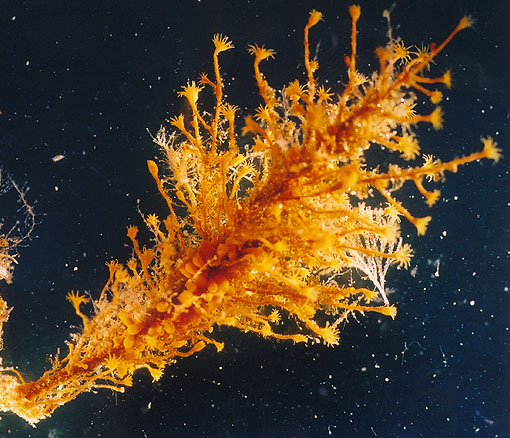
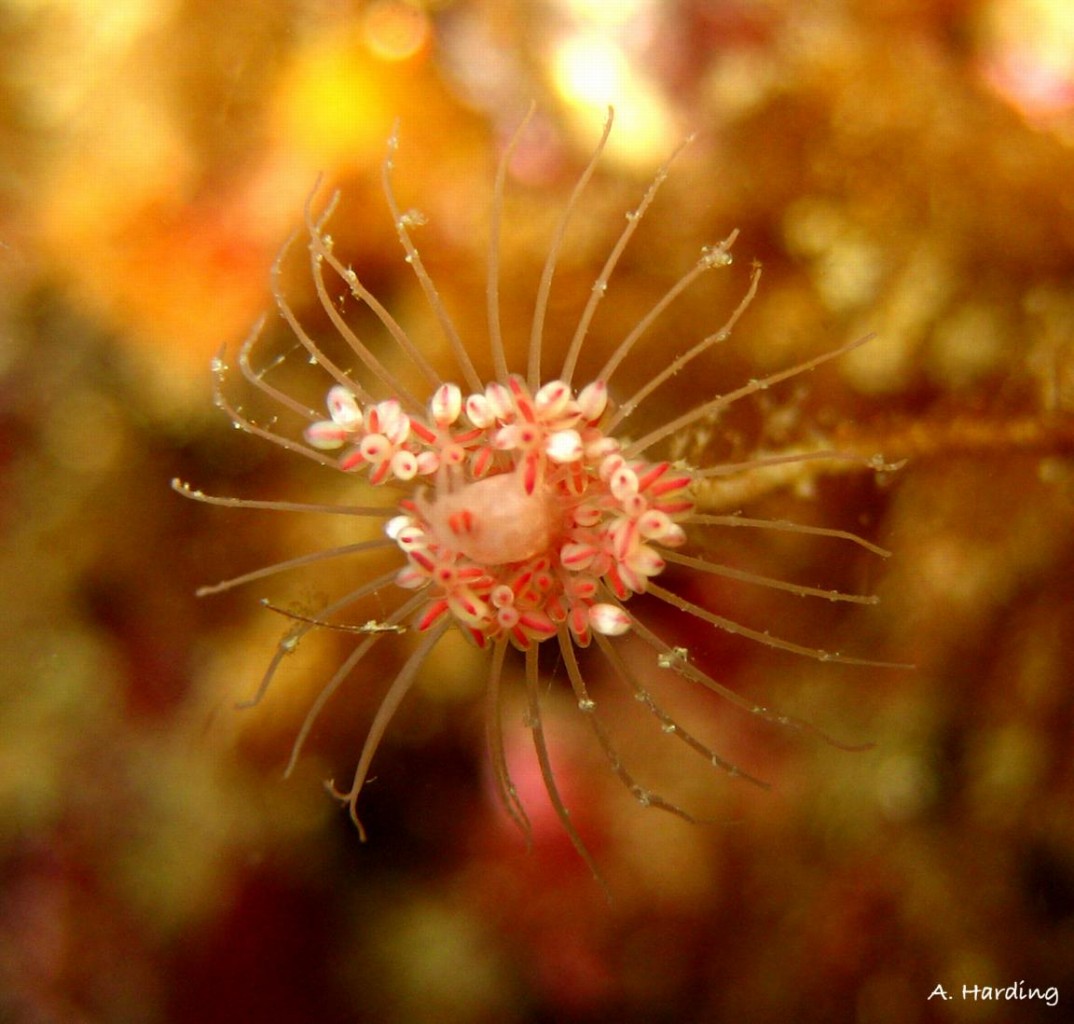
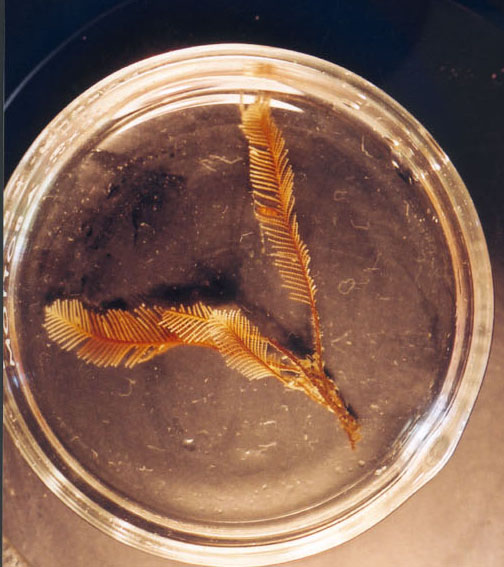
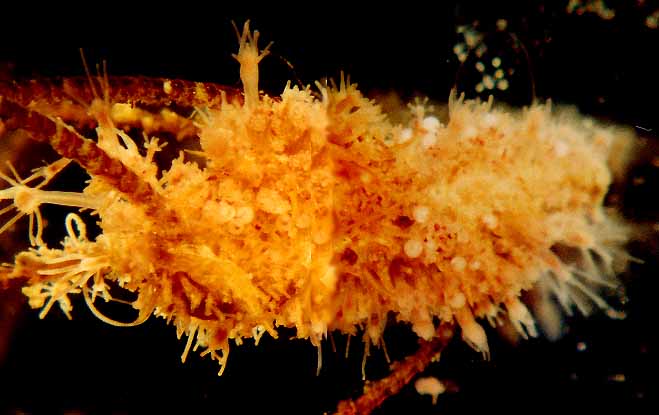
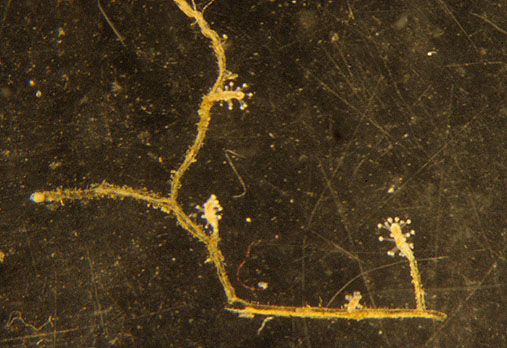
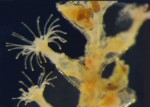
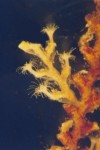
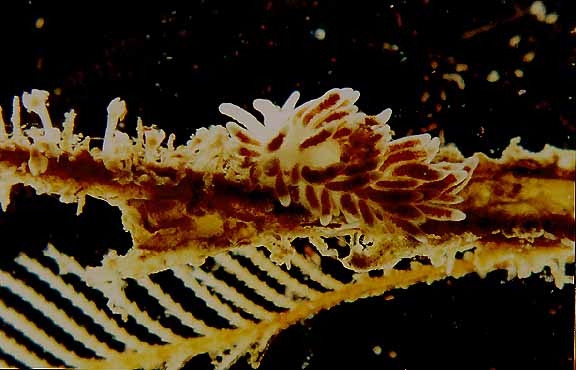
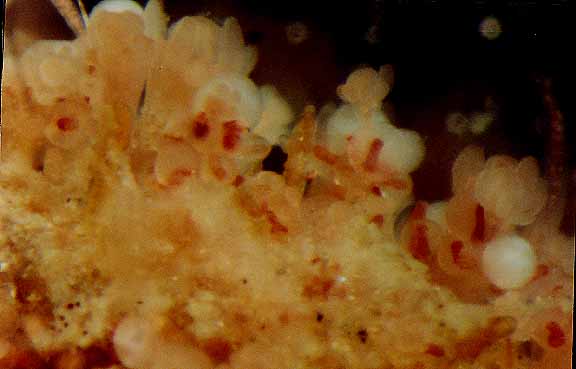
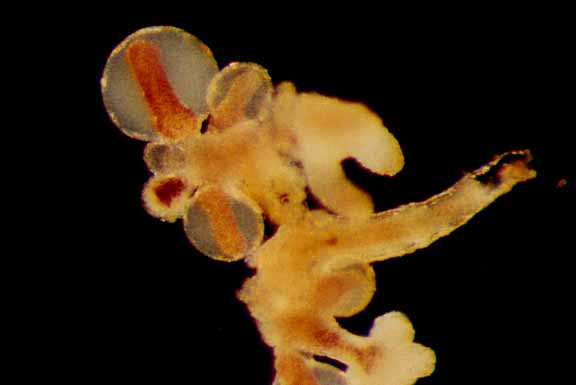
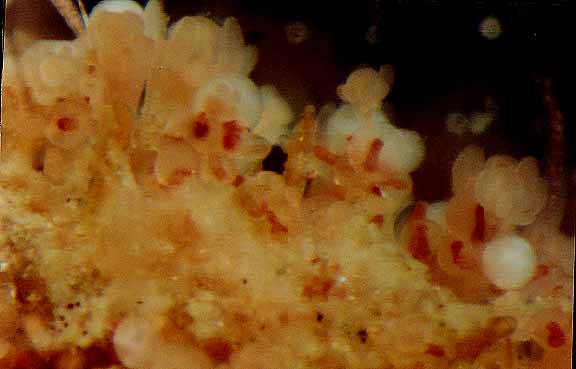
Campanularia sp. (Hydrozoa, Leptothecatae, Campanulariidae) Race Rocks, low intertidal.

| Domain |
Eukarya |
| Kingdom |
Animalia |
| Phylum |
Cnidaria |
| Class |
Hydrozoa |
| Order |
Leptothecata (=Leptomedusae) |
| Family |
Campanularidae |
| Genus |
Campanularia |
| Species |
sp. |
| Common Name: |
This file is provided as part of a collaborative effort by Lester B. Pearson College and local scientists. Copyrighted 1999-All Images on this page are the property of: Dr. Anita Brinckmann- Voss..They can not be used or modified without her written permission.
see this link for other hydroids: https://www.racerocks.ca/tag/hydroid/
Research paper indicating possible medicinal properties: accessed July, 2014
Marine Natural Products Laboratory, Chemistry Department, Aberdeen University, Aberdeen AB24 3UE, Scotland, U.K.
J. Nat. Prod., 2005, 68 (3), pp 453–455
DOI: 10.1021/np049666n
Publication Date (Web): February 26, 2005
Copyright © 2005 American Chemical Society and American Society of Pharmacognosy
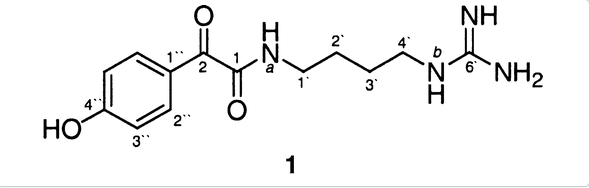
A new compound, N-(4-guanidinobutyl)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-oxo-acetamide (1) was isolated from the aqueous extract of the hydroid Campanularia sp. Its structure was elucidated using NMR spectroscopic techniques and mass spectrometric analysis. The most stable conformation was determined using molecular modeling and the results of a NOESY experiment. Although compound 1 shows structural similarities to some highly potent histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi), e.g., suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) (2) and trichostatin A (TSA) (3), it does not inhibit the growth of ARP-1 cells at 100 μM concentration, a significant indication that it has no inhibitory activity to HDACs.