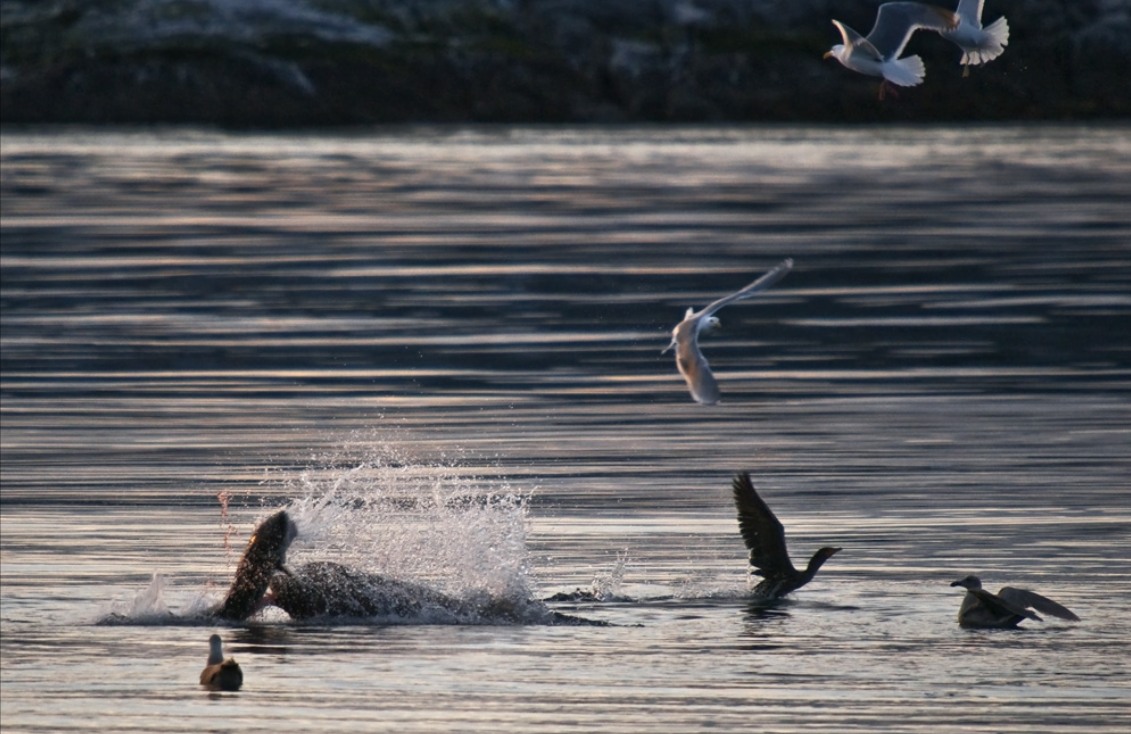
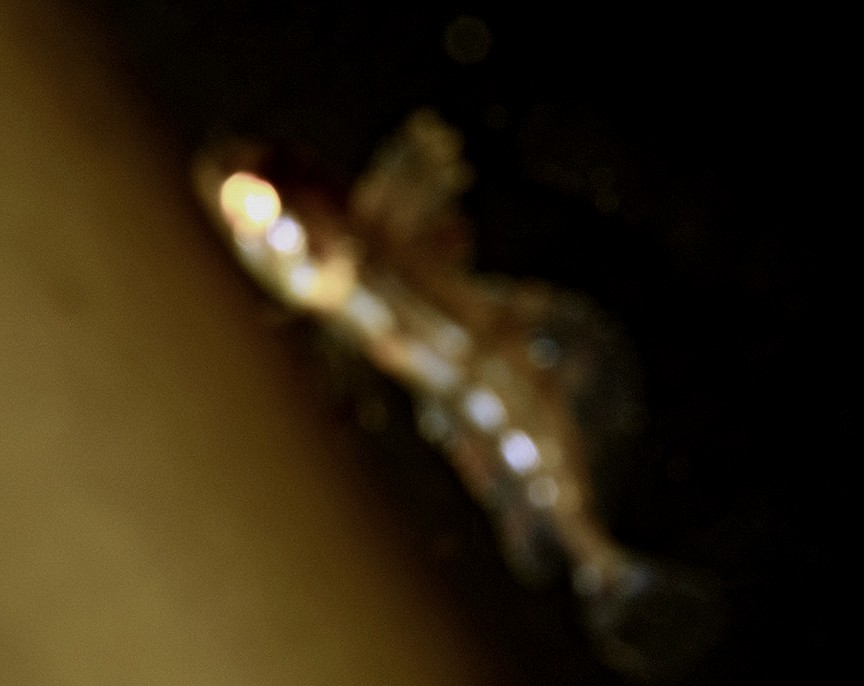
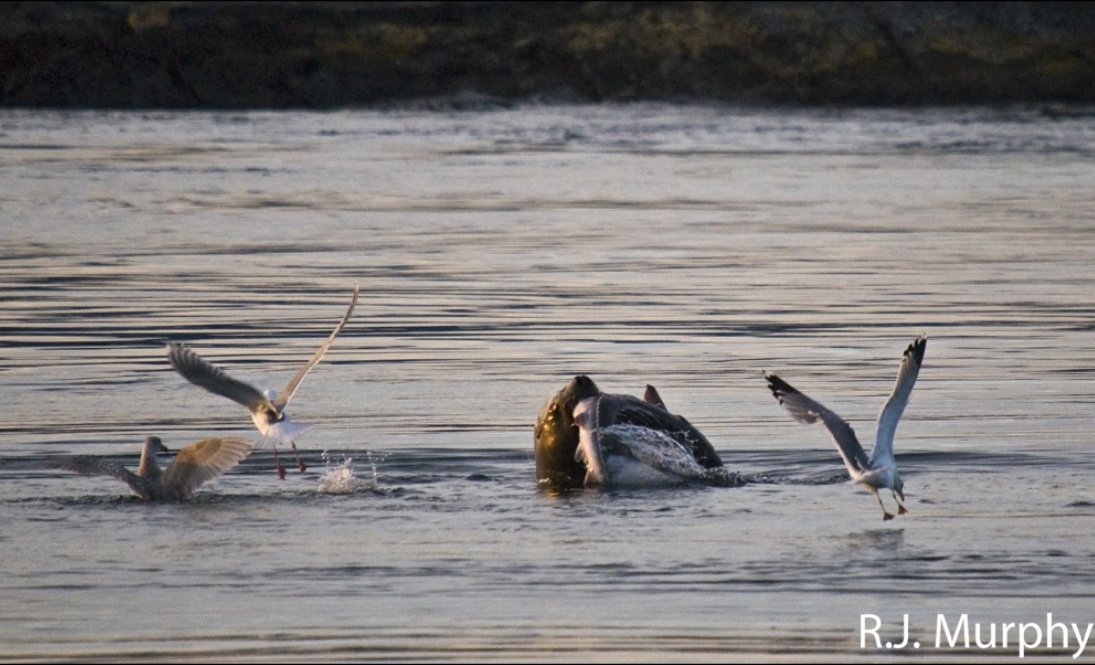
In this amazing picture, Ryan captured the spray of blood from the sturgeon as the northern sealion takes a bite. This is a first record we have for sturgeon in the Race Rocks Ecological Reserve. These images were taken by Ryan Murphy on the evening of March 2, 2009.
-

-
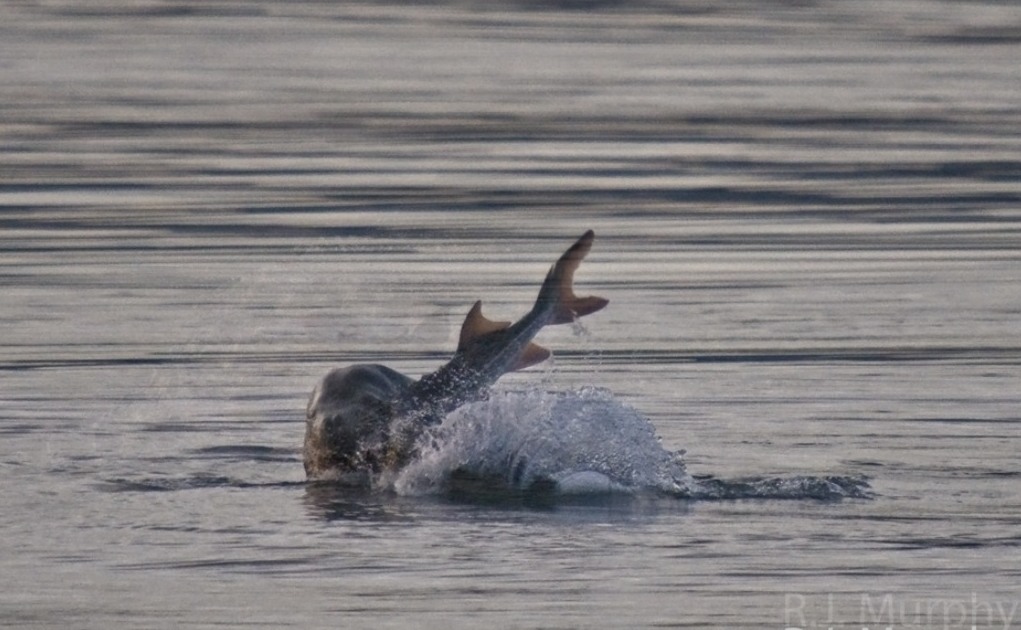

-
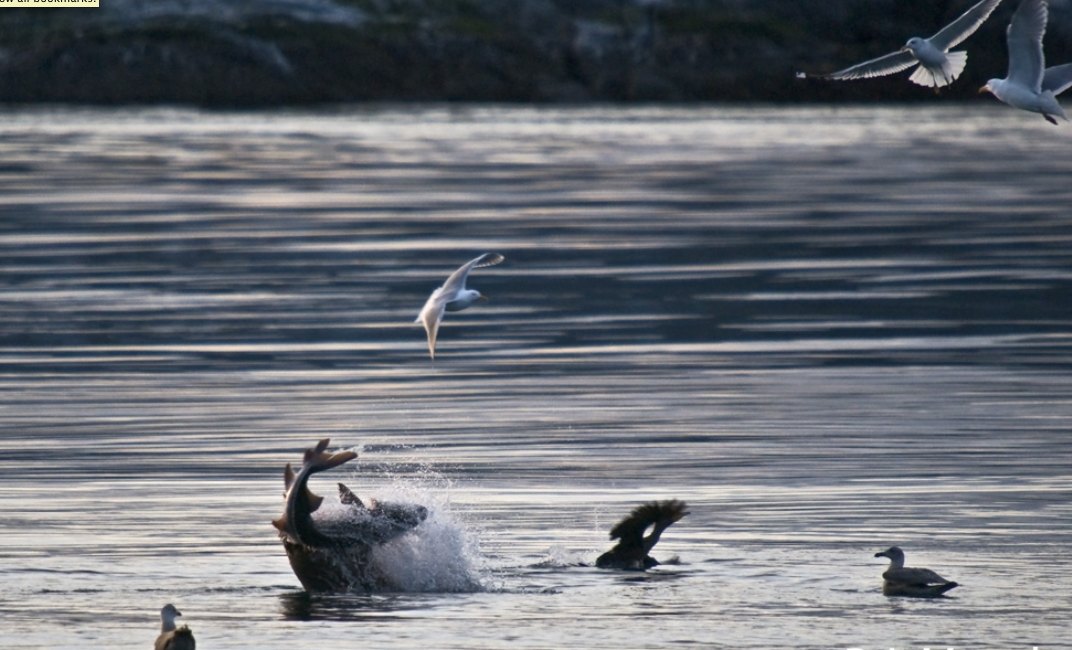

-
Click all photos to enlarge
-
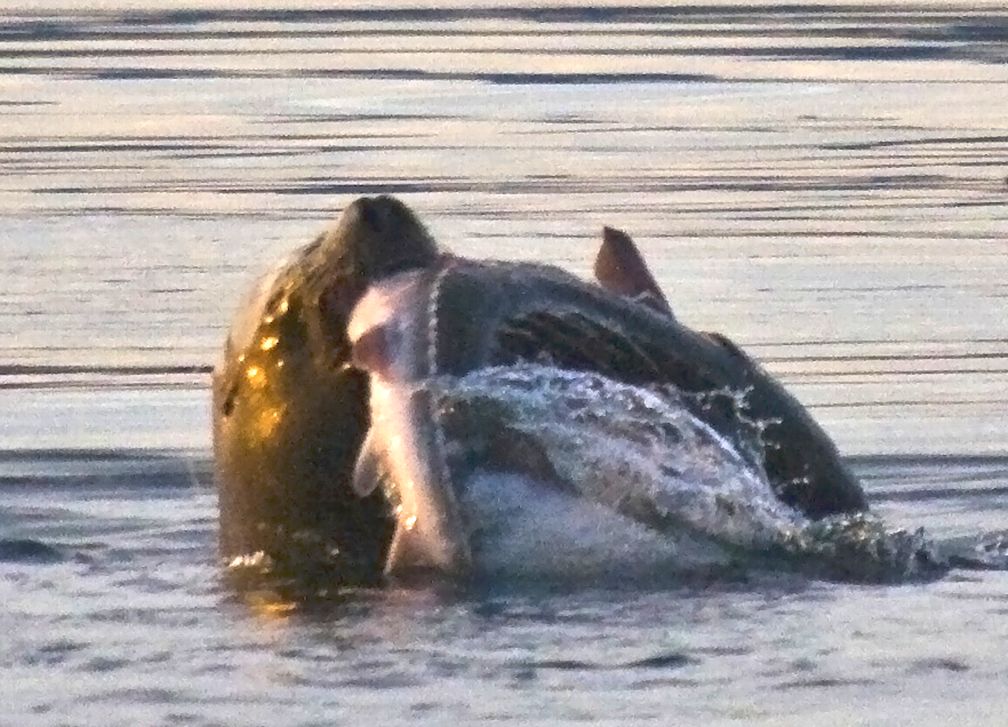

-
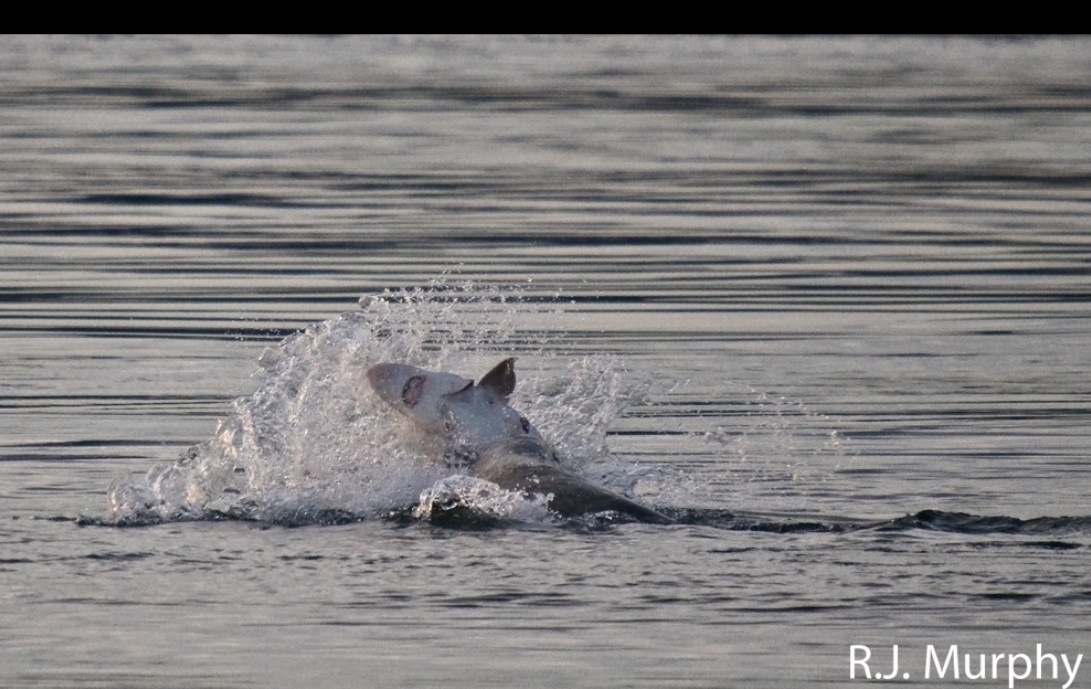

-
Note the ventral mouth
For confirmation of the identity of this fish, we contacted Lisa Spaven of DFO in Nanaimo and she helped us get in touch with a number of Canadian and American specialists in Sturgeon. There were some initial considerations that it may be a Green Sturgeoon but as the following conversation indicates, they have settled on the White Sturgeon:
Mar 06,2009,
From Chris Wood:
Conservation Biology Section
Science Branch, Fisheries and Oceans Canada Pacific Biological Station:
Hi Troy
White or green?
——————————–
Mar 08,2009
From Troy Nelson: Director of Science
Fraser River Sturgeon Conservation Society
” I have looked at the pics of the sturgeon at Race Rocks and think it
may indeed be a white. Although darker/tinted coloration is present, I think this may be partially caused by the low sun and color of the sunset (see the pinks in the water behind the fish in the last pic).Most notable is the lack of a dark stripe on the bottom side of the sturgeon, anterior of the pectoral fins. There is one shot of the bottom of the sturgeon and this section looks devoid of any dark stripe.I have attached pics of a confrimed green sturgeon (from the Albion Test Fishery); note the dark stipe that ends in an “arrowhead” shape on underside of the upper body. I have copied Olaf Langness (WA DFW) who works with green sturgeon; he may be able to confirm if the Race Rocks sturgeon is a green (or white) in 10 seconds or less”.
——————————————
March 9, 2009
From Chris Wood
“Thanks Troy, I was expecting it to be a green sturgeon in that location, but in one
picture, there seemed to be a (too?)close spacing of lateral scutes
between the pelvic and anal fin. We’ll see what Olaf says”…
——————————————
March 9, 2009
Olaf Langness Fisheries Biologist (Washigton State Department of Fish and Wildlife)
“Thanks Troy for sending this to me.
I would say your assessment is correct. I think the Race Rock sturgeon was a white sturgeon. Besides your comments about the lack of a belly stripe, I also think the lateral scutes look small and plentiful, more that of white sturgeon than green sturgeon. As to the pink coloration, I agree that some of that may be the result of time of day when the photo was taken, but also would not be unusual for a sturgeon under stress to pink up on the lighter belly area, and even to darken slightly on top. Furthermore, there are way more white sturgeon identified in the surrounding waters of Race Rocks (off southern tip of Vancouver Island, in the Straits of Juan de Fuca) than green sturgeon, based on tagging studies and commercial or recreational landing reports. As you know, white sturgeon are being attacked this time of year, just below Bonneville Dam on the Columbia River. Many of these fish are mature adults, taken by large Steller (Northern) Sea Lions. The more prevalent California Sea Lions are smaller than the Stellers, so they tend to go after salmon and mostly leave the sturgeon alone. While we have been authorized to kill up to 85 California Sea Lions a year, the Steller Sea Lion is listed under our Endangered Species Act. So our marine mammal hazement program is focused on reducing predation on spring chinook salmon, and limited on what can be done to control the predation on sturgeon. This is of great concern to sturgeon managers in Washington and Oregon, especially due to the sea lions targeting of the spawning broodstock .”
———————————–
March 9,2009
Chris C. Wood
Species transmontanus
Common Name: White sturgeon
Pacific White Sturgeon
Domain Eukarya
Kingdom Animalia
Phylum Chordata
Subphylum Vertebrata
Class Actinopterygii
Order Acipenseriformes
Suborder Acipenseroidei
Family Acipenseridae
Subfamily Acipenserinae
Genus Acipenser
Species transmontanus