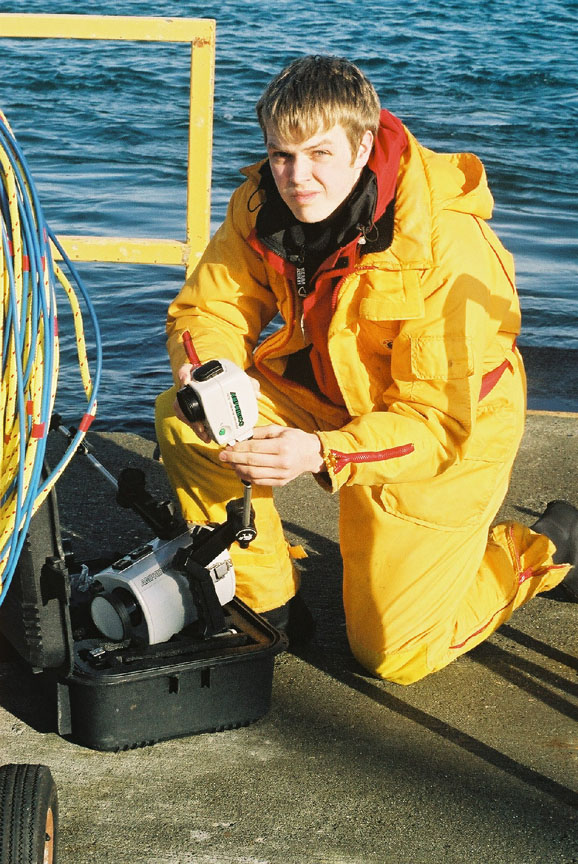
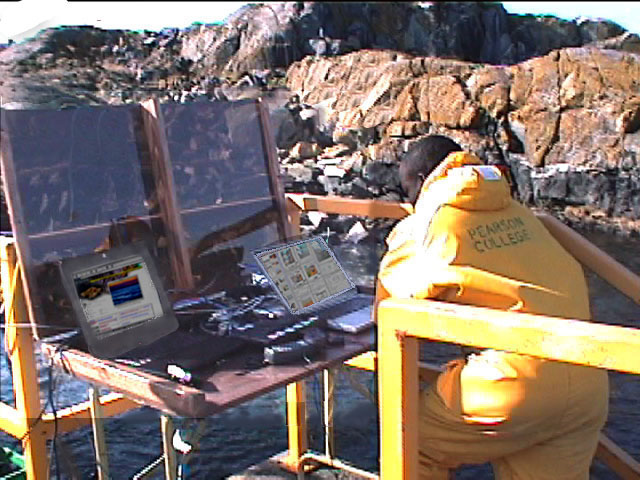
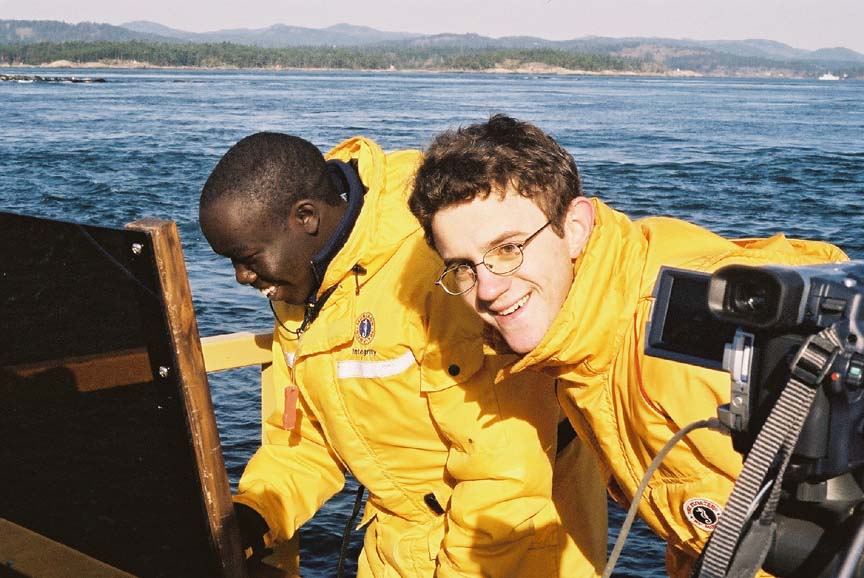
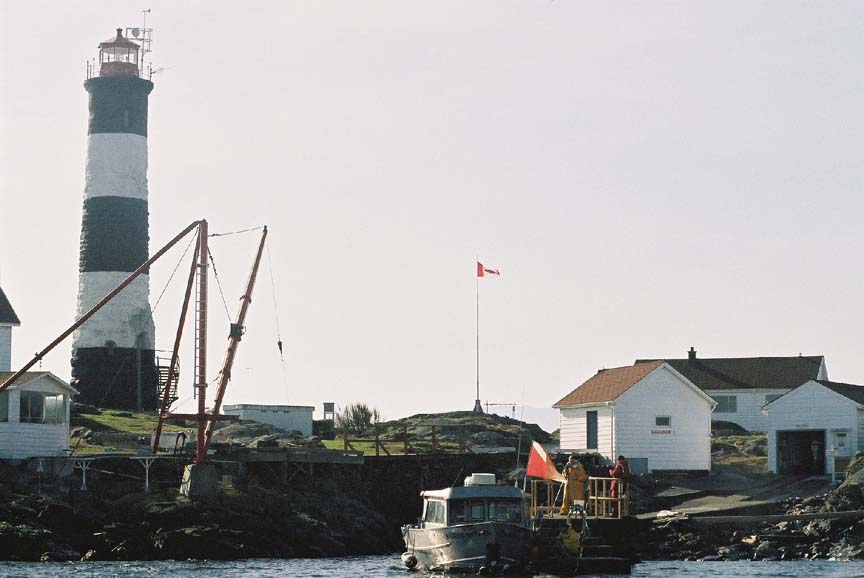
‘Mike gave me a lift over this morning to work on the data computer, I will be going back to “civilization?” at noon tomorrow. Students are all off on Project week this week so it is rather quiet around the campus. The pair of Black Oystercatchers was active here with their high pitched calls down by the docks this afternoon. One can hear them occasionally these days on cameras 1 and 3. I also noted an eagle perched on the subtidal island directly to the West this afternoon at low tide. You may often see an eagle along the island rock crests in presets 2 and 4 of the remote camera if you pan along the cliff edge. I noted an absence of gulls this evening. They don’t stay around at night until they have established territories and taken up nesting. Go to the video archives for recent website additions: several new videos in the invertebrate section and a new Northern Sea Lion video–Garry
Category Archives: ER Warden Report
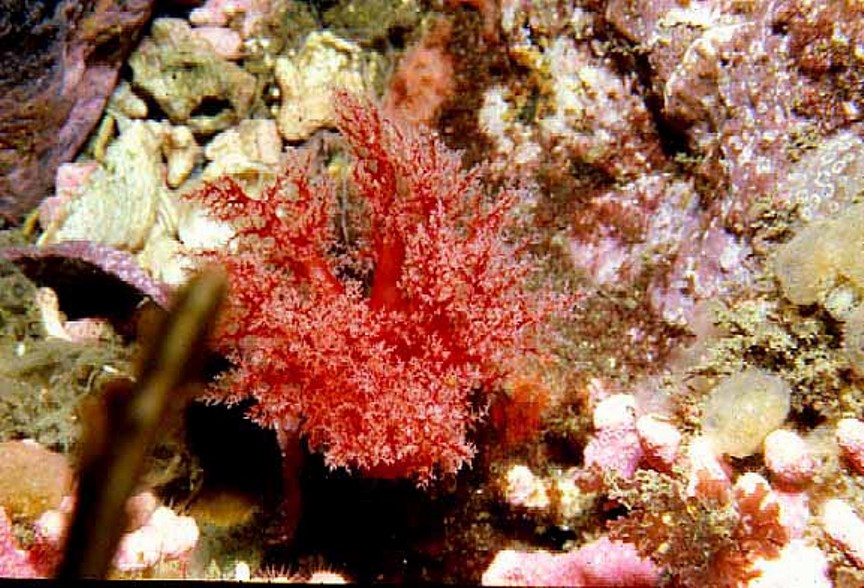
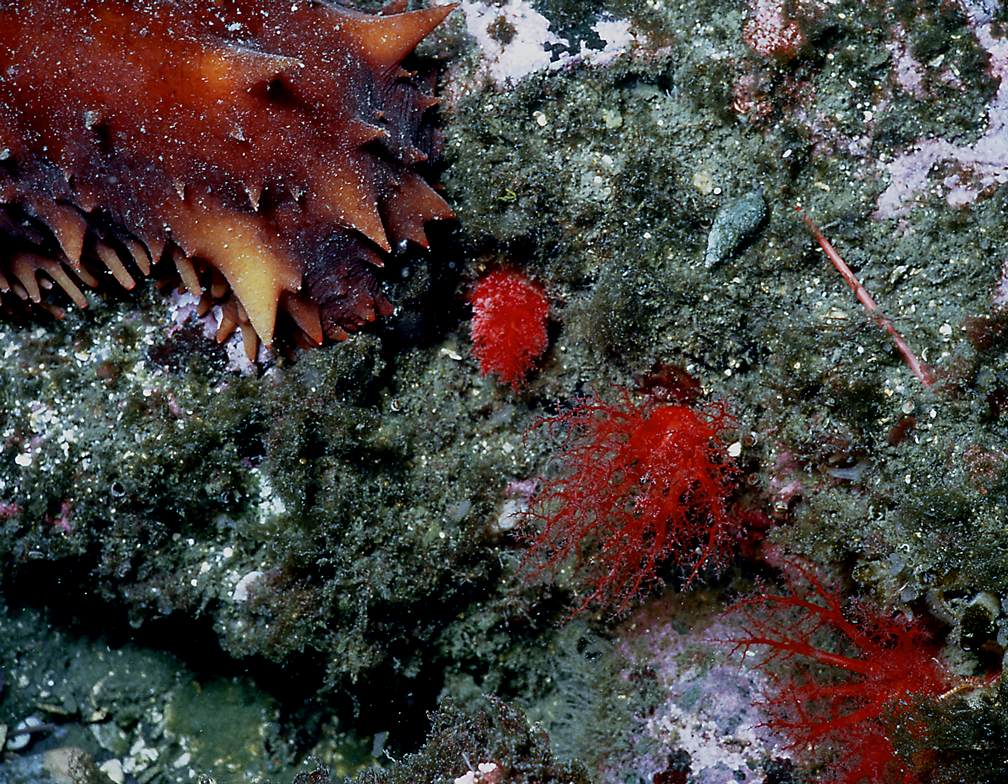
Ophlitaspongia pennata: velvety red sponge–The Race Rocks taxonomy
The red sponge, Ophlitaspongia pennata and the nudibranch Rostanga sp. were found at a low tide in the late evening in November near the end of the docks, just beside the slipway at Race Rocks. These images are from the video below.
- Note grooves in the surface of the sponge which are grazing paths.
- The nudibranch Rostanga grazing on the red sponge.
There are likely to be several types of encrusting red sponges growing in narrow crevices and on the undersides of overhanging ledges. Indeed, there are about ten intertidal species of red to orange encrusting sponges along the Pacific coast. Ophlitaspongia pennata is a beautifully coral-red form characterized, especially after drying, by starry oscula; its surface is velvety. De Laubenfels (1932) remarked that it occurs clear up to the half-tide mark (higher up than any other sponge), especially on vertical rocks under pendant seaweed, hence shaded from direct sunlight. Ophlitaspongia pennata is recorded from (Vancouver Island), British Columbia, to near Puertocitos, Baja California.
| Domain | Eukarya |
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Porifera |
| Class | Demospongiae |
| Order | Poecilosclerida |
| Family | Clathriidae |
| Subclass | Ceractinomorpha |
| Genus | Ophlitaspongia |
| Species | pennata |
| Common Name | Velvety Red Sponge/ Red Midtide Sponge |
This type of Red Sponge can be colored bright red to almost a dull orange-red. It has a smooth and tough surface. It has holes scattered around on it: the holes are about 2 millimeters wide. Its predators are nudibranchs, snails and seastars. They feed on shrimp, crabs and many other organisms.These tiny flat red to orange colored sponges encrust vertically on rocks shaded from sunlight.Biotic Associations: Often found with a predator, Rostanga pulchra
| This file is provided as part of a collaborative effort by the students, faculty, staff and volunteers of Lester B. Pearson College | February 2002 | Sarah MonsalveR. Colombia PC Yr 28 |
Usando Internet para Protección Ecológica
 Usando internet para protección ecológica
Usando internet para protección ecológica
m.m.burkle@sussex.ac.uk
Por MARTHA BURKLE
GRUPO REFORMA
El domingo de la semana pasada tuve la suerte de visitar un interesante proyecto en el que la web es utilizada para crear una dinámica experiencia educativa en estudiantes de preparatoria de todas las regiones del globo. El proyecto “Race Rocks” (www.racerocks.ca/) toma su nombre de una isla ubicada en el punto geográfico más al sur de Canadá. La isla tiene una historia de más de un siglo, cuando en 1860 las fuerzas británicas vieron la necesidad de establecer un faro náutico para poder orientar sus navíos en una zona marítima en la que las corrientes de agua y los vientos cambian de manera vertiginosa.
En 1974, el Colegio Pearson fue abierto en la región de Victoria, Columbia Británica, como parte de un proyecto internacional llamado “United World Colleges” -Preparatorias Unidas del Mundo – (www.uwc.org/uwchome.html).
Fundado en 1962 con el soporte de la ONU, la misión del proyecto internacional es formar a jóvenes entre 16 y 19 años de edad, procedentes de todas las regiones del mundo, en los valores de responsabilidad, vida comunitaria, conciencia ecológica y en la promoción de los ideales de justicia, paz, comprensión y cooperación internacional. A nivel mundial existen solamente 10 colegios como este (dos en norteamérica, uno en sudamérica, tres en Europa, uno en Africa y tres más en Asia), y año con año, estudiantes de preparatoria buscan ser seleccionados entre los 100 mejores (cada colegio admite solamente a cien estudiantes por año), en el aspecto académico y de compromiso con la comunidad.
El proyecto de investigación de ‘racerocks.com’ nace prácticamente con la fundación del colegio de Pearson, al sur de Canadá. Diseñado para proveer contenidos y experiencias de investigación en los diversos programas educativos dentro del colegio, los profesores de Pearson College alimentan la página web con el propósito de motivar en sus estudiantes el interés por la vida marina en la isla.
Utilizando una interesante combinación entre tecnología de punta y cuadernos de notas, los creadores del proyecto (con el patrocinio de Apple y Sony) instalaron cámaras digitales en diversos puntos de la isla para la transmisión en vivo, 24 horas al día, de la actividad marina en la zona. Dos cámaras registran la ecología marina en las costas de la isla, una cámara transmite vida acuática en las profundidades del océano, y una más es utilizada para eventos especiales en vivo. Seguramente usted, querido/a lector, compartirá conmigo cierta fascinación al conocer este único lugar, si visita la web que le permitirá escuchar en vivo los diversos sonidos producidos por focas, leones marinos, elefantes marinos, gaviotas y demás habitantes de la región.
A pesar de ser una red tecnológica relativamente pequeña, la tecnología involucrada en el proyecto de Racerocks.com es bastante sofisticada. Prácticamente todos los aparatos que configuran la red pueden ser adquiridos en el mercado, pero lo que los hace únicos es la original visión que los integró. Ambos, el colegio y la isla, comparten una red local. La infraestructura de la red es provista de velocidad por switches y routers que utilizan módems rápidos para proveer video y audio. Como la isla en sí está ubicada a varios kilómetros de la costa del colegio, era importante que la red tuviera alta capacidad y lograr esto fue difícil. Al inicio del proyecto, tres eran las opciones más viables: el uso de una conexión vía satélite, la transmisión inalámbrica, o la fibra óptica marina.
El proceso de toma de decisión respecto a cual seria la tecnología más propia, tuvo que tomar en cuenta factores económicos y de conservación del medio ambiente. El uso del satélite apareció como una vía muy costosa y poco probable; por su parte, utilizar fibra óptica submarina, era costoso también y además presentaba algunos problemas técnicos y otros involucrados con la protección ecológica del área. Finalmente, la opción del uso de microondas apareció como la más viable.
Radios modelo “Tsunami” y equipos de construcción de la compañía de telecomunicaciones “Glen Tel” fueron adquiridos e instalados en la parte superior del faro náutico en la isla.
Esta mañana, y mientras escribo esta columna, Racerocks.com está transmitiendo en vivo imágenes submarinas desde la isla a un congreso que se lleva a cabo simultáneamente en California. Probablemente lo más interesante de estas imágenes es el hecho de que son los mismos estudiantes, chicos y chicas en edad adolescente, quienes se encuentran ahí, haciendo la transmisión debajo del agua. Los y las estudiantes involucrados en el proyecto, registran eficientemente los cambios ecológicos en la isla, y comparan sus datos con los obtenidos por previas generaciones en el siglo XIX y cuidan de los equipos electrónicos.
México tiene a dos de sus mejores estudiantes de preparatoria en el Colegio de Pearson. Fue emocionante platicar con ellos y ver su compromiso de trabajo y dedicación.
La autora es doctoranda en Políticas de Ciencia y Tecnología en la Universidad de Sussex, Inglaterra
Reprinted with permission of the author.
Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis: Green sea urchin –The Race Rocks taxonomy
Green Sea Urchin: average size is 50-60 mm, but may reach a maximum size of about 85 mm.
Distribution: The green sea urchin is one of the most widely distributed of all Echinoderms. It has a circumpolar distribution, which extends into the Arctic regions of both the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. It commonly inhabits the rocky subtidal zone from the low-tide mark down to a depth of 1200 m, but also occurs intertidally in tide pools.
Diet: The green sea urchin primarily grazes on seaweeds (kelp being its preferred food source), but will also consume a wide variety of organisms including mussels, sand dollars, barnacles, whelks, periwinkles, sponges, bryozoans, dead fish, and – when hungry enough – other sea urchins.
This shows the grazing action of sea urchin teeth, arranged in a complex assemblage of small bones, the five teeth gouged out this star pattern in the stipe of a Pterygophora.
The skeleton of the sea urchin is called a “.test”. The radial symmetry is reflected in the placement of all the tube feet holes. Here you can see the size of a green urchin compared to a red urchin
Reproduction: Green sea urchins release their gametes into the water column where the eggs are fertilized by the sperm. The sexes are separate. The resulting larva (termed an “echinopluteus”) undergoes development planktonically for a period of one to several months before settling on the sea floor and metamorphosing into the adult form. Reproduction occurs on an annual cycle with spawning occurring in the spring, generally between February and May, but sometimes as late as June. See the Lab on Sea urchin Embryology.
This video from underwater Safari shows a wolf eel crunching a sea urchin…
Behavior: Where urchins occur at high density, destructive grazing can produce habitats devoid of seaweeds. These areas may be termed “sea urchin barren grounds”.. When sea urchins are removed from these sites, either manually or by disease, the reduction in grazing pressure often results in the development of highly productive kelp forests. These kelp beds provide shelter for a wide variety of marine organisms (e.g. fish, lobsters, crabs, sea stars, bivalves, gastropods, bryozoans) and the habitat is typically much more diverse than barren grounds. Hence, sea urchins are one of the principal factors controlling habitat diversity in the rocky subtidal environment.
| Other Members of the Phylum Echinodermata at Race Rocks |
and Image File |
 The Race Rocks taxonomy is a collaborative venture originally started with the Biology and Environmental Systems students of Lester Pearson College UWC. It now also has contributions added by Faculty, Staff, Volunteers and Observers on the remote control webcams. The Race Rocks taxonomy is a collaborative venture originally started with the Biology and Environmental Systems students of Lester Pearson College UWC. It now also has contributions added by Faculty, Staff, Volunteers and Observers on the remote control webcams.
Aldo Caixeta (PC yr 28)/strong> |
Cucumaria miniata: Orange sea cucumber–The Race Rocks Taxonomy
The orange Cucumaria miniata sea cucumber is a common resident just off the docks at Race Rocks in 5 to 10 meters of water. In this video they occur in a high concentration relative to other areas. Each orange tuft is the tentacle mass. If disturbed, it quickly withdraws into the sea cucumber body which is always buried under loose rocks.
Note the name Cucumaria miniata should be on the following video instead of C. curata
| General Description:The Orange sea cucumber received its Latin name, Cucumaria because it resembles a cucumber. The orange pigment that separates it from other sea cucumbers comes from a chemical called cinnabar or vermilion. Although it seems to be completely soft and fragile, it actually has bone-like plates in the body wall called ossicles. To stay attached to the holes between the rocks, the cucumber uses tube feet that you can see in the image above in 5 rows around the circumference of the body. If you ever want to keep one as a pet, don’t get too attached because they usually only live about 5 years, sometimes 10 if they’re lucky.
Habitat: Sea cucumbers live in between boulders and sheltered rock formations. Because they are able to stay attached to surfaces, they prefer to live in areas with stronger currents, making it harder for predators to reach them. Feeding: The orange sea cucumber is a suspension feeder. This means that it catches food in its tentacles. After the food is caught, it removes the food with its eating arms and scrapes it into its mouth. Sea cucumbers eat plankton and detritus. Reproduction: Unfortunately, sea cucumbers aren’t very intimate creatures. In fact, their mating process can’t have any less contact. When the time comes to make a new cucumber and two cucumbers are physically (and emotionally) ready, one will release eggs into the water and the other will release sperm. From that, the two elements meet in suspension and that’s it. Predators and Defenses: The cucumbers main predators include fish, and even humans. That’s right kids, there are some people in the world that actually eat these things. To protect itself, the cucumber has many defenses. Their skin is some of the most amazing tissue found on an animal. The compound is made of a material called ‘catch collagen’ which can change from liquid to solid when neurologically triggered. It does this so can squeeze into small spaces and then harden again. Another defense is they “pee” out all the water in their system and shrink into a small, hard rock. The “peeing” usually occurs when the cucumber is removed from its habitat. If that’s not enough for you, they also can bust out a defense called evisceration. What happens here is if the cucumber is stressed and scared enough, it will spew its guts out. That means everything, intestines, gonads, respiratory organs, everything. Now after that, you would think that’s the end but if it can get itself to a safe habitat, it can actually regenerate its organs. Biotic Associations These guys are generally really passive, and they don’t really interact with any other organism or with between each other really. |
|||||||||
| References:http://oz.plymouth.edu/~lts/invertebrates/Primer/text/holothuroidea.html
http://www.afsc.noaa.gov/hodiak/photo/cuke03.html |
|||||||||
Domain Eukarya
Kingdom Animalia
Phylum Echinodermata
Class Holothuroidea
Family Cucumariidae
Genus Cucumaria
Species miniata
Common Name: Orange Sea Cucumber
| Other Members of the Phylum Arthropoda at Race Rocks |
and Image File |
 The Race Rocks taxonomy is a collaborative venture originally started with the Biology and Environmental Systems students of Lester Pearson College UWC. It now also has contributions added by Faculty, Staff, Volunteers and Observers on the remote control webcams. The Race Rocks taxonomy is a collaborative venture originally started with the Biology and Environmental Systems students of Lester Pearson College UWC. It now also has contributions added by Faculty, Staff, Volunteers and Observers on the remote control webcams.
March OctoberFebruary , 2002, Andres Jennings (PC yr 28) |
Psolus chitonoides: creeping pedal sea cucumber
Predation of a Psolus chitinoides by a sea star is examined and discussed by Laura and Nadege. The stomach of the sea star surrounds the sea cucumber and the soft neck and mouth of Psolus is well inside the cavity of the sea
Sea cucumbers have inhabited the world’ s oceans for about 400 million years. Psolus chitonoides is an unusual species of these marine invertebrates. Its diverse characteristics have given it 4 common names: Armoured sea cucumber, Creeping armoured sea cucumber, Slipper sea cucumber and Creeping pedal sea cucumber.

Compare the tentaclesof Psolus with the end of the California Sea Cucumber to the left. Photo by Dr.A.Svoboda
A-Description
As all echinoderms, the creeping pedal cucumber has a spiny skin. Also, its appearance is closer to a chiton than to a sea cucumber (here is the origin of its name “chitonoides“).
1-External features:an oval body (7cm long to 5.8 cm wide) domed dorsally with stiff, shingle-like scales, flat, flexible sole ventrally. Its tentacles(8-10) are dendritic, equal in size, or 8 large and 2 small. Also observing the body, it could be compared to an elongate cylinder lying on its side with the mouth at one end and the anus at the other. The rows of tube feet run the length of the body
2-Internal features: the tentacle ampullae, the rete mirable and cuverian organs are absent . On the other hand, we can observe the presence of retractor muscles. Respiratory trees are “y shaped”. Note that its madreporic body is attached to a dorsal mesentery. Its internal calcareous skeleton is composed as following:calcareous ring with anterior processes only. Psolus chitonoides is characterized by typical skin ossicles, where one type of circular perforated plate (some with knobs coalesced into a raised network) occur only in the ventral sole.
Domain Eukarya
Kingdom Animalia
Phylum Echinodermata
Class Holothuroidea
SubclassAspidochirotacea
Order Dendrochirotida
Family Psolidae
Genus Psolus
Species chitonoides
Common Name: Creeping pedal sea cucumber
B-Physiology and Biology
1-Suspension feeder: tentacles trap larger particles (larger than 2mm) by bending inwards to form a cagelike enclosure. The mouth lips extend toward the particle as the nearest tentacle pushes it into the mouth .
2-Reproduction : the reproductive organs of a sea cucumber generally consist of 1 or 2 tufts of elongated tubules in the forepart of the body cavity.Spawning occurs annually, from mid March ot late May, commonly in the early morning. A spawning male will swab its genital papilla with its tentacles, then lift the tentacles to disperse the sperm . Females release long ropes of brick red eggs; fertilized eggs develop into pelagic lecithotrophic vitellaria larvae. Late larvae and early juveniles are negatively phototatic and settle gregariously.
3- Respiratory system: its water vascular system is a hydraulic system made up of tubes and valves that operate rows of extendible tube feet . As other sea cucumbers, Slipper sea cucumbers respire through their tube feet, body wall and respiratory trees.
4-Chemicals: there are toxic chemicals (saponins) on its tentacles, discouraging predators from nipping the tentacles. For example, even the Kelp Greenling (Hexagrammos decagrammus), which feeds on sea cucumbers, avoids this species.
C-Predators, parasites and commensals
1-Sea stars and fish are the main predators of the Psolus chitonoides.
2-Parasitic forms of flatworms and snails can live inside the sea cucumber
3-Commensal organisms are mostly scales that mimic the colour of sea cucumbers, and crawl on their skin.
D-Habitat
From exposed coast to sheltered inlets; although it seems to prefer clean, vertical rock that is free of sediment. Its soft, flat sole enables it to attach firmly to rock.
E-Range
Aleutian Islands to Baja California ; intertidal to 247m ; common in shallow subtidal areas.
References:
Kozloff, E.N. Keys to the Marine Invertebrates of Puget Sound , the San Juan Archipelago, and Adjacent Regions.
Lambert, P. 1997. Sea cucumbers of British Columbia, Southeast Alaska, and Puget Sound. UBC Press,
| Other Members of the Phylum Echinodermata at Race Rocks |
and Image File |
 The Race Rocks taxonomy is a collaborative venture originally started with the Biology and Environmental Systems students of Lester Pearson College UWC. It now also has contributions added by Faculty, Staff, Volunteers and Observers on the remote control webcams. The Race Rocks taxonomy is a collaborative venture originally started with the Biology and Environmental Systems students of Lester Pearson College UWC. It now also has contributions added by Faculty, Staff, Volunteers and Observers on the remote control webcams.
March October 2003- Rahilla (PC) |
Webcasting for QuickTime Live
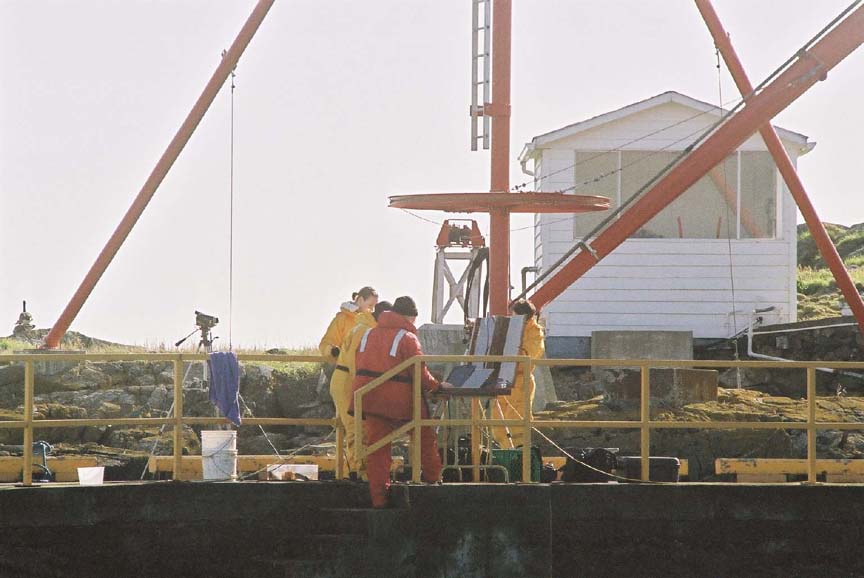
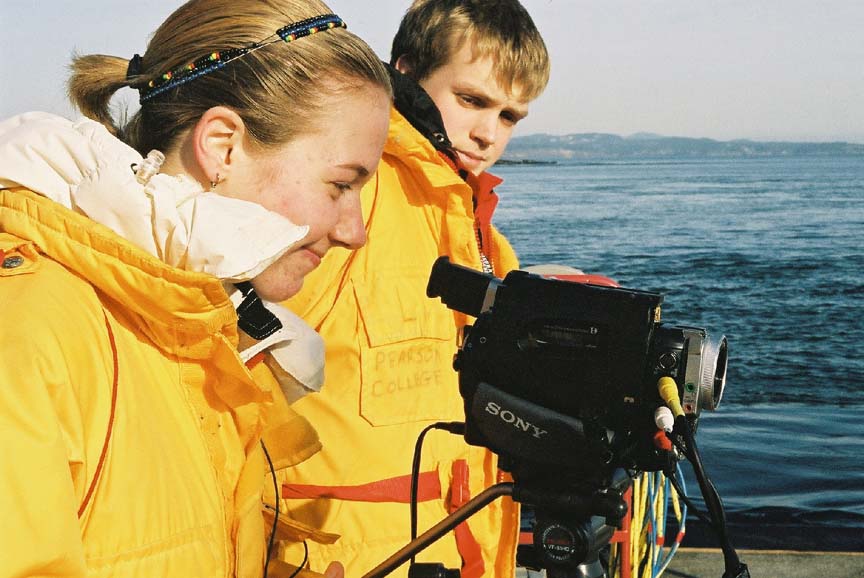
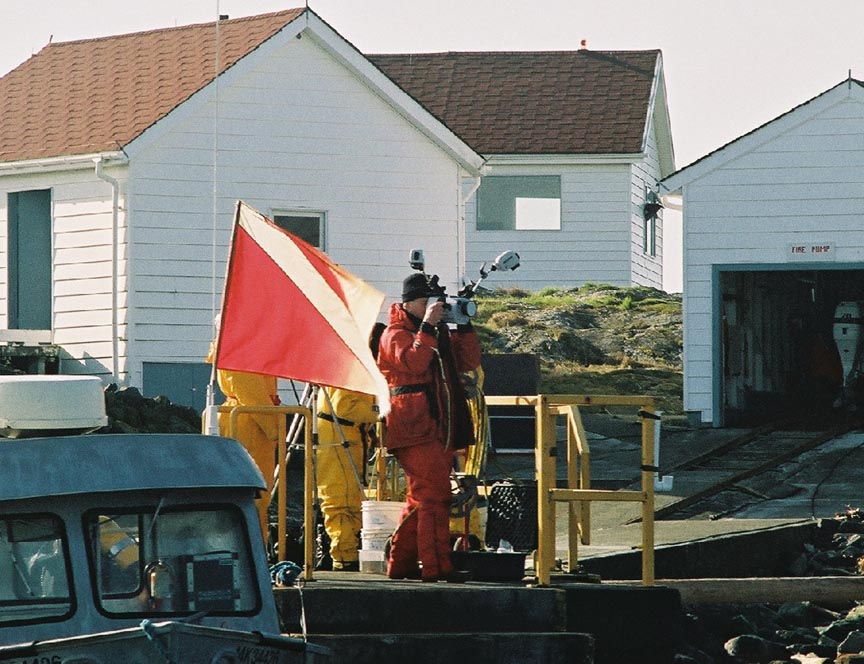
On February 14 , 2002, we did a live webcast for Keith Mitchell of ALI ( Apple learning Interchange) in his presentation at QuickTime Live in Hollywood California. This was the first time we tried out the new webcasting software “LiveChannel” from our new partners Channel Storm.
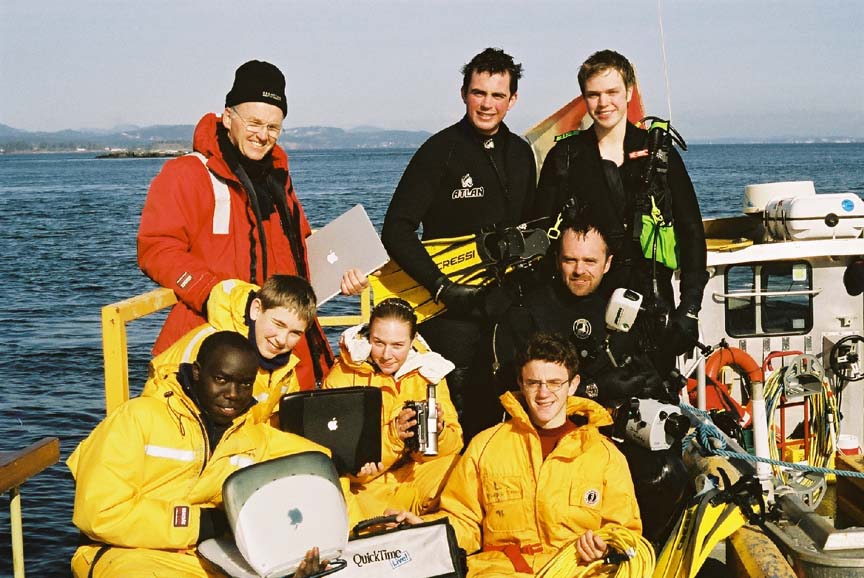

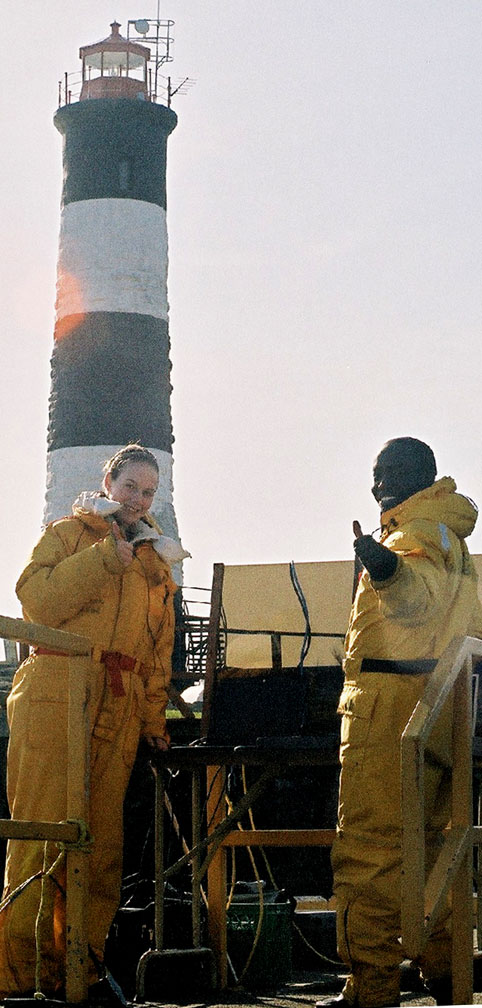
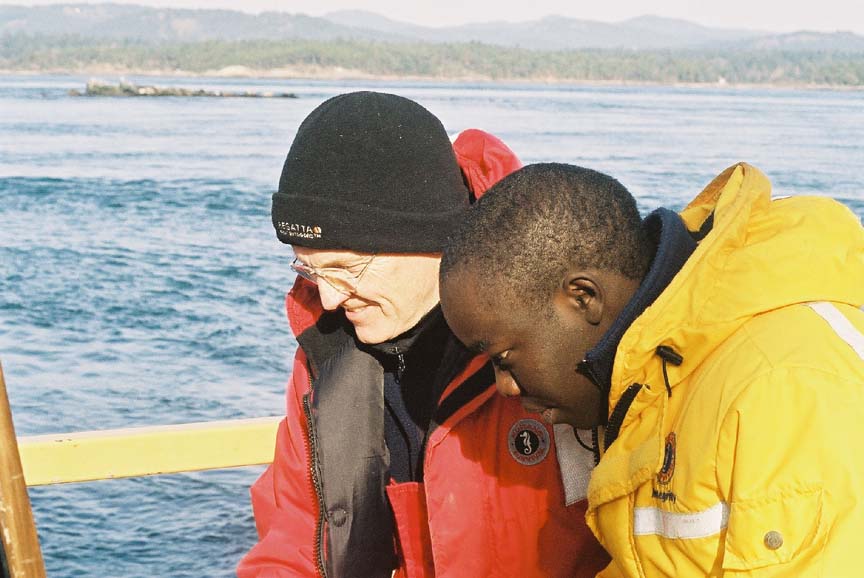
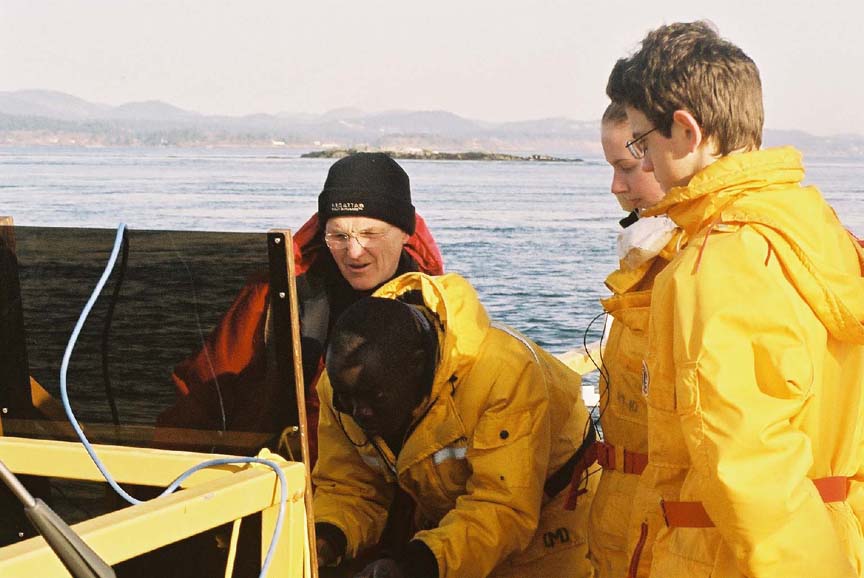
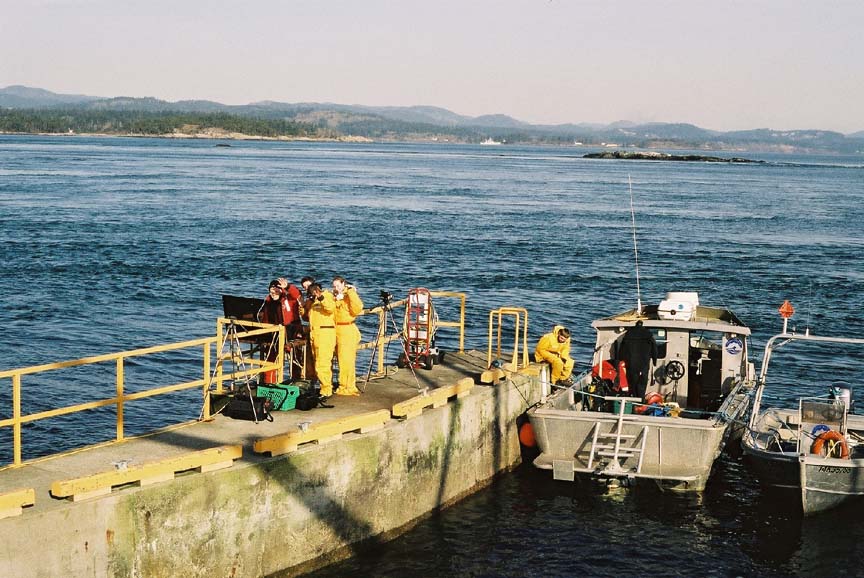
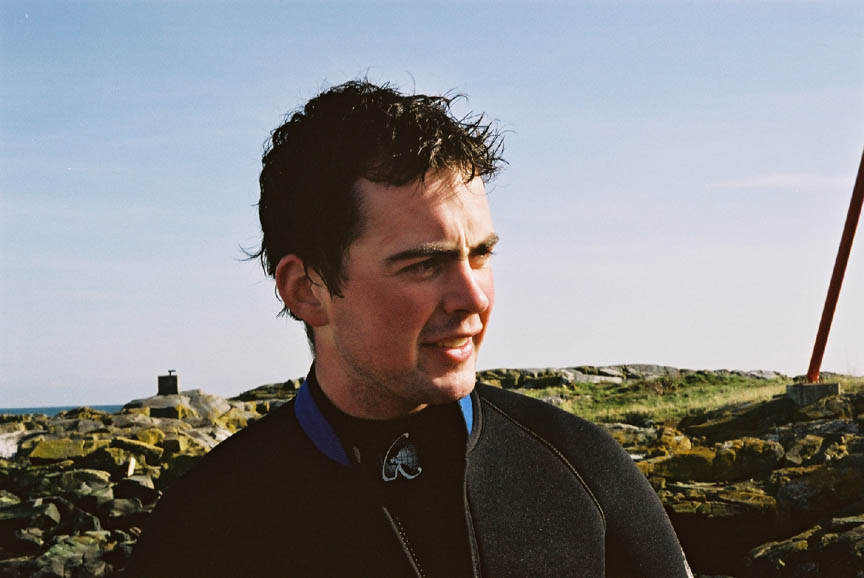
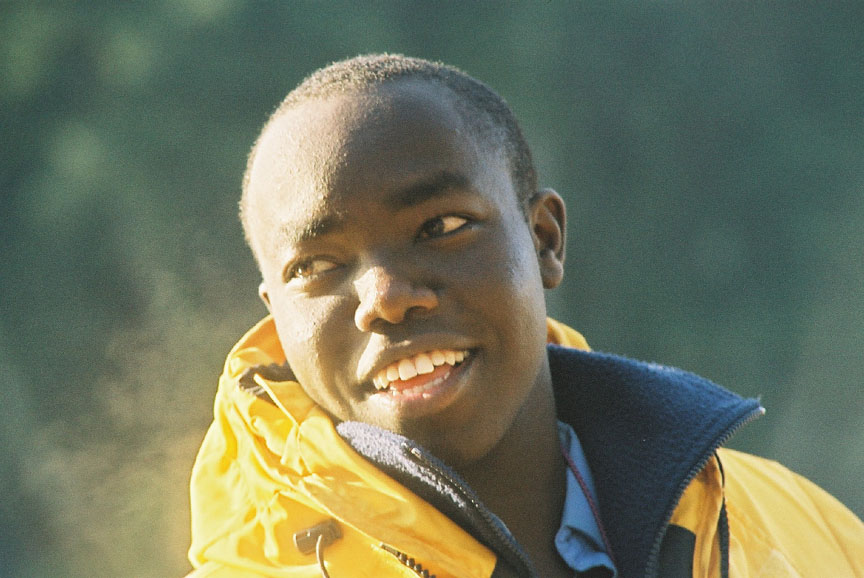
(L to R back) Garry,Damien, Nigel (L to R front) Kiprop, Ian(visitor), Monica, Olend, Chris . Thanks to Angus Matthews for the photos– Monica claims full responsibility for the commentary on this page!! Also see this write-up which appeared in the Pearson College Newsletter
The Race Rocks group setting up before the big day! Monica and Nigel peer intently into the eye of one of the cameras and Garry tests out the underwater cam before the dive, looking a bit like Roger Rabbit in the process.
- Monica and Kiprop give two big thumbs up.
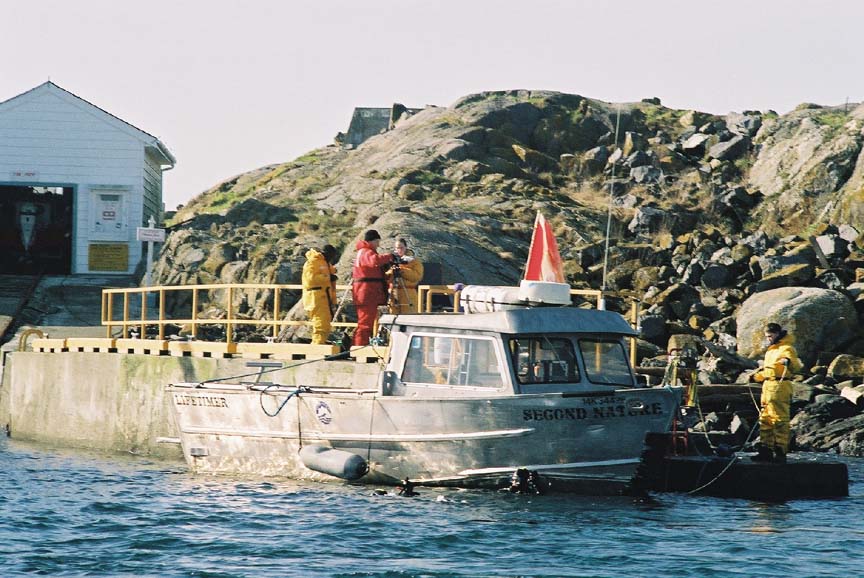
- On the bottom of the picture, you can see the divers about to go under with the underwater cam. In the bottom right corner, you can see the camera cable, which is attached to one of the computers.
- Garry and Kiprop study the computer screens displaying the live webcast.
- Uh-oh…that’s what we look like when our live webcast dies on us!
- The diving Nigel, looking after the underwater cam.
- Kiprop has the LiveChannel webcaster on the G4 and the G3 does the monitoring of the webcast.
- Yes! Valentine’s Day on the island, and the webcams are working…long-distance relationships, anyone?
- A general picture of the day — the tower, the boat, the dive flag…what more could you want?
- Waving goodbye to the camera as we pack up to leave.
- Damien, looking quite serious and official after his dive.
- This is the kind of picture you want to send home to your parents…Kiprop smiling after a successful webcast.
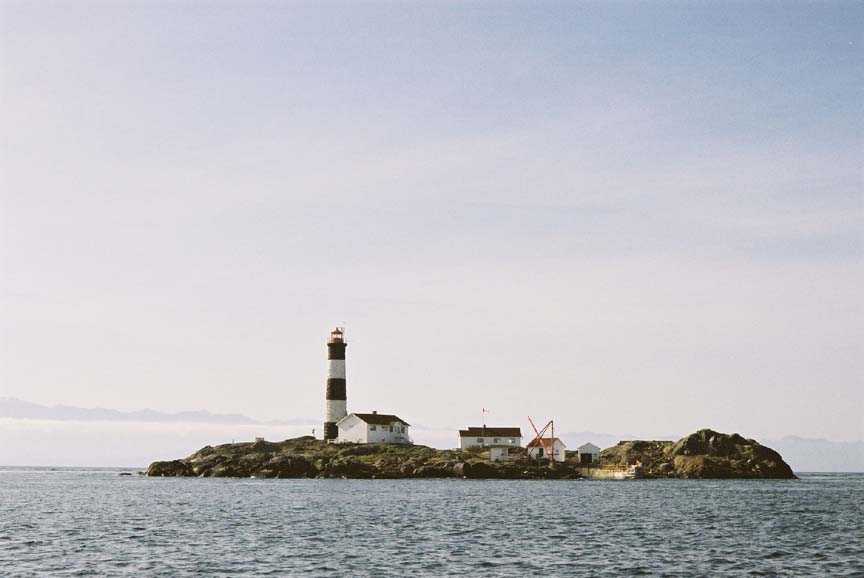
- Oh, Race Rocks …the gorgeous island!
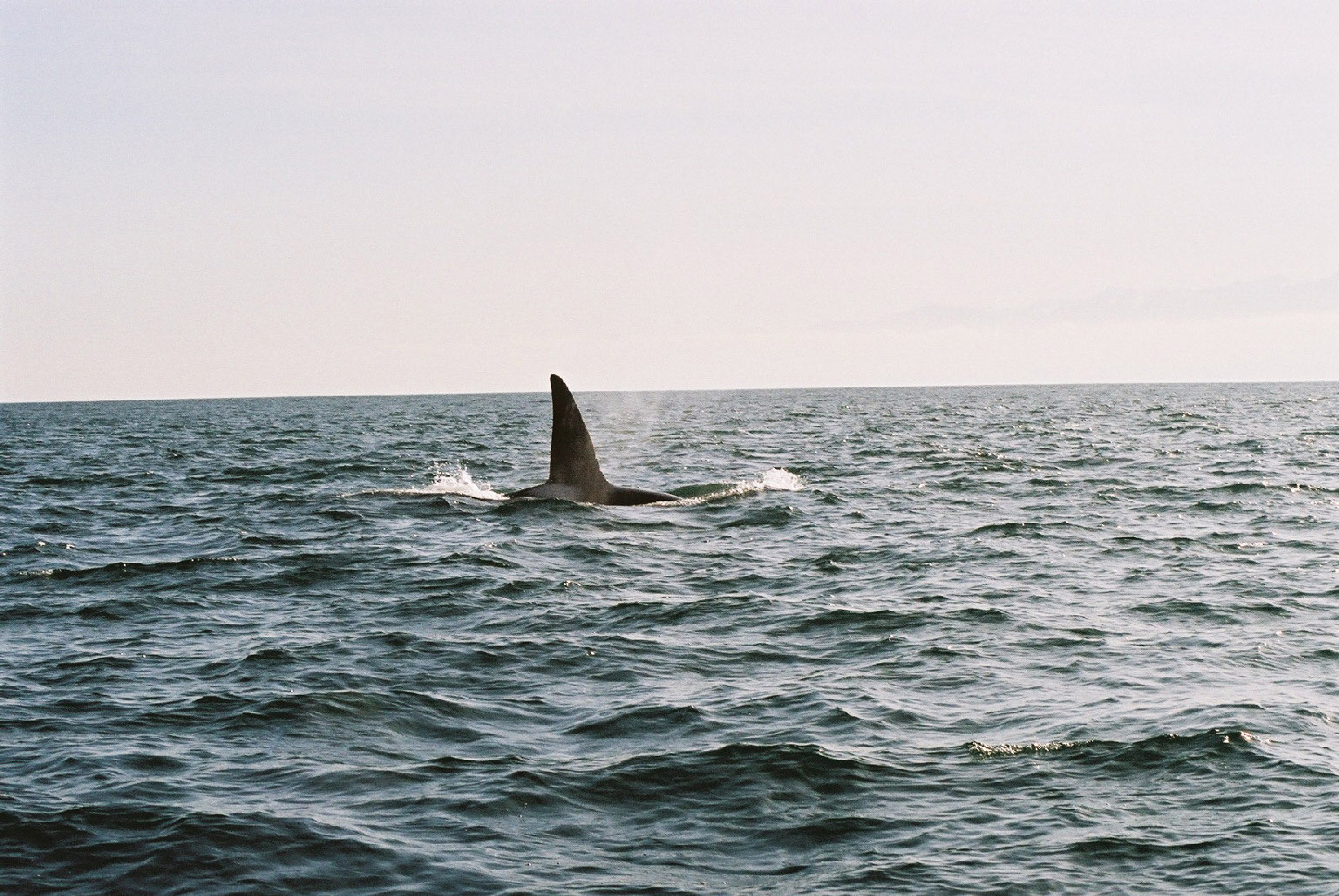
- Note from John Ford “that’s T14, a relatively distinctive male thanks to old scars at the base of the fin on the leading edge. These scars are from a VHF tracking transmitter that was attached to his fin during a temporary capture in 1976.
- We spotted an Orca on our way back to Pearson College from Race Rocks. An exciting end to an exciting day.
Pycnopodia helianthoides: Sunflower star–The Race Rocks taxonomy
- Loreen Pindera displays the oral side of the pycnopodia to shore-bound visitors.
- The dorsal side , with grey tufts where the gills are loated. White pincers on the dorsal side are the pedicellaria
- Photos by Pearson College Divers.
- The tube feet of the Pycnopodia
- Adam Harding took this picture of the red eye spot at the end of a tentacle.
- forcep-like structures used to defend the surface. A good habitat image of bith Pycnopodia and the giant red urchin.
- Close up of pedicellaria, tiny forcep-like structures used to defend the surface.
- Pycnopodia : These three last photos are derived from photos by Dr.A.Svoboda
- Dorsal surface showing gills
Pycnopodia tend to be found thriving in regions rich in seaweed, in low intertidal zones on rocky shores. They have an arm radius that ranges from forty to sixty-five centimeters. Small juveniles have five arms but develop twenty four by the time they are adults. Pycnopodia have an aboral surface and are usually pink, purple or brown in color. Occasionally they will be red or yellow in color. They also have the ability to regenerate lost arms. Pycnopodia are the largest, heaviest and most active of the Pacific coast sea stars. Pycnopodia feed on Stronglyocentrotus purpuratus (the purple sea urchin), bivalves, polychaetes, chitons, snails, hermit crabs, crabs, sea cucumber, and Leptasterias sea stars . The Pycnopodia utilize over fifteen thousand sucker feet when capturing prey. Their prey is swallowed whole and digested internally, and they have the ability to partially evert their stomach. Antagonistic, combative behavior has been observed when two Pycnopodia encounter one another. The key predator of the Pycnopodia is the King Crab. A fourfold increase in speed has been noted when the Pycnopodia is in contact with a predator. If the Pycnopodia does not escape, the predator will latch on to one of its many arms and begin to feed.
The sea star Pycnopodia helianthoides is one of the largest invertebrate predators at Race Rocks. In this close up view, on the dorsal side, the pinkish tufts contain the pedicellariae (small pincers) and the dermal branchiae (for gas exchange) On the ventral view, the central mouth is surrounded by many tube feet.
In October, 2001, federal Fisheries Minister Herb Dahliwal and the Provincial Environment Minister Joan Sawiki visited Race Rocks to officially proclaim the opening of the Race Rocks MPA. In this video, Ryan Murphy shows the ministers a Pycnopodia.
Domain Eukarya
Kingdom Animalia
Phylum Echinodermata
Class Asteroidea
Order Forcipulatida
Family Asteriidae
Genus Pycnopodia
Species helianthoides
common nameSunflower Star
References cited:
Marine Invertebrates of the Pacific Northwest, Eugene N Kozloff, 1996, University of Washington Press
Intertidal Invertebrates of California, Robert H Morris Donald P Abbot and Eugene C Haderlie, 1980, Stanford University Press
Pacific Seashores- A Guide to Intertidal Ecology, Thomas Carefoot, 1977, J.J. Douglas Ltd
| Other Members of the Phylum Echinodermata at Race Rocks |
and Image File |
 The Race Rocks taxonomy is a collaborative venture originally started with the Biology and Environmental Systems students of Lester Pearson College UWC. It now also has contributions added by Faculty, Staff, Volunteers and Observers on the remote control webcams. The Race Rocks taxonomy is a collaborative venture originally started with the Biology and Environmental Systems students of Lester Pearson College UWC. It now also has contributions added by Faculty, Staff, Volunteers and Observers on the remote control webcams.
December 2001- Hannah McKinnnon (PC) |
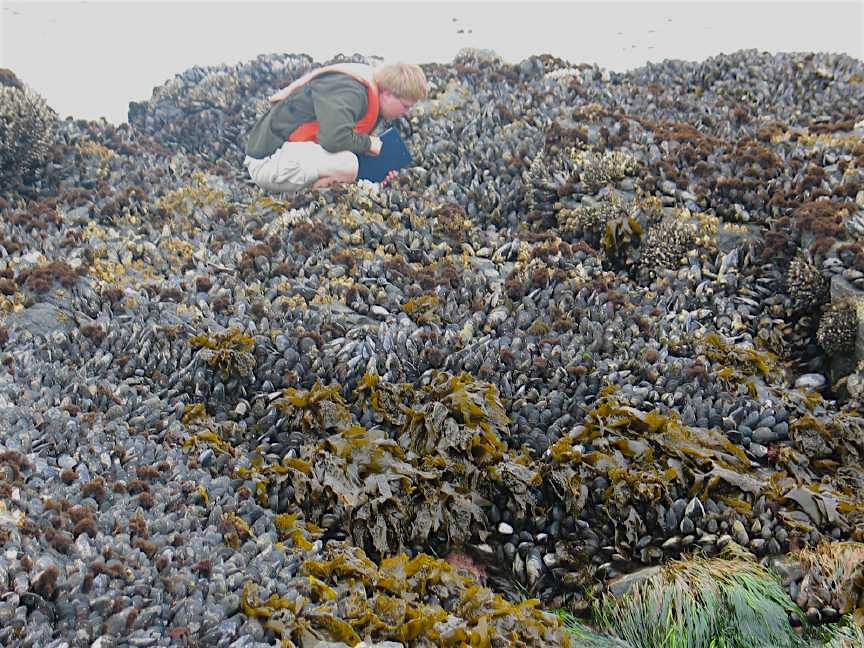
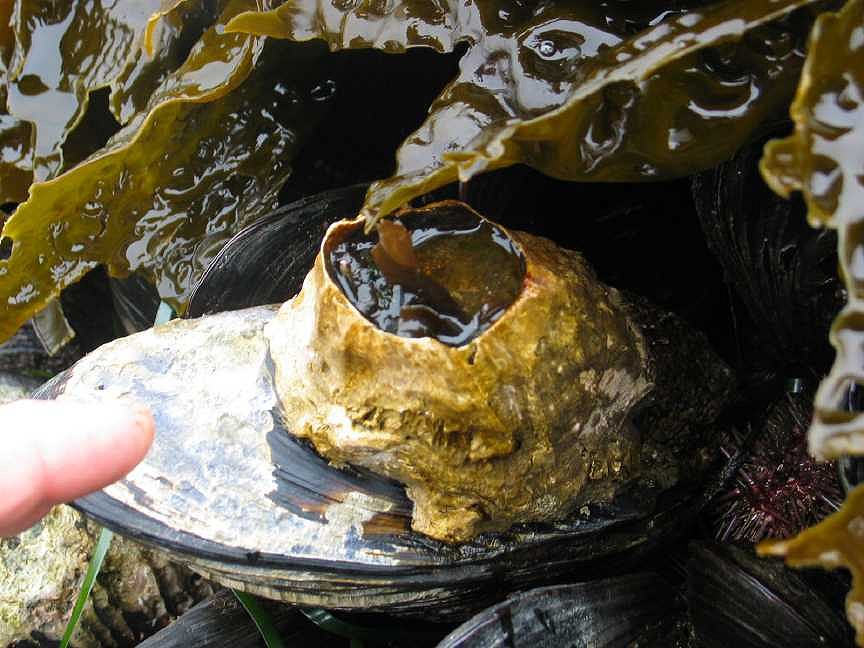
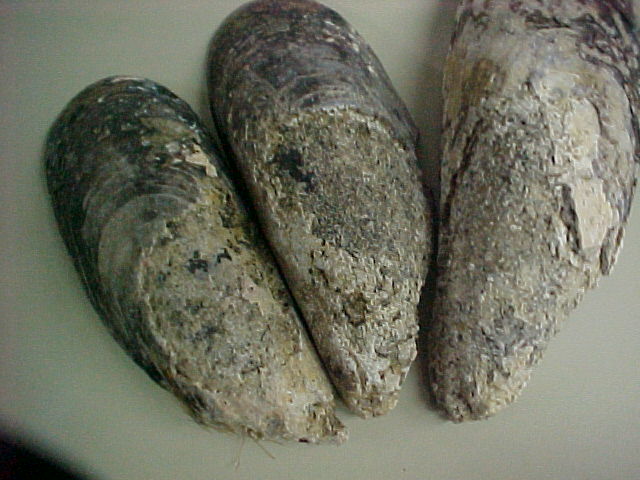
Mytilus californianus: California Mussel
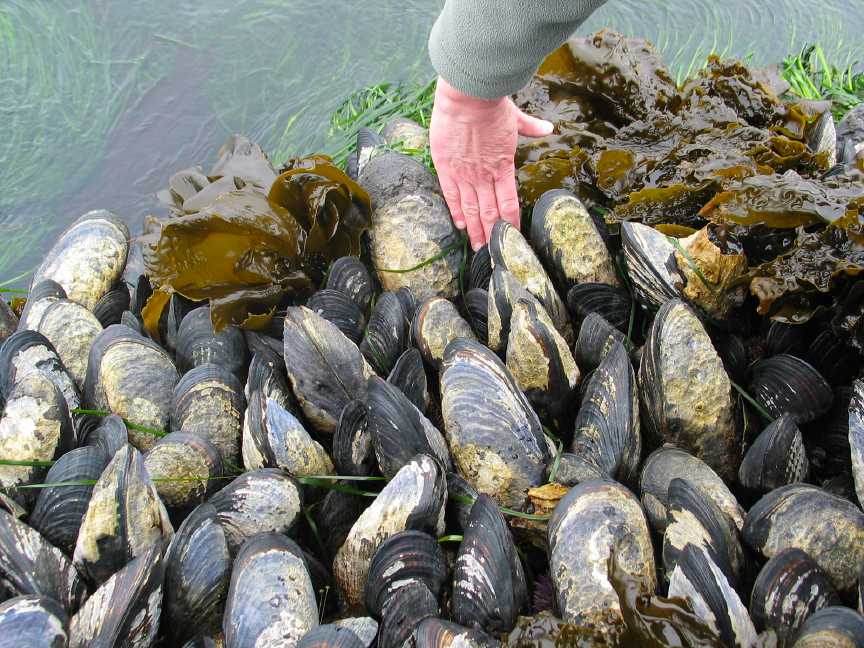

Very old and large Mytilus californianus in the intertidal zone at Race Rocks. This is one of the advantages of long term preservation of the area as an Ecological Reserve.
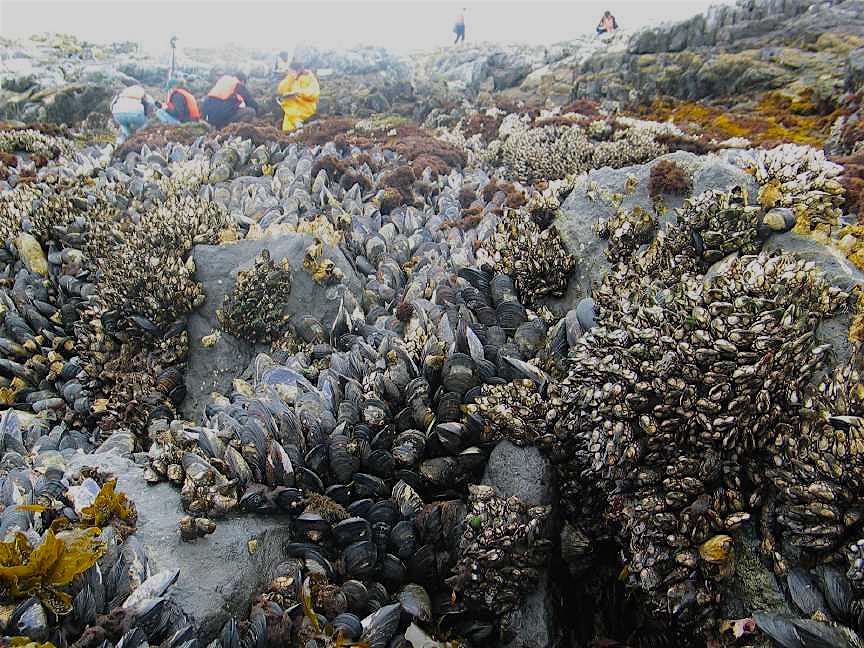
- At low tide on the South West corner of Great race Rock, the mussel beds lie on a horizontal reef,no space exists without some organism attached.
- Mussel beds and goose neck barnacles exist in close proximity. G. Fletcher photos
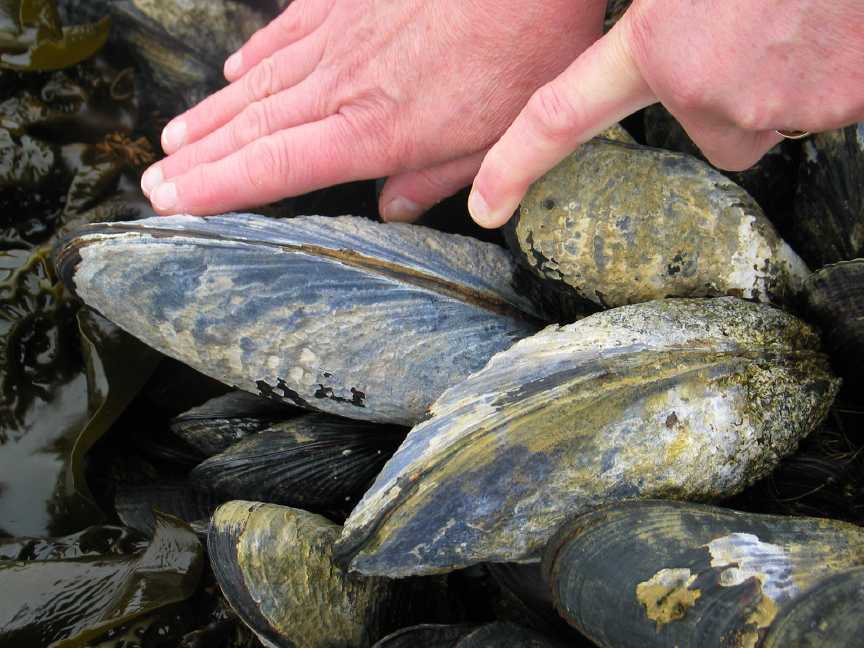
- The size of the mussels here is in the range of 35 cm.
- This mussel will no doubt have a competition for food with this barnacle.
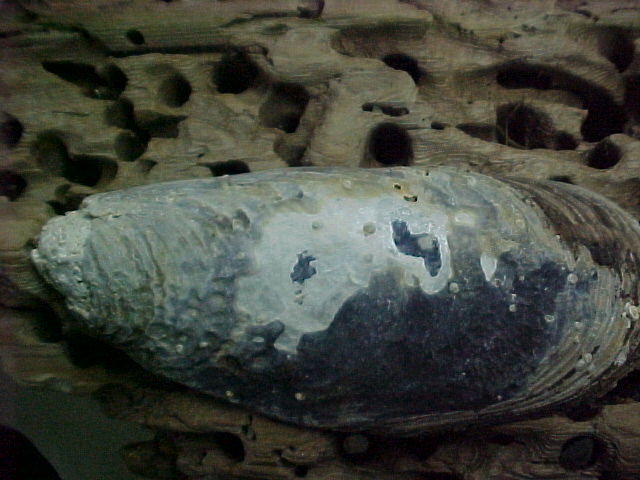
- These shells are also heavily parasitised
- The shells of old mussels become riddled with parasites.
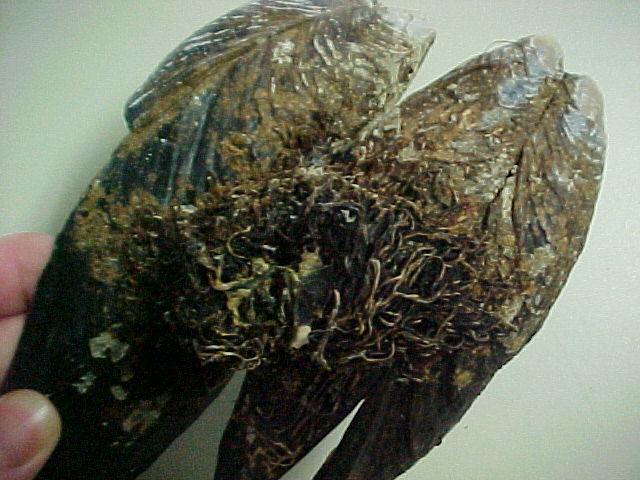
- Often kelp attaches to mussels and then uproots it when wave action gets severe. This shows a kelp holdfast attached.
- The pea crab (as one can see in the picture), Fabia subquadrata is found in many mussels.
The pea crab (as one can see in the picture), Fabia subquadrata is found in 1 to 3% of California mussels along the central California coast and 18% of mussels along Vancouver Island. This is a parasite that lives within the shell, because they rob food from their host and sometimes damage one of the gills. Public health codes usually prohibit the marketing or serving of parasitized animals but since the pea crab is very tasty, organisms with this crab are sometimes sold. Moreover, in a small portion of the population you can find imperfect pearls. These are of no value. http://www.lanecc.edu/science/zonation/mussel.htm (accessed 31 January 2002)
Morris, R., P. Abbott and E. Haderlie. 1980. Intertidal Invertebrates of California. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California. 690 pages.
Domain Eukarya
Kingdom Animalia
Phylum Mollusca
Class Bivalvia
Subclass Pteriomorpha
Order Mytiloida
Family Mytilidae
Genus Mytilus
Species californianus
Common Name: California mussel
Other Members of the Phylum Mollusca at Race Rocks.
and Image File |
 The Race Rocks taxonomy is a collaborative venture originally started with the Biology and Environmental Systems students of Lester Pearson College UWC. It now also has contributions added by Faculty, Staff, Volunteers and Observers on the remote control webcams. The Race Rocks taxonomy is a collaborative venture originally started with the Biology and Environmental Systems students of Lester Pearson College UWC. It now also has contributions added by Faculty, Staff, Volunteers and Observers on the remote control webcams.Simon Michaud PC Yr. 28 |
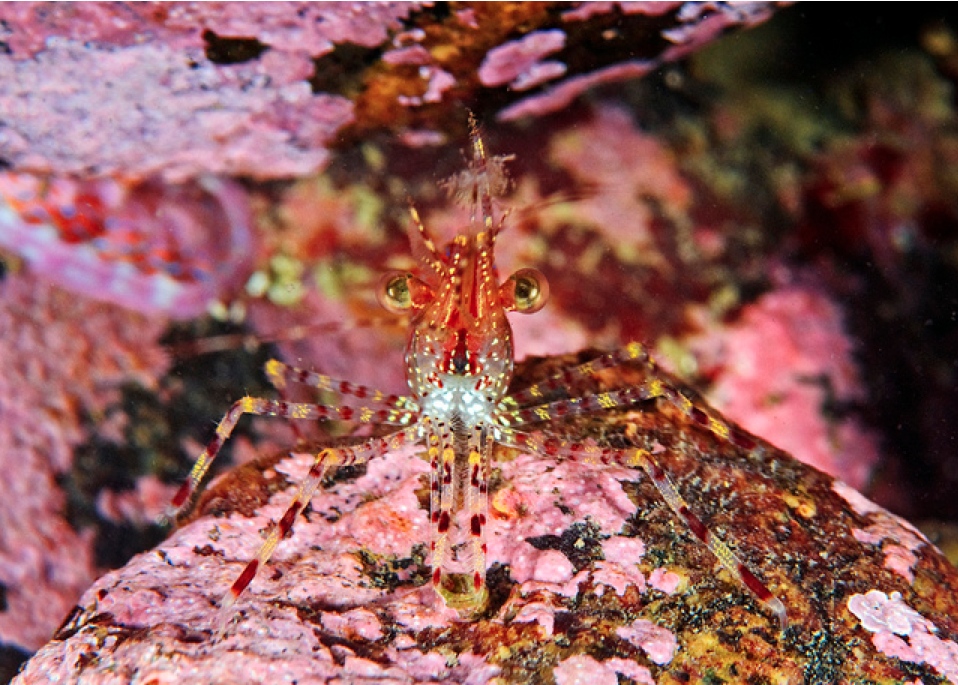
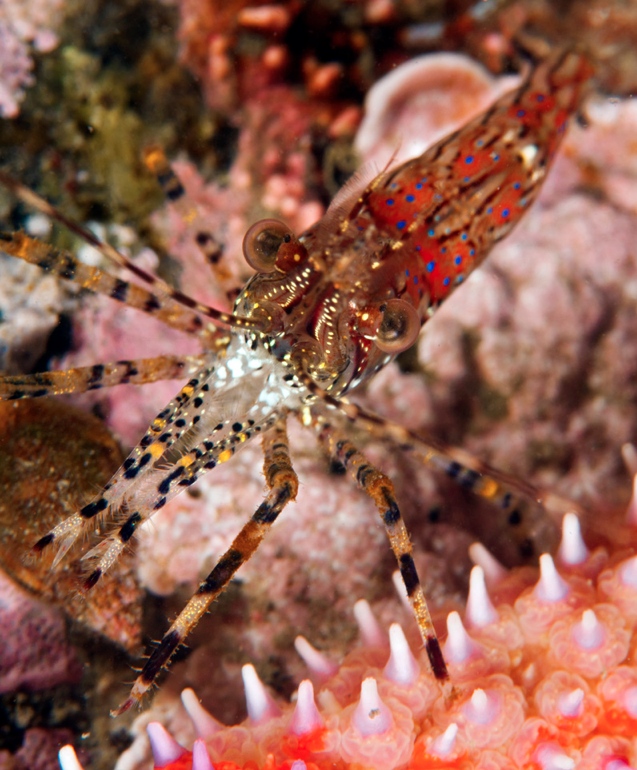
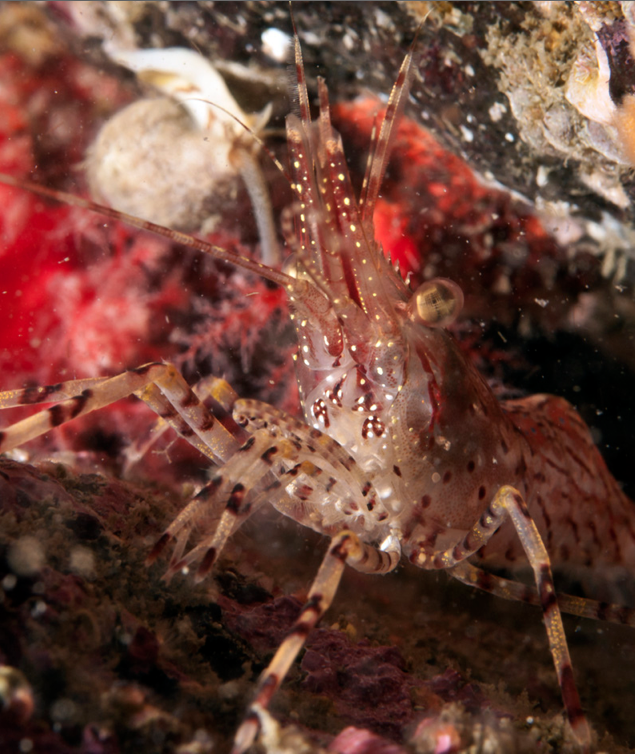
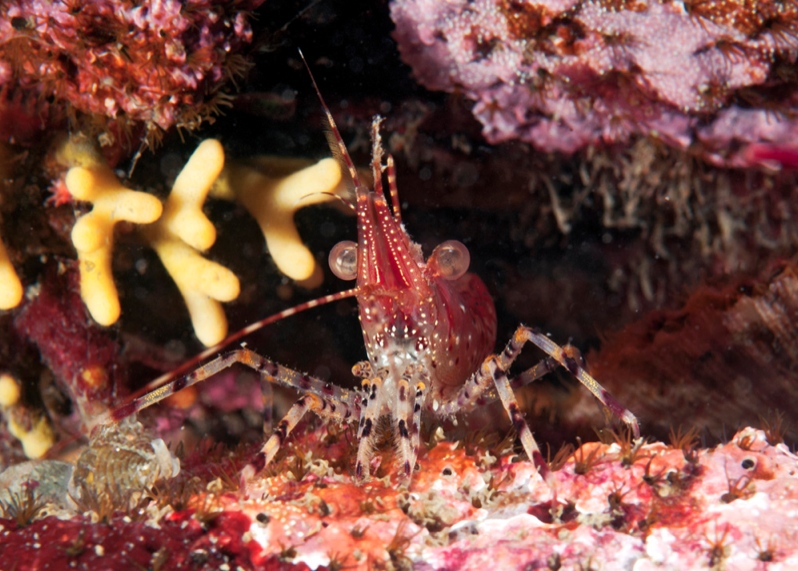
Pandalus danae: Coonstripe shrimp –The Race Rocks Taxonomy
Ryan Murphy took the pictures on this page and followed up in getting the identifications sorted out between this shrimp and Pandalus stenoplepsis and verification from Greg Jensen of the University of Washigton.
- Pandalus danae
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The coonstripe shrimp has large eyes, a thick shell and a surface finely pitted. The color of the shrimp is transparent, milky, and has irregular stripes and spots of chocolate brown all over the body, including its antennae. The antennae are long and heavily banded. Total length of the male shrimps can become about 123mm and the females about 140mm.
HABITAT
As one of the common names suggests, the dock shrimp is often living on or by wooden wharves, in shallow water bays and inlets. The coonstripe shrimp ranges from Alaska to central California.
FEEDING
The diet of the shrimp consists mainly of amphipods, mysids and polychaete worms.
PREDATORS
Lingcods are the main predators, except for humans who exploit the shrimp in the prawn industry.
REPRODUCTION
The shrimp lives about three years. Each of the shrimps starts the life cycle as male and the first fall, breeds come. By the time the shrimp has reached its second spring, the shrimp becomes a female and breeds come fall. After that happens as a female the shrimp holds the fertilized eggs until the hatching come spring.
REFERENCES
Links:
http://www-heb.pac.dfo-mpo.gc.ca/english/programs/fhiip/species/coonstrp.htm
References:
A Bibliography of Shrimps of the Family Pandalidae by J.C. Scrivener
Shrimps of the Pacific Coast of Canada by T.H. Butler
Pacific Coast Crabs and Shrimps by Gregory C. Jensen
Other Members of the Phylum Arthropoda at Race Rocks.
and Image File |
 The Race Rocks taxonomy is a collaborative venture originally started with the Biology and Environmental Systems students of Lester Pearson College UWC. It now also has contributions added by Faculty, Staff, Volunteers and Observers on the remote control webcams. The Race Rocks taxonomy is a collaborative venture originally started with the Biology and Environmental Systems students of Lester Pearson College UWC. It now also has contributions added by Faculty, Staff, Volunteers and Observers on the remote control webcams.
This file was originally written by Anna Ihle Thingnaes, Pearson College student year 28 in January 2002 |