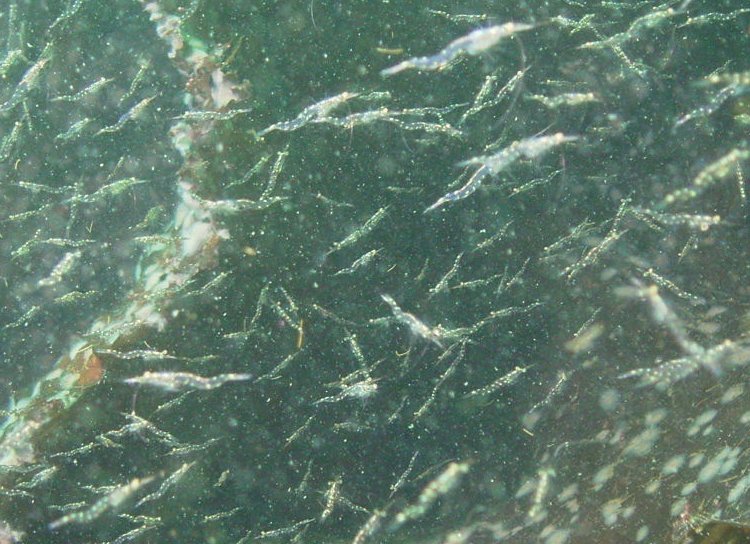
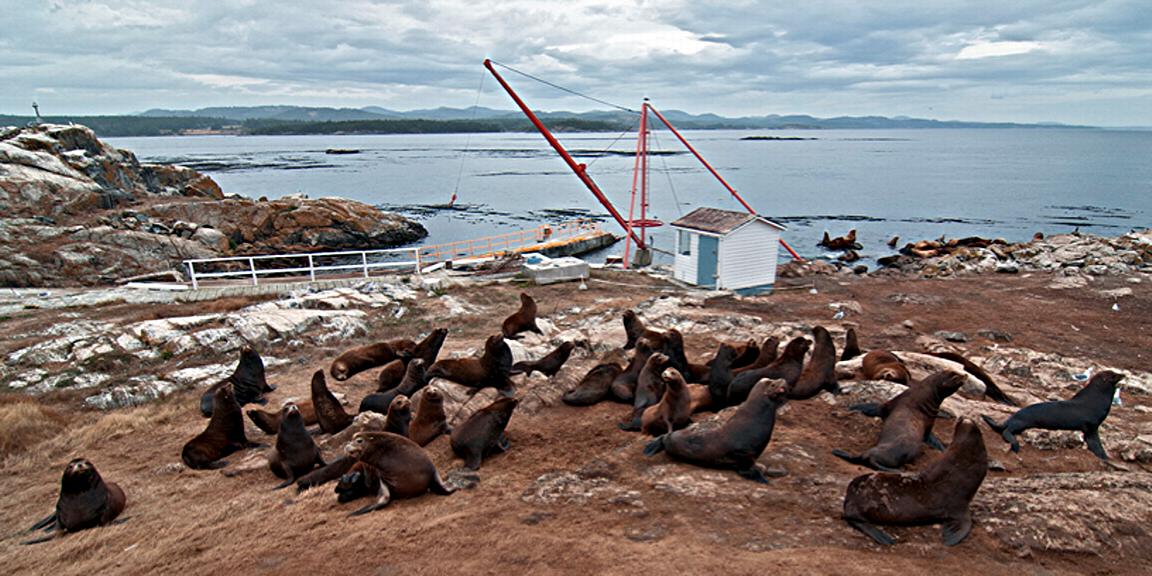
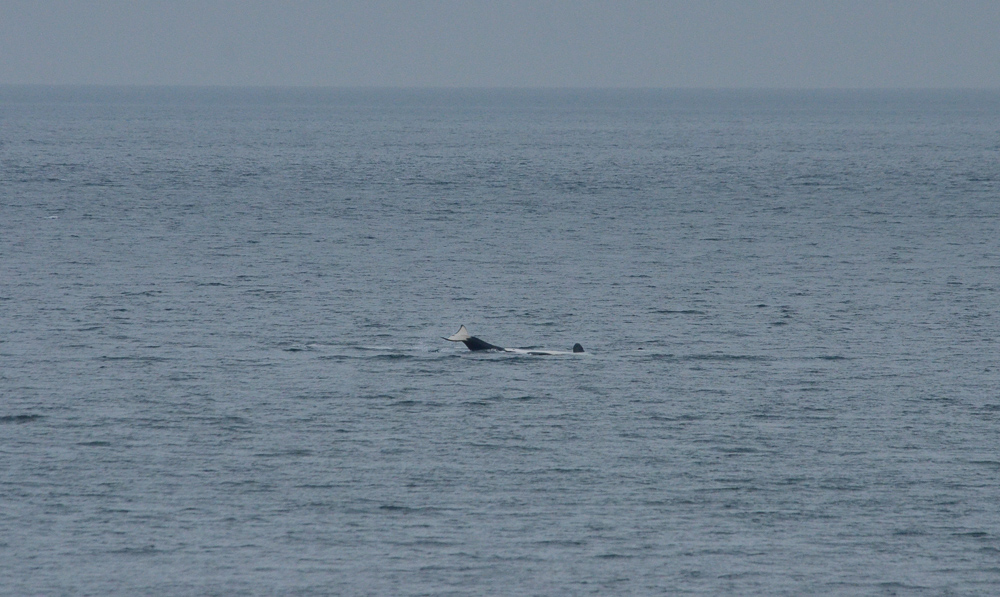
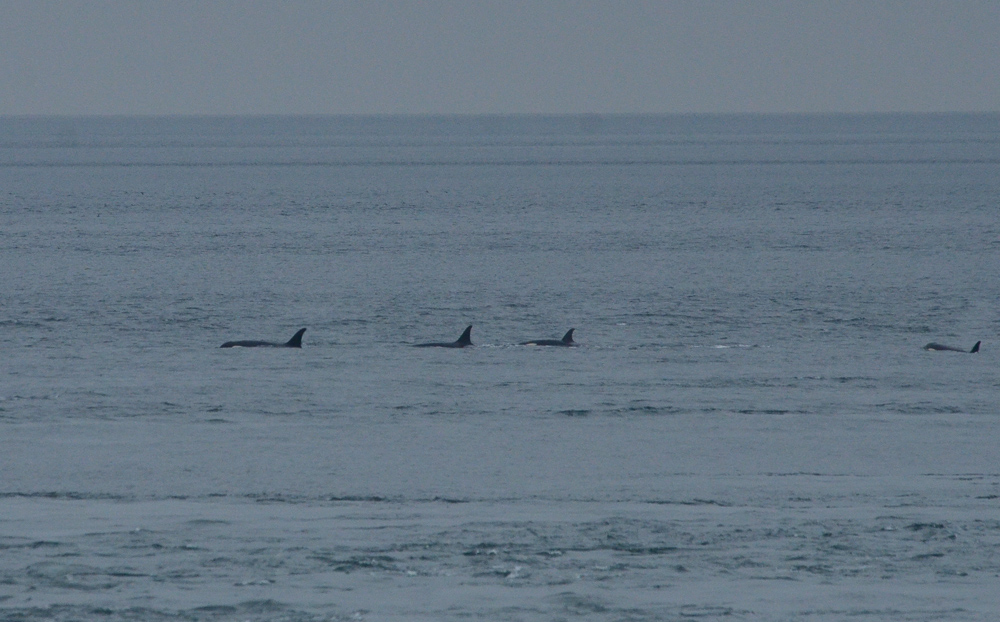
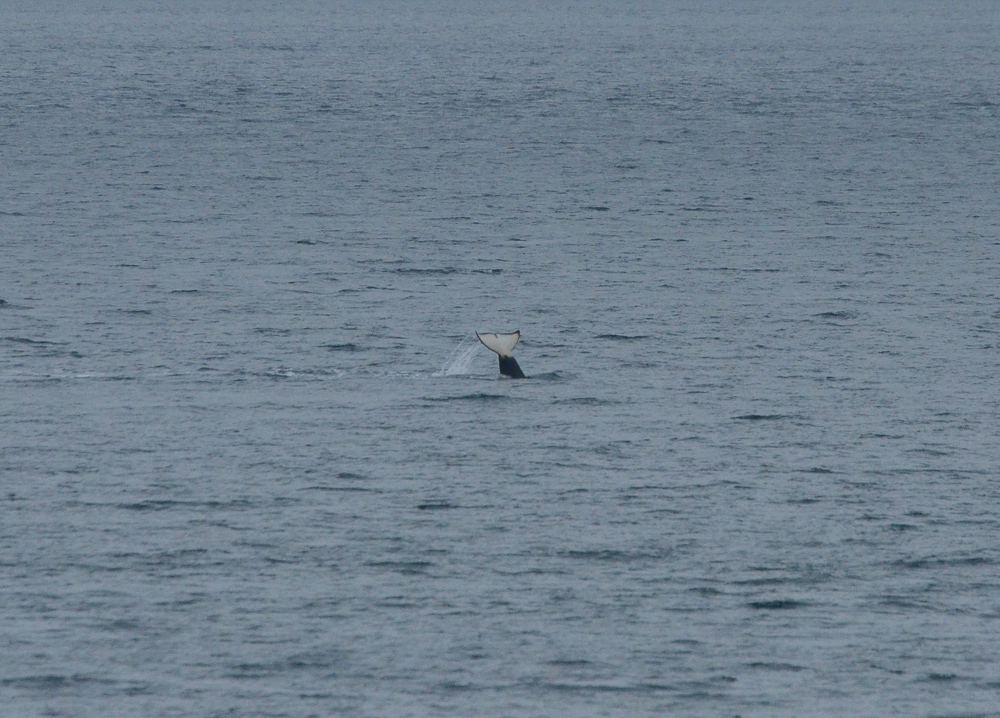
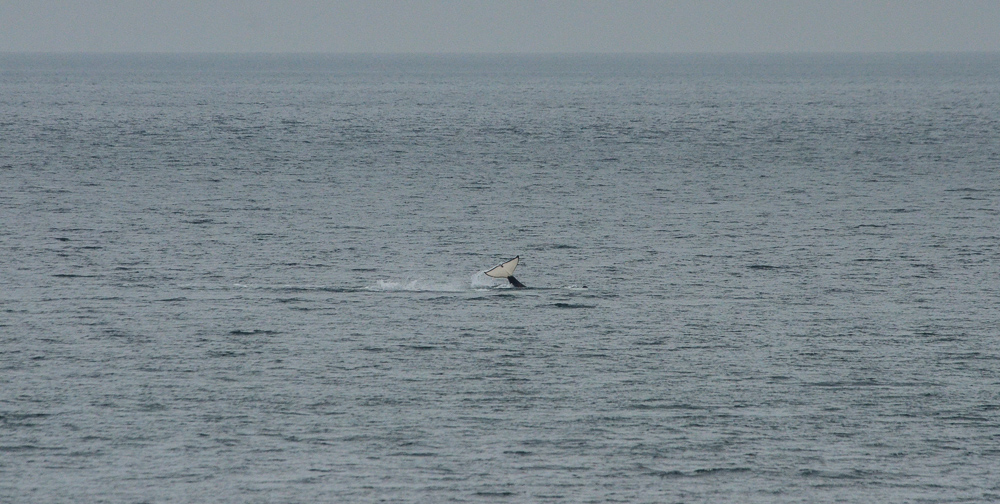
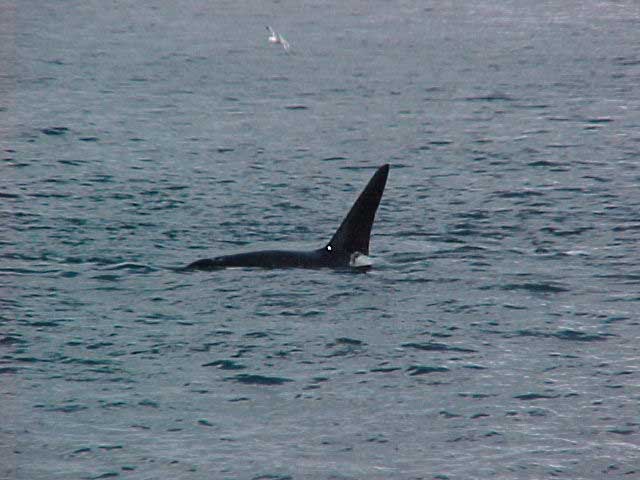
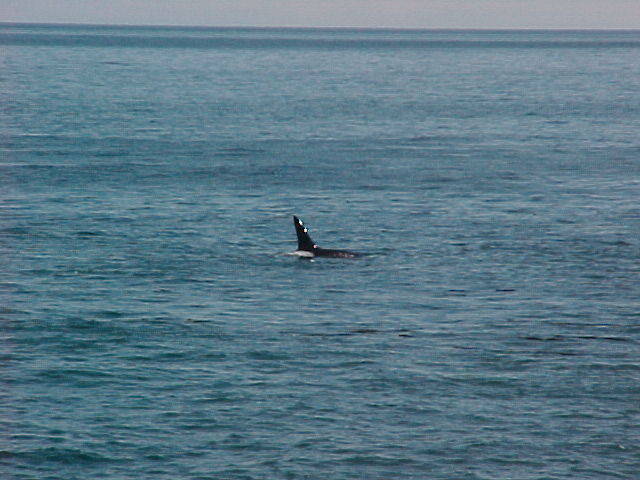
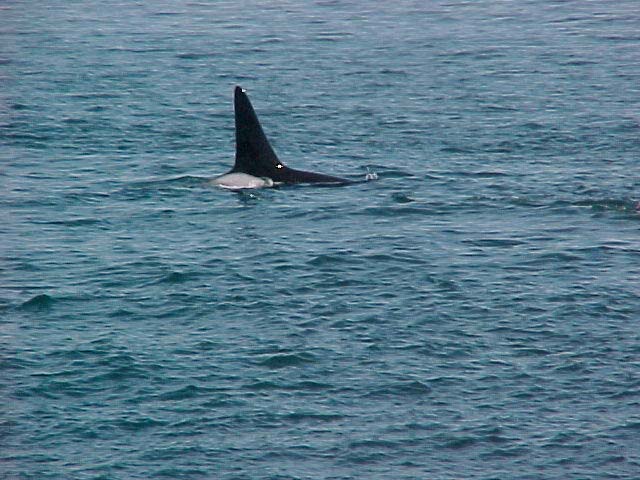
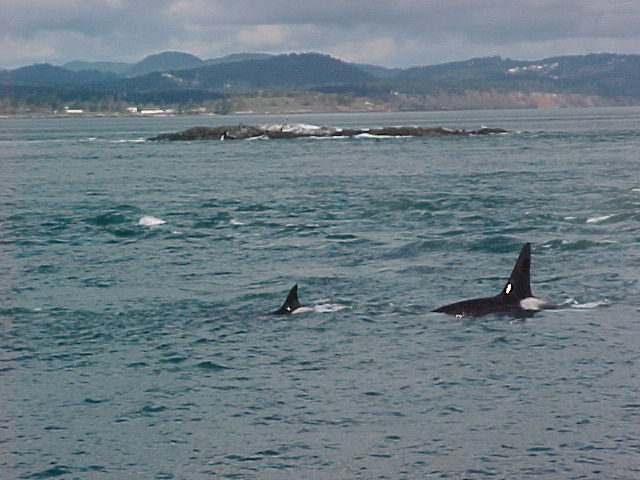
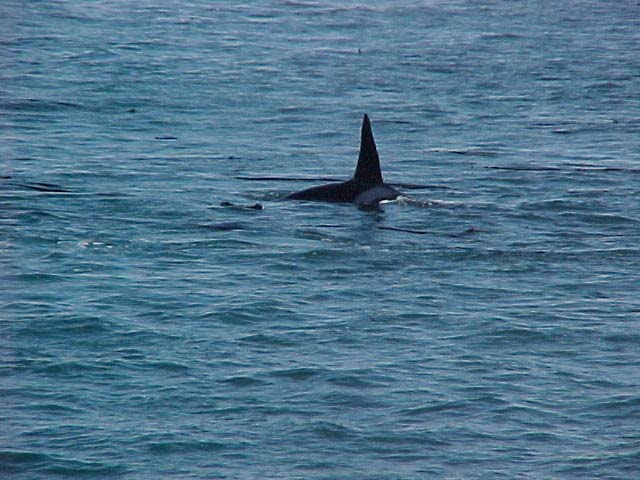
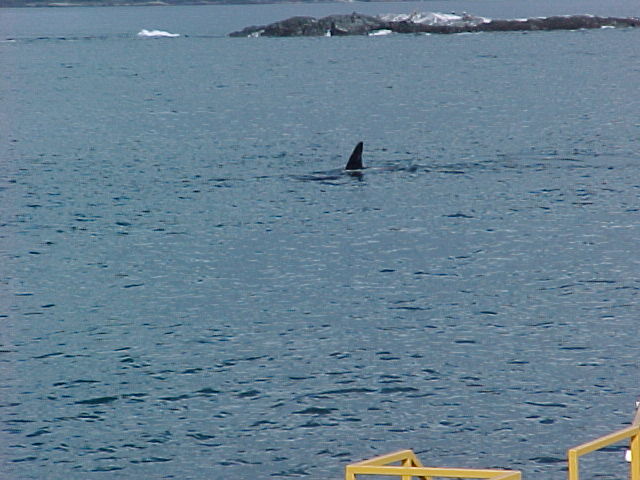
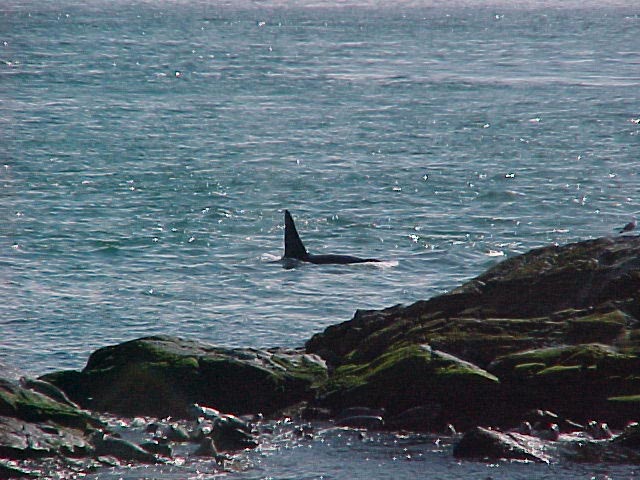
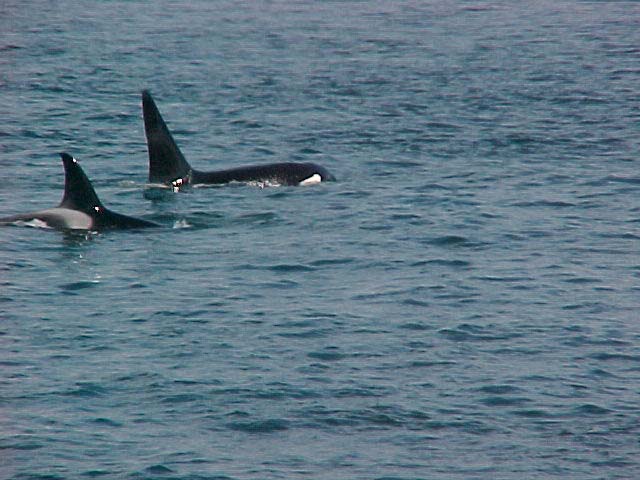
A swarm of krill in a kelp bed. November 2006 PC Divers Euphausia pacifica is, with Thysanoessa spinifera, the most common krill off the West coast of Vancouver Island.General description Krill are shrimp-like in appearance (Body plan of krill).The abdomen is large, and well-developed. Antennules are long, biramous and may be modified in males. Antennae are equipped with large scales. The mandibles usually have a palp and the two pairs of maxillae are small and flattened. All the thoracic legs are similar, and carry a gill formed from a typically branched epipodite and natatory setea. The last one or two pairs of legs however are often reduced or vestigial The first two pairs of pleopodes are modified as copulatory parts in males. along the British Columbia coast range up to 25 mm (1″) in length, but average 16 mm (5/8″) in length. Habitat Krill undergo a daily or ‘diurnal’ migration, where they spend the daylight hours in the twilight depths of the ocean (~100 m or 300 feet), out of sight of their predators. As the daylight decreases, the krill rise to the surface to feed in the dark on phytoplankton. In the morning, as the sky gets brighter, the krill will return to the twilight zone. A clear day may push the krill as deep as 150 m (450 feet); on a cloudy day, the krill may be at depths of only 60 m (180 feet). Krill are not distributed evenly within a body of water; they form characteristic ‘clouds’ or patches of high biomass in some areas, whereas other areas may be devoid of krill. Euphausia pacifica is found by the Pacific ocean’s coast from the south of USA to Japan (Distribution of Euphausia pacifica). Feeding Most krill are herbivorous, but some are omnivorous feeders. Adults migrate diurnally to the surface at night, to feed on the phytoplankton. They are exclusively filter-feeeders: water enters in a “filter” as the animal swims, and food is shoved forward to the mouth. Reproduction Males produce spermatophores in the dilated terminal part of the sperms ducts, and transfer them to the female with the aid of the first abdominal appendages. The female stores the male’s sperm and releases it to fertilize her eggs, which appear as small bubbles in her feeding basket. Females can produce many sets of eggs (totaling more than 20 000) during the summer spawning season. Krill larvae emerge from their shells at depths of several hundred meters, where, safe from predators, they subsist on yolky materials. Eggs hatch as non-feeding nauplii and pass through protozoea, zoea, and postlarval cyrtopia stages. Predators Their predators are mainly finfish and baleen whales (picture of krill: stomach content of Bryde whale). Krill are a large dietary proportion of many local finfish (hake, herring, rockfish, salmon) and if krill stocks should fall, finfish could be affected. Humans are also a predator. A emerging commercial krill fishery exists on the B.C. coast with a current annual limit of 500 tonnes. Krill in B.C. are harvested mainly as a feed supplement for both fish farms (gives salmon their ‘pink’ colour) and aquariums. In other areas of the world (e.g., Japan) they are also used for human consumption in limited quantities. Fresh, uncooked euphausiids have almost no taste. Frozen or dried krill develop a strong, rather discouraging flavor. They constitute the ocean’s richest source of protein and are rich in vitamins (especially vitamin A) Biotic association Some organisms are associated with the Euphausia pacifica but it seems that few are identified. Some of the identified ones are cilliates attached to eggs of the krill, and the parasite Thalassomyces fagei that belongs to the family Ellobiopsidae (Protista (Incertae sedis)) and infests the euphausiids. The Ellopbiopsidae have been classified at various times as protistans, colorless algae, fungi, or protozoans. They are multinucleate protistans with reproductive structures outside the host (here Euphausia pacifica) and absorptive portions inside. The organ of fixation has fine protoplasmic filaments, which are believed to absorb nutrients from the host. The parasite usually affects the maturation, molting, and growth of the Euphausia pacifica. Traditionally, krill and other plankton have been captured with net tows. Now the use of bioacoustics allows for the detection of plankton at a much greater rate than net sampling, but does not provide any information about what species and what age classes are being sampled. |
Other Members of the Phylum Mollusca at Race Rocks.
and Image File |
 The Race Rocks taxonomy is a collaborative venture originally started with the Biology and Environmental Systems students of Lester Pearson College UWC. It now also has contributions added by Faculty, Staff, Volunteers and Observers on the remote control webcams. The original text for this file was written by Marie-Noelle Belanger-Levesque (Quec, Canada) PC Year 28 The Race Rocks taxonomy is a collaborative venture originally started with the Biology and Environmental Systems students of Lester Pearson College UWC. It now also has contributions added by Faculty, Staff, Volunteers and Observers on the remote control webcams. The original text for this file was written by Marie-Noelle Belanger-Levesque (Quec, Canada) PC Year 28 |