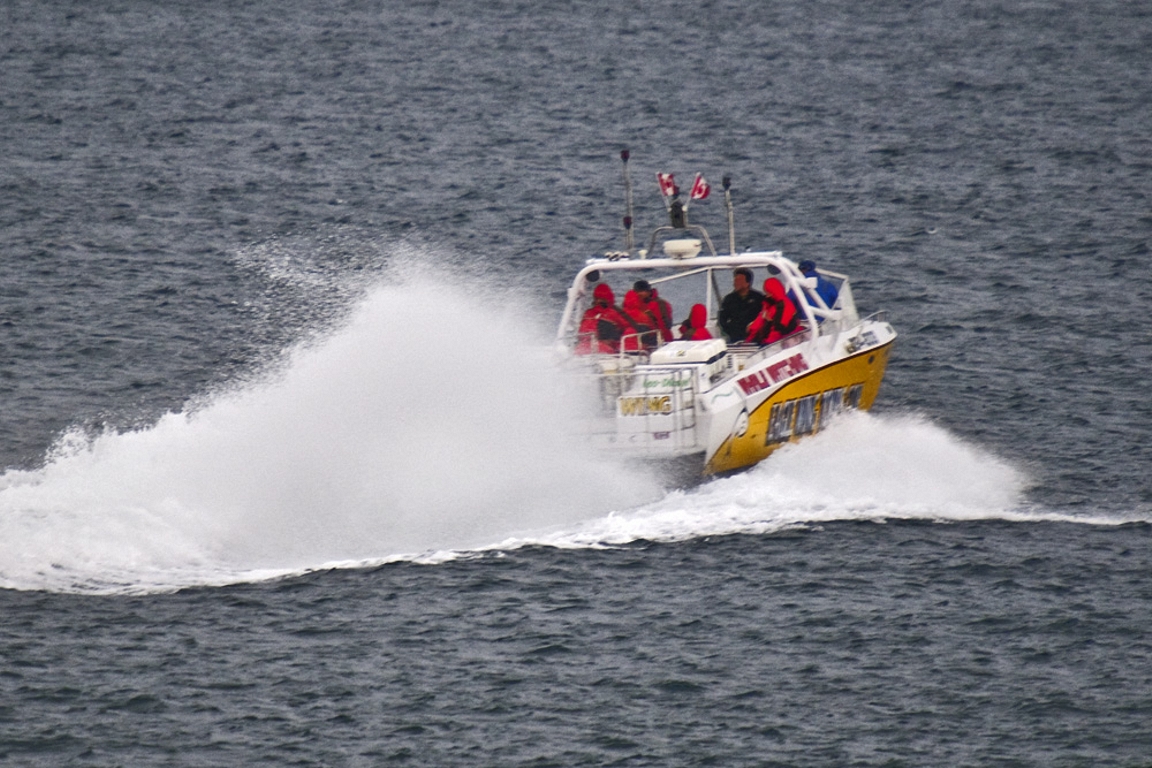
- February 28, 2016 A too-close monster boat
- February 26, 2016
- February 26 2016
- February 12, 2016
- February 9, 2016
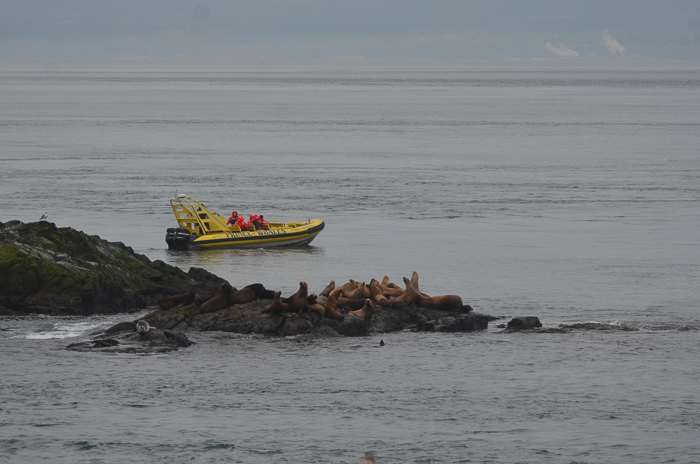
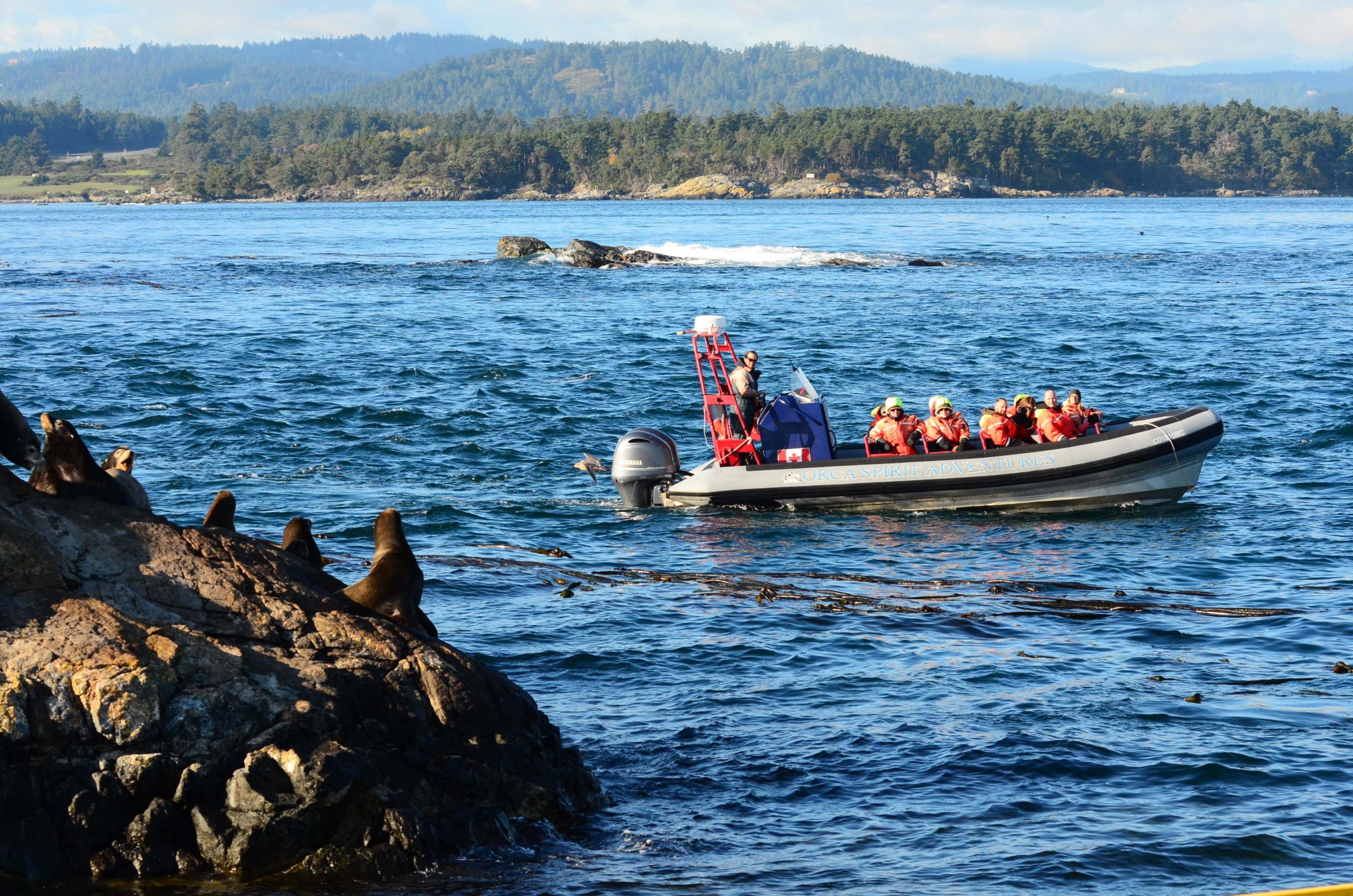
- Jan. 5, 2016 The vessel appears much closer than 100 meters to sealion on Turbine Rock
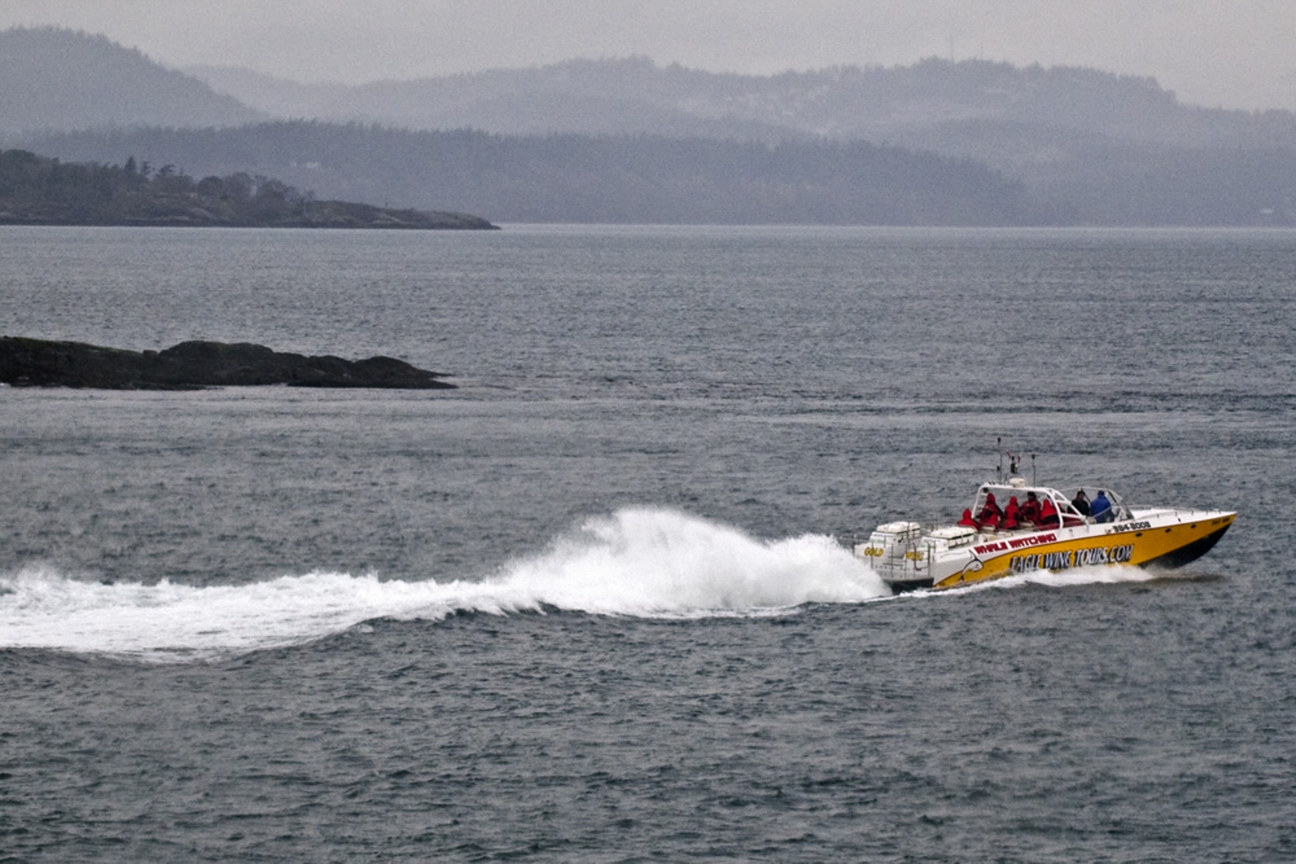
- November 9, 2015 Whale watching closer than is allowed by the guidelines
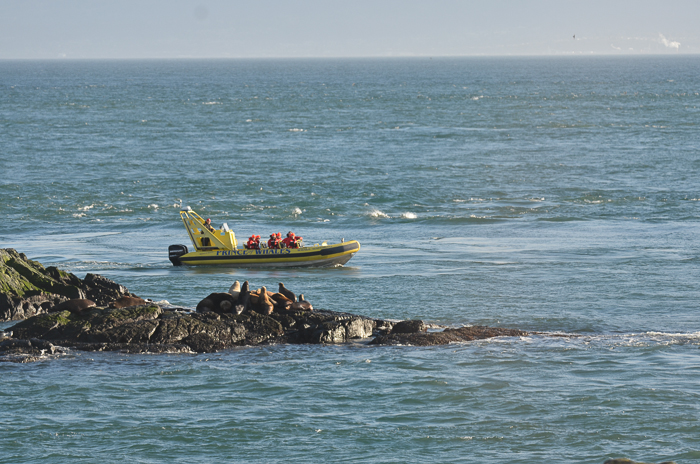
- October 19, 2015 They behaved well once they came closer and saw us.
- April 6, 2016 This may be a better position for viewing, although still very close and there are animals in the water, near the boat, which has propellors turning to maintain position.
We are well aware that the marine ecotourism industry is important to the economy of the Victoria and Sooke area, and over the years have had good record of cooperation with the whale watching companies in the observation of regulations for marine mammal and bird viewing at Race Rocks. There are times however when the operation of individuals in their fleet of vessels within the reserve is not in keeping with the ultimate goal of ensuring sustainability of this resource.
The Recommendations for Marine Mammal observation at Race Rocks:
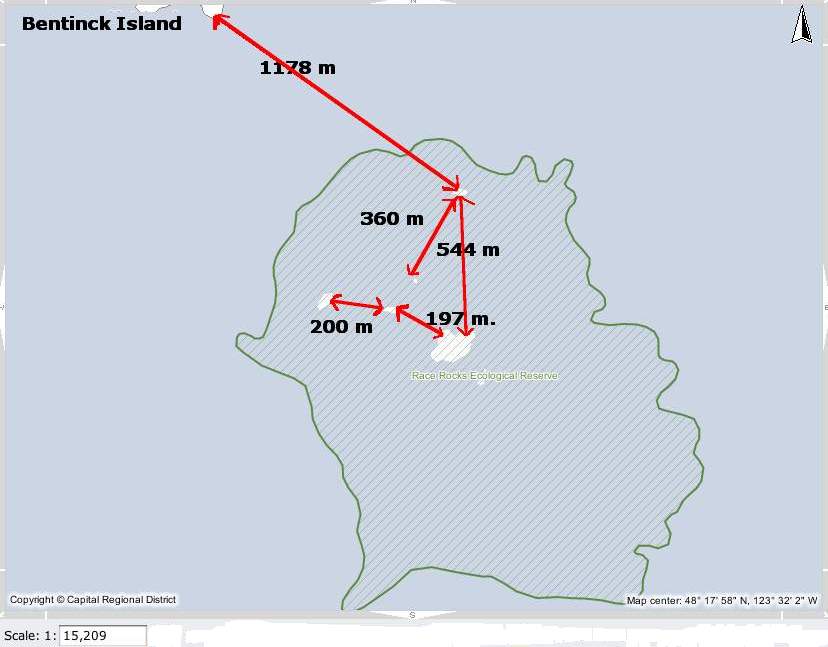
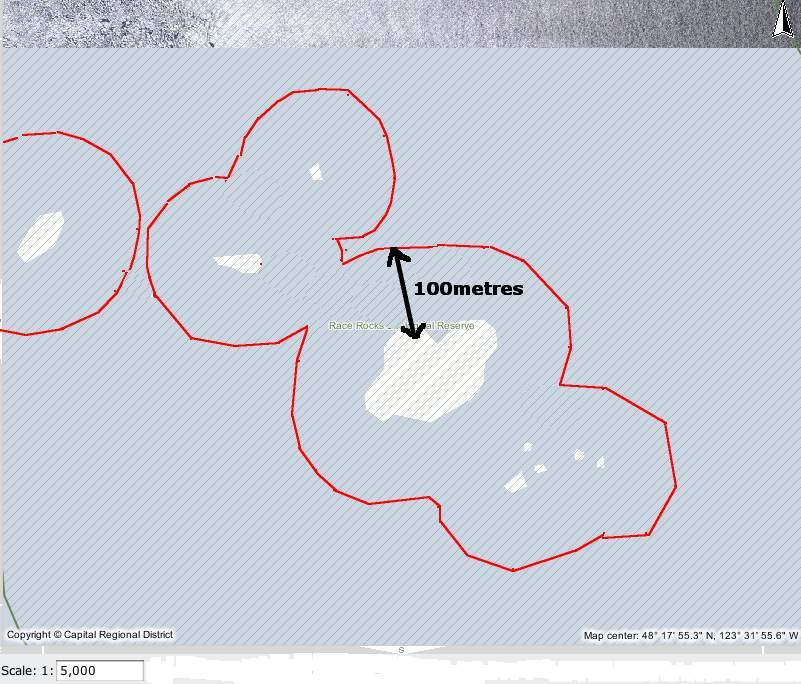
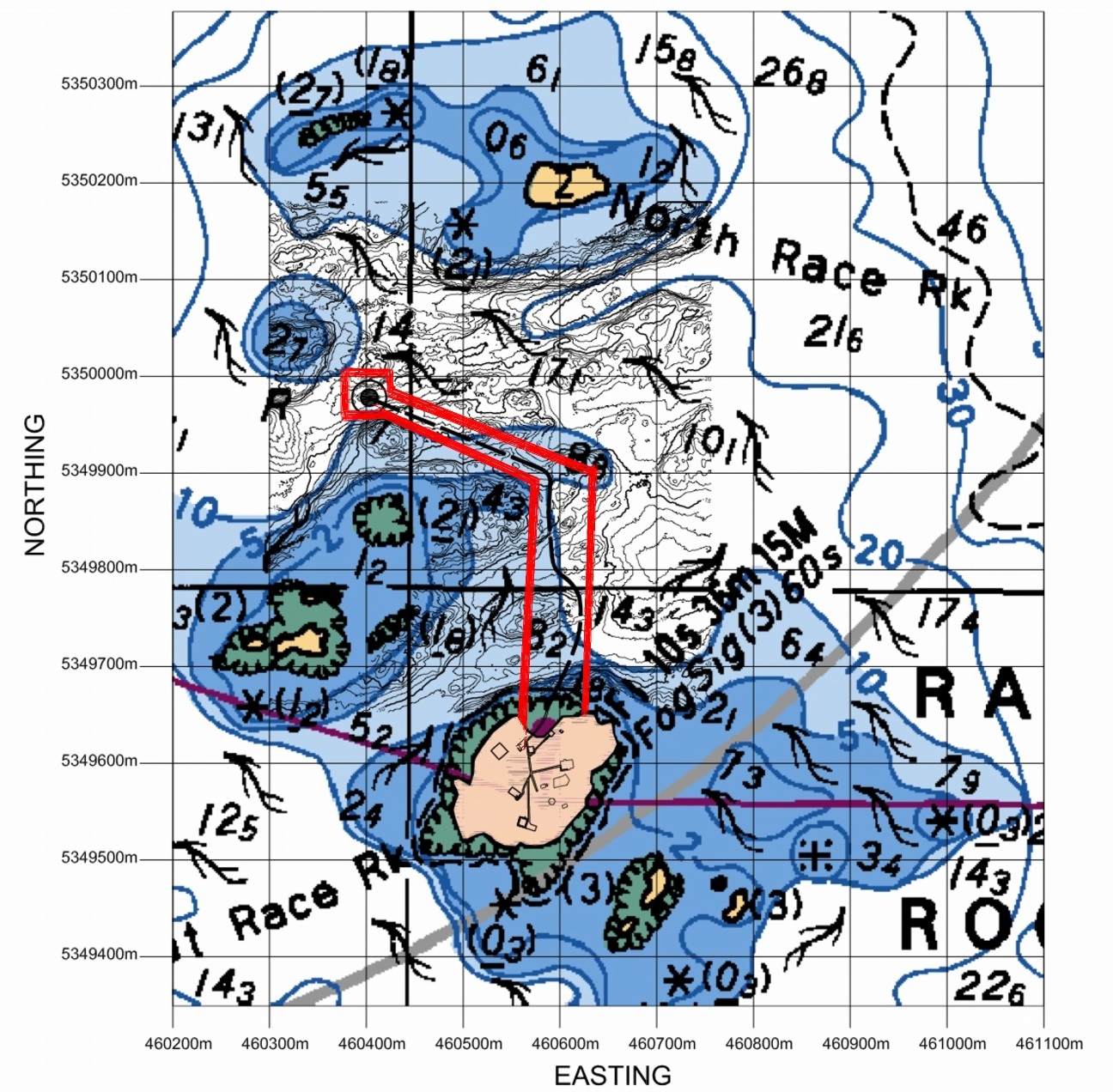
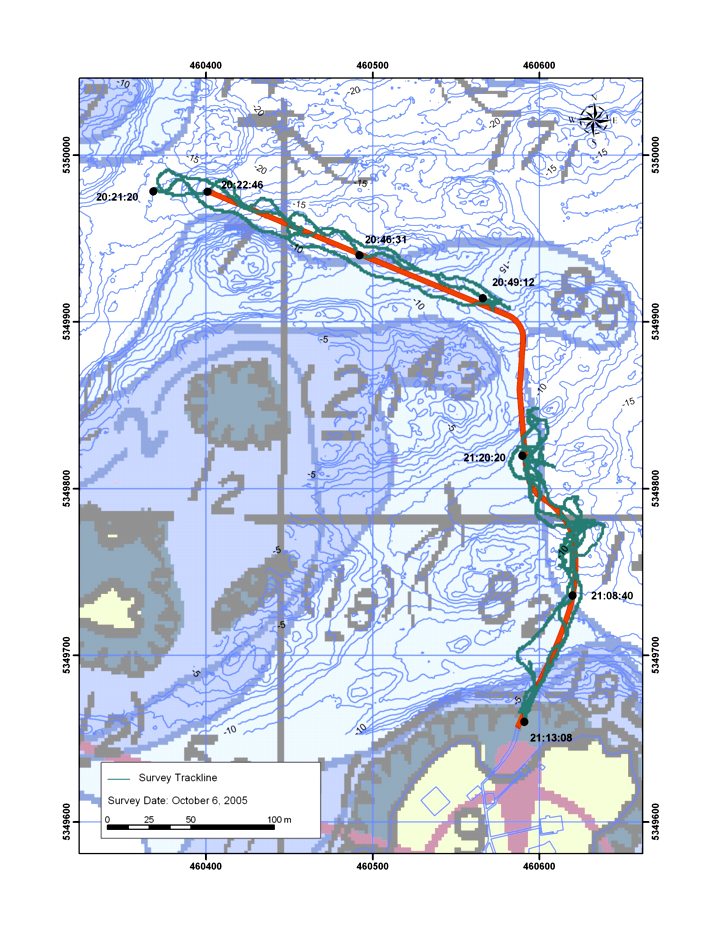
These two maps show the reality of the distances involved at Race Rocks:
- Measured distances in the Race Rocks Archipelago. recommended minimal viewing distance from nesting birds or marine mammal haulouts.
- The red line shows the 100 metre distance from the land masses at Race Rocks North rock omitted form this view.
The regulations for Marine bird and mammal viewing as DFO policy is 100 metres. In the early negotiations about a marine protected area for Race Rocks, stakeholders agreed that the distance between the middle islands and Great Race be in under 200 metres would preclude any vessel from using that passage. It was agreed with the ecotourism community that they could transit that area near the centre line, either drifting or slowly under motor. The 200 metre zone would be respected however for all other parts of the Ecological Reserve .
The Pacific Whale-watch Association lists the folllowing regulations for the
RACE ROCKS SPECIAL OPERATING AREA
1. “Go Slow Zone” = 1/8 mile (220 yards) from any rock or landmass around Race Rocks.
2. Vessels will slow on their approach to Race Rocks such that speed at 1/8 mile (220 yards) from any rock or landmass is reduced to approx… 7 knots (minimal wake and wash, relative to the condition of the seas state at the particular time).
3. Vessels in the Go Slow Zone will remain as close to mid-channel as is practicable between the major rock outcroppings known as Great Race, North Race Rock, West Race Rock, and Helicopter Rock.
4. While in the Go Slow Zone vessels will transit the area with the current whenever conditions are suitable to do so. Drifting is encouraged relative to other boat traffic and where safe navigation is not compromised.
5. Vessels exiting the area may increase speed gradually outside the Go Slow Zone.
6. Vessels will remain 1/8 mile (220 yards) outside the Go Slow Zone whenever any whale species are present in the Race Rocks Reserve (Go Slow Zone).
This is the ” Be Whale Wise advice” from DFO for marine mammal viewing
Quote: from DFO: ” Why do we need guidelines?”
“The diversity and complexity of marine life in the coastal waters off British Columbia and Washington is truly extraordinary. It is a fragile world. Pollution, global climate change and other impacts are taking their toll at all levels of the coastal food web. Many species of marine wildlife, such as the endangered southern resident killer whales, are showing signs of vulnerability. Meanwhile, vessel traffic in our waters is steadily increasing, placing added pressures on marine animals and their habitats. We need to minimize our impact. These guidelines are designed to help you enjoy your wildlife encounter, and reduce the risk of disturbing marine wildlife.”
I have documented the History of how amendments to Marine Mammal Viewing regulations worked on over a decade have still not been included in the current Marine Mammal Viewing regulations at this post: https://www.racerocks.ca/?p=19751
Why we need updated regulations is clear from the following examples recorded at Race Rocks: Also see this tag for logs of vessel observations on viewing recommendations at Race Rocks.

March 2010: Unfortunately there are a very few individuals in the whale watching industry who continue to give a bad name to the usually cooperative group of skippers and operators. The following sequence of images was taken on March6, 2010. The ecotour boat made a short tour of the reserve but was in a rush to leave, accelerating in the waters between Great Race and North Rocks creating wake as it sped out of the reserve.
Below, a viewer on the remote camera 5 captures a sequence of one tour boat with an impact on the sea lions in November 2007.
- Note vertical posture of sea lions alerted. (Time 14:27:41)
- The tour boat continues its approach
- The sealions stampede into the water.
- The viewer did note that ” … the tour boats of that company are normally more considerate than this…..”
- Almost all the sealions are gone from the north side. The boat turns back and heads to the south side.
- The time elapsed recorded on each picture shows that this took place in the span of 6 minutes.
- Entering the south channel between Middle Rock and Great Race Rocks
- Now the boat comes around to the south side of middle Rock and proceeds to scare off the remaining Northern Sea lions clustered there. (Time 14:30:20)
- Unfortunately a few minutes were missed as another viewer took control of the camera and moved it away from the scene. At the end of their “tour” no sea lions were left on the middle islands. (Time 14:33:29)
Ecotourism can have both positive and negative effects. In this video, you see two ecotourist whale-watching boats from Victoria B.C. that demonstrate two methods of viewing marine mammals. The yellow boat, rounds the middle rock inside the kelp bed, much too close to the island which is covered with northern sea lions and a few California sea lions. Since the animals on the North side of the island do not see the boat coming at this close distance, they are startled and about 25 of them take to the water. The high profile of the boat is increased by the individuals standing on the top of the boat, probably adding to the scare value.
The white boat, comes down the main passage between Great Race and the middle rock. They have approached slowly, drift with the current and present very little impact on both the sea lions on the middle rock and the harbour seals hauled out on the main island down in the foreground. Missing from this video however is video of their departure from the reserve where they swing in very close to the end of the docks, causing a stampede of a dozen sea lions in that area. Disturbance of any marine mammal colonies by vessel operators is against the law. Every time an animal has to change it’s behaviour because of human behaviour, there is a cost in terms of energy expenditure.
September 8, 2009: some whale watching boats still fail to stay a good distance off shore for viewing. It is questionable whether voluntary guidelines are adequate to ensure the ongoing sustainability of this resource as the number of whale watching boat visits continues to increase. In this video, the extent of ecotourism on a calm day and the effects on marine life are discussed.