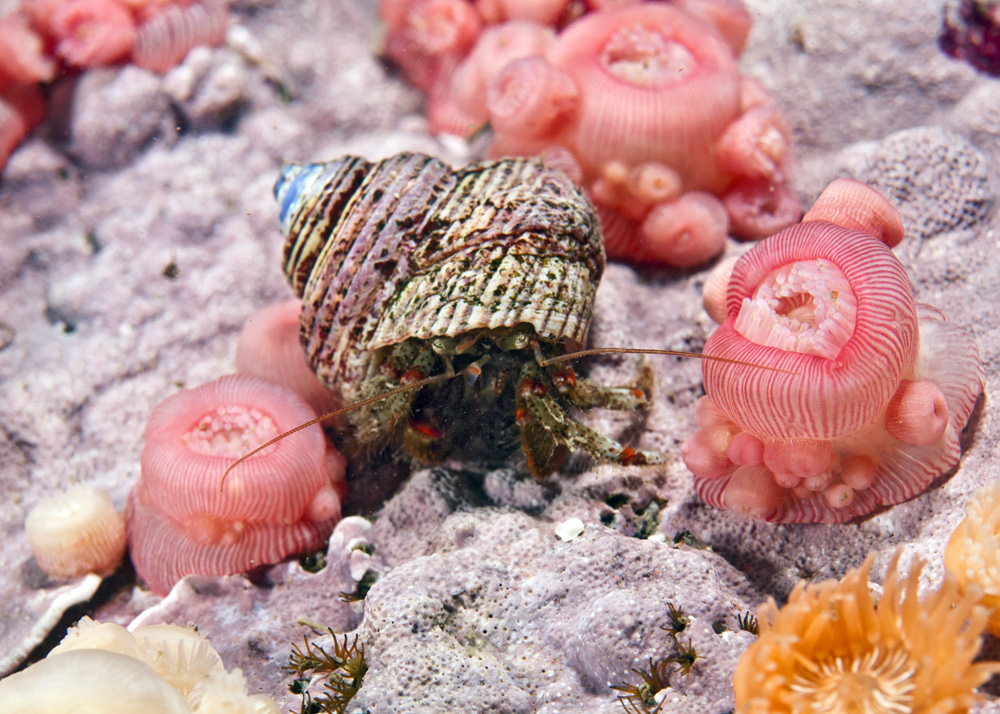
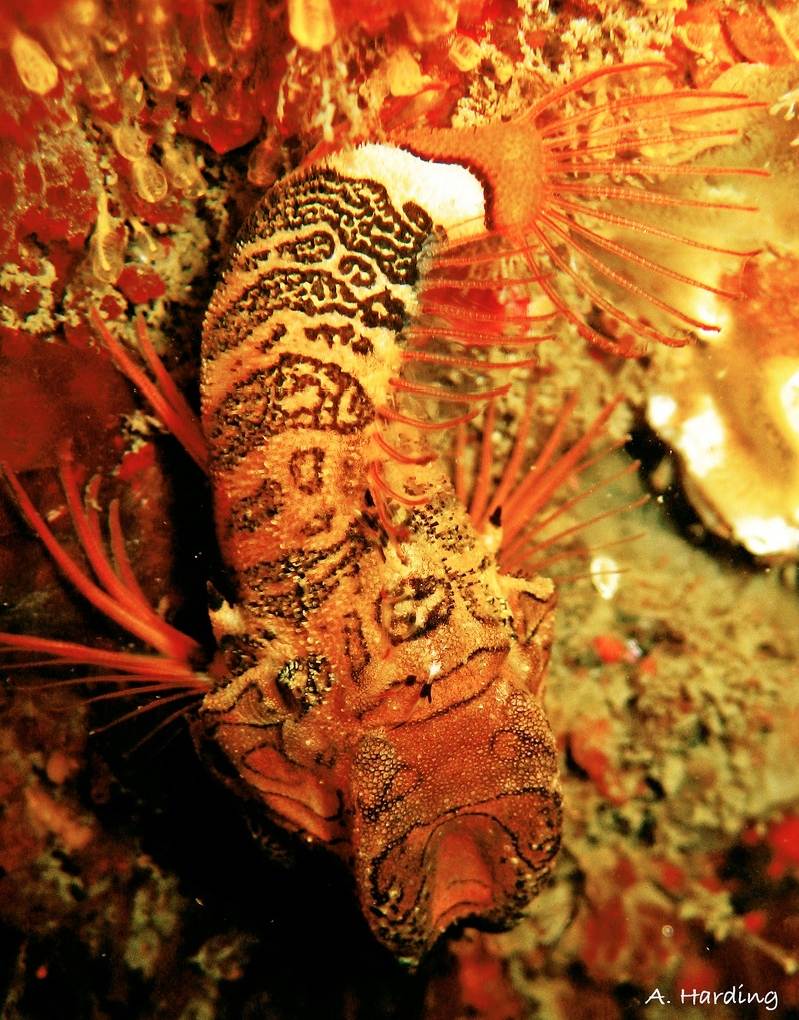
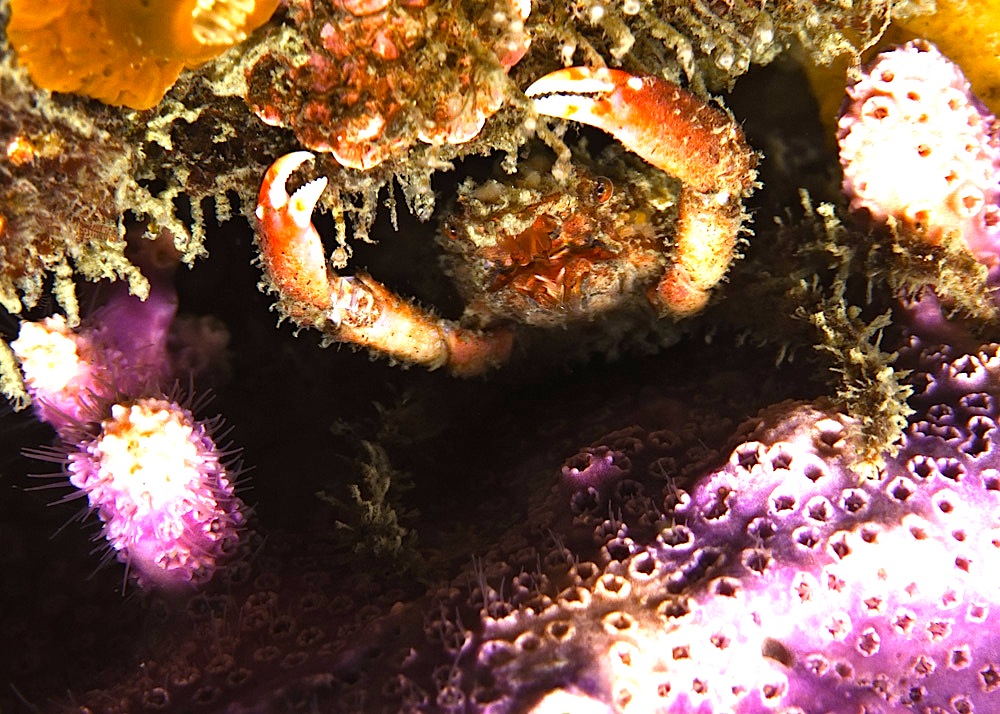
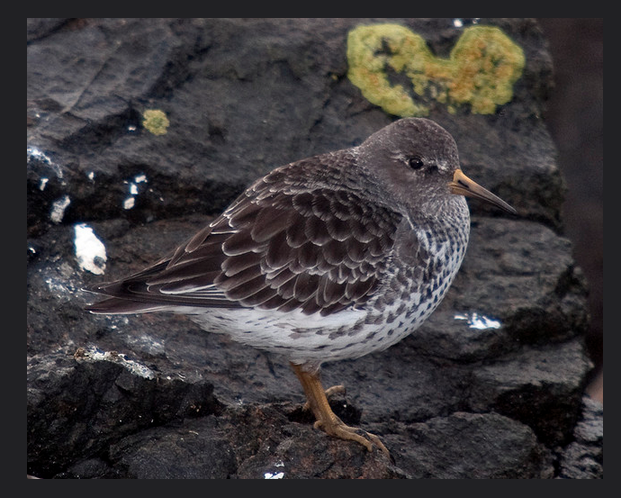
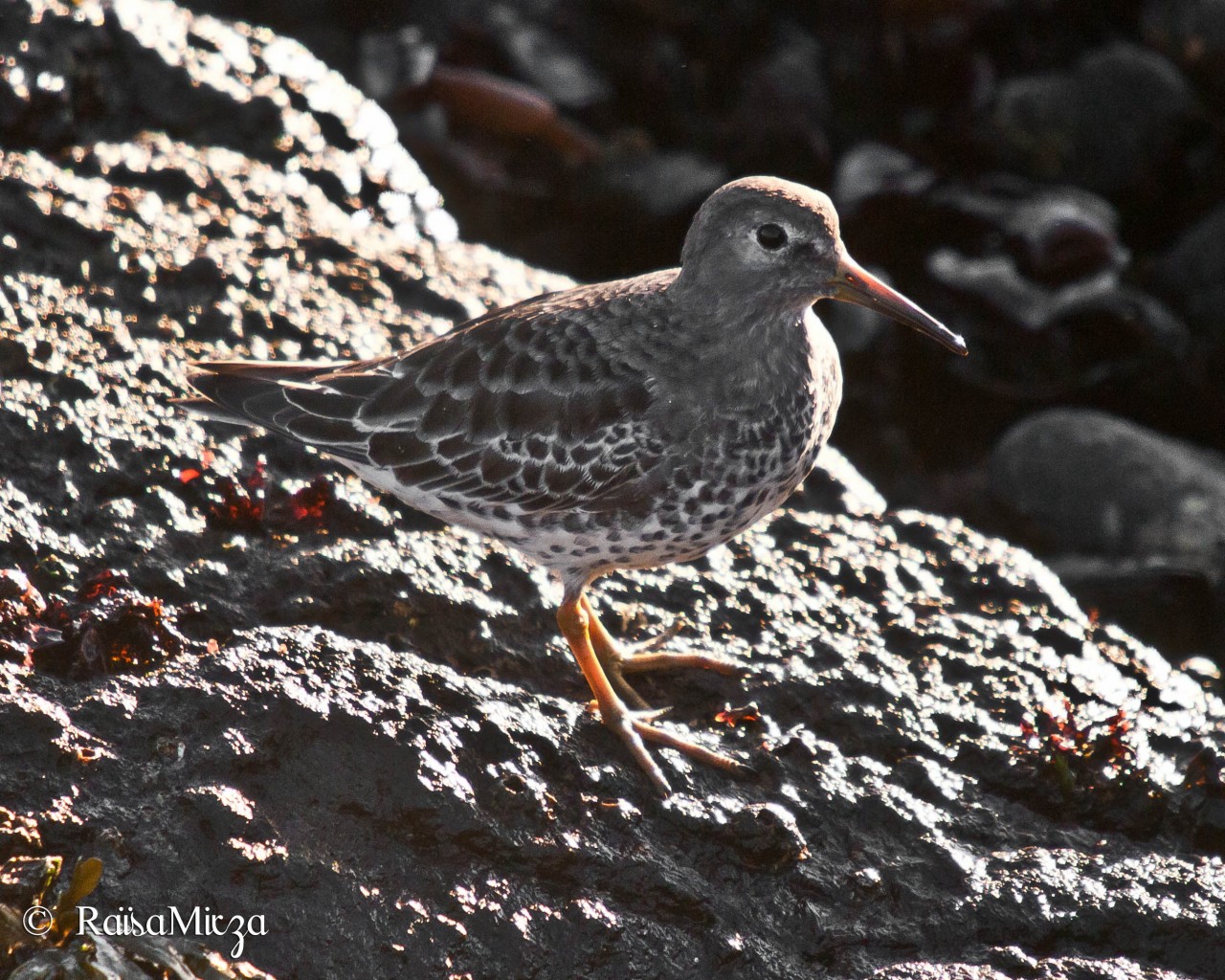
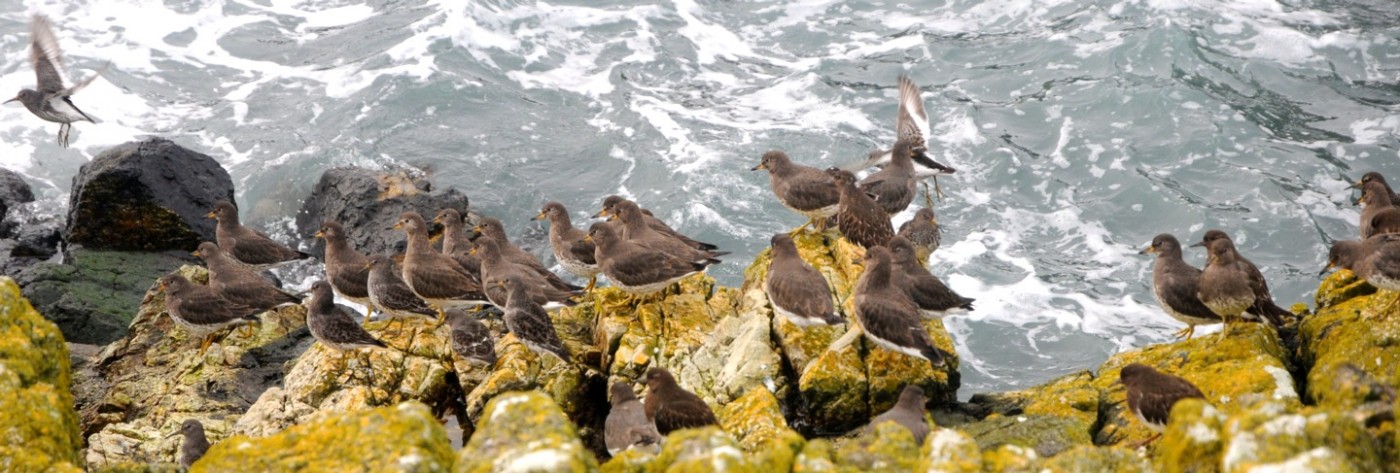
Pagurus beringanus, The Bering hermit crab. photo by Ryan Murphy, 2010
This is a tentative identification of Pagurus Beringanus – the Bering Hermit Crab is an animal that is found from the Bering Sea to Monterrey, California. They are also found at Race Rocks. Commonly found at depths from intertidal to 365 meters.
This Pagurus is identifiable by their pale grey-blue shells (carapaces) mottled with grey, red and yellow spots. Legs are also pale blue with red bands at the joints. Claws are reddish and densely covered with spines. Bering Hermit Crabs all have characteristic green, irridescent eyes
Habitat – rocky, intertidal areas with cold water.
Behavior – Adults are inactive during the day. Starting late afternoon and carrying on through the night they become active and feed. This is because the retinal pigments in the eyes with position of the day and the night, only in response to the ambient light in the water.
Bering Hermit Crabs are scavengers, which makes the fact that they taste good puzzling. They eat dead plant materials and dead animal matter.
They themselves are prey to several types of fish, including pine perch, the California sheephead and the spotted kelpfish.
Females have been recorded with eggs mainly in April and May but some as early as February. During courtship, the male carries the female around for a day or more, knocking their shells together. The actual mating lasts less than a second, and both animals come almost completely out of their shells to perform the act.
References:
Intertidal Invertebrates of California. Morris, Abbot, Haderlie, 1980
Pacific Coast Crabs. Gregory C Jensen, 1995
Between Pacific Tides. Ricketts, Calvin, Hedgpeth, 1997
Classification:
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Arthropoda
Class: Crustacea
Order: Decapoda
Superfamily: Paguridea
Family: Paguridea
Genus: Pagurus
Species: beringanus
Common Name: Bering Hermit Crab
Other Members of the Phylum Arthropoda at Race Rocks.
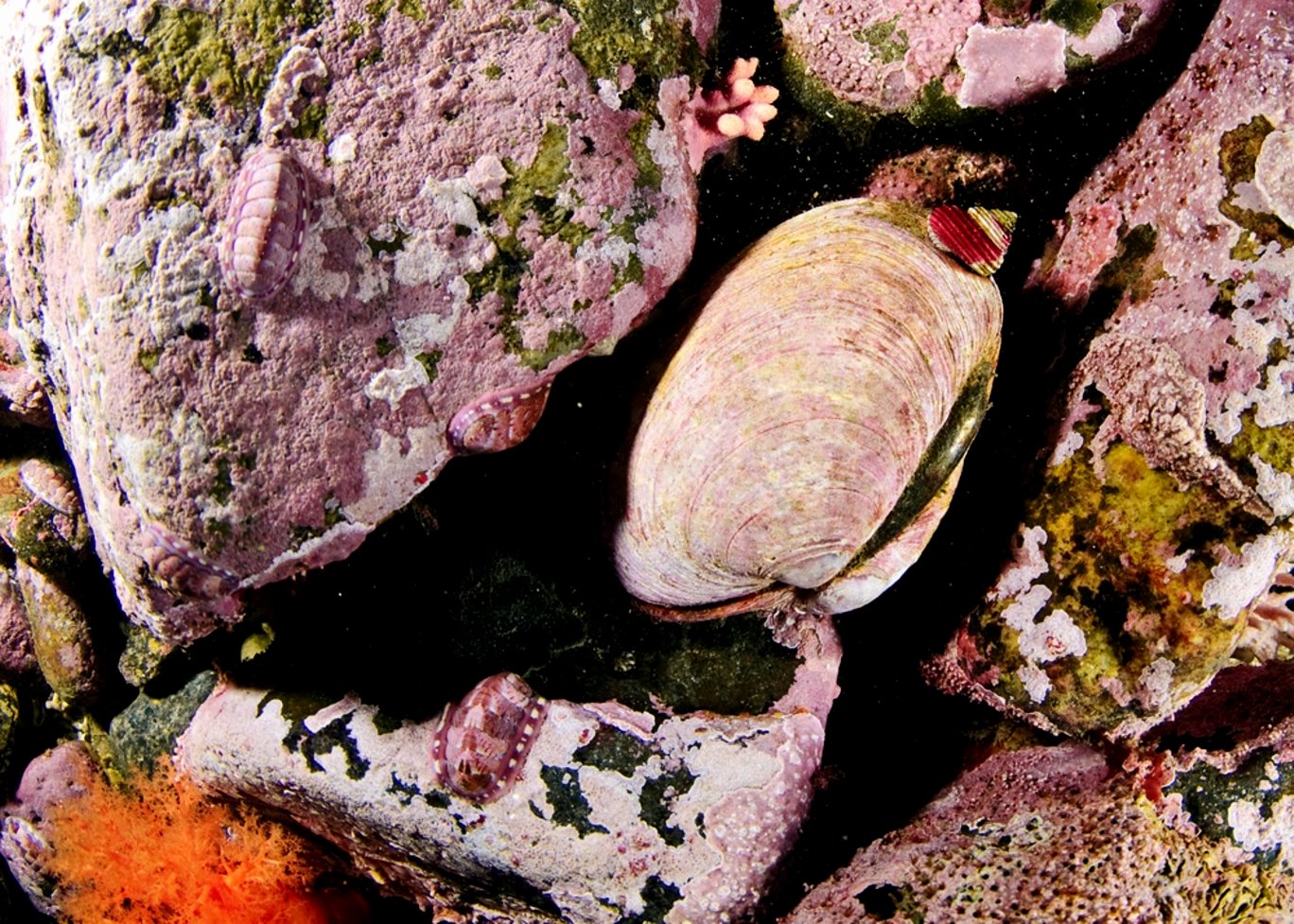 Saxidomus gigantea by Ryan Murphy, April, 2010
Saxidomus gigantea by Ryan Murphy, April, 2010 The Race Rocks taxonomy is a collaborative venture originally started with the Biology and Environmental Systems students of Lester Pearson College UWC. It now also has contributions added by Faculty, Staff, Volunteers and Observers on the remote control webcams. March 15 2010- Garry Fletcher
The Race Rocks taxonomy is a collaborative venture originally started with the Biology and Environmental Systems students of Lester Pearson College UWC. It now also has contributions added by Faculty, Staff, Volunteers and Observers on the remote control webcams. March 15 2010- Garry Fletcher