Sunny
Wind: 0-13 knots SW in the morning, NE from mid morning to afternoon and SW in the evening
Air Temperature: Low 9.9°C, High 13.2°C
Ocean Temperature: 9.0°C
Three Pearson students came to Race Rocks this morning. Karen, Sunny and Hanne joined Martin, who has been here since Monday.
The students did some work this afternoon: sweeping all 99 steps of the lighthouse and continuing the process of stowing the chopped wood in all the nooks and crannies of the buildings, to be used next winter to heat the main house.
There was DND blasting happening in the morning and early afternoon on Bentinck Island, less than 1km away from the ecological reserve.
Today’s high temperature of 13.2°C, as measured at the ground weather station, was the highest recorded since 2006, when the weather station was installed. A high of 14°C was recorded by the instruments at the top of the lighthouse.
Three eco tour boats visited the reserve. One boat came very close to a group of sea lions swimming and others hauled out on the South Islands.
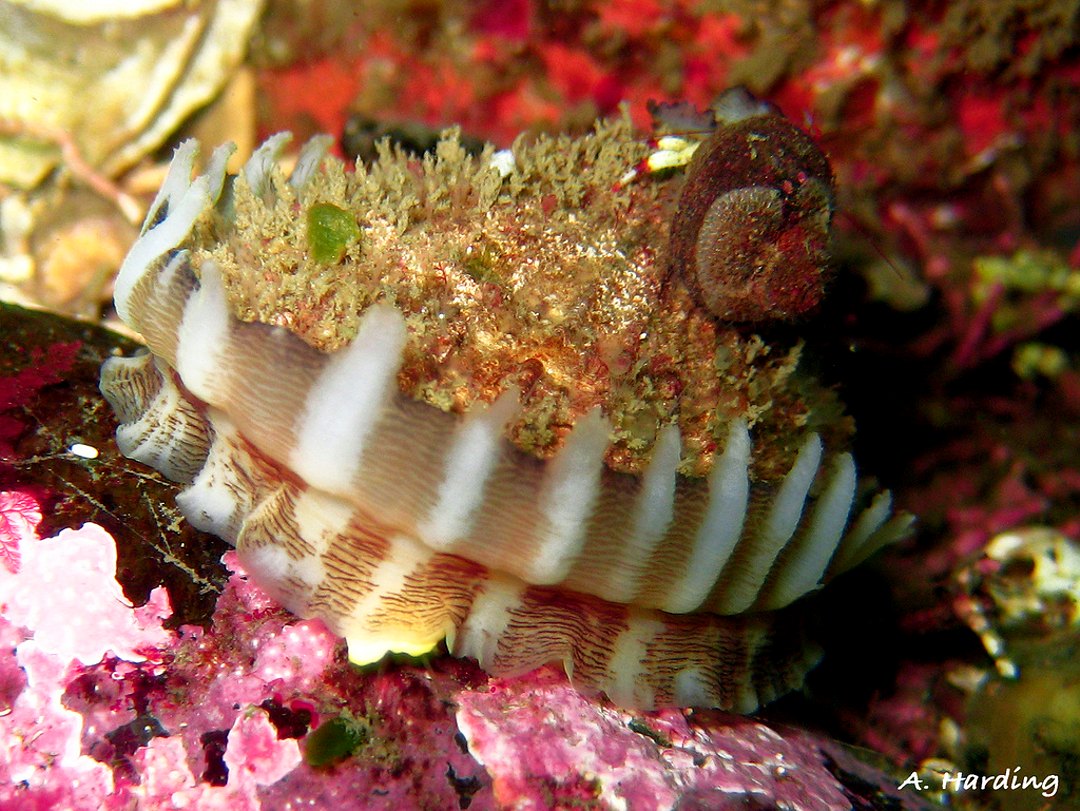
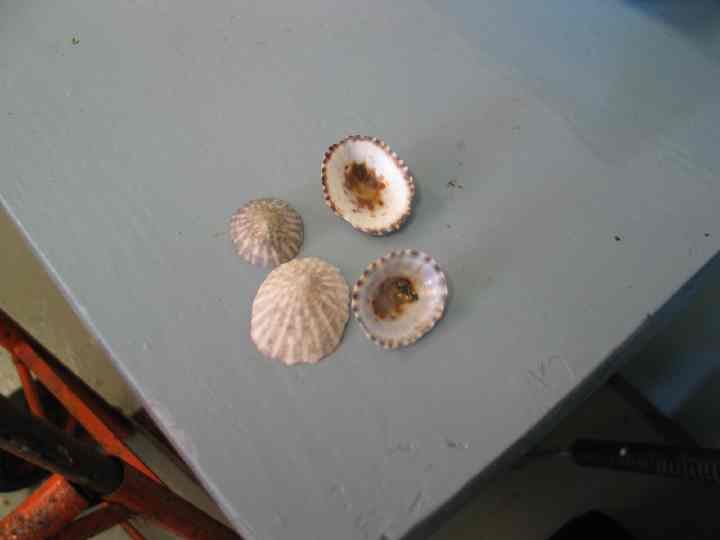
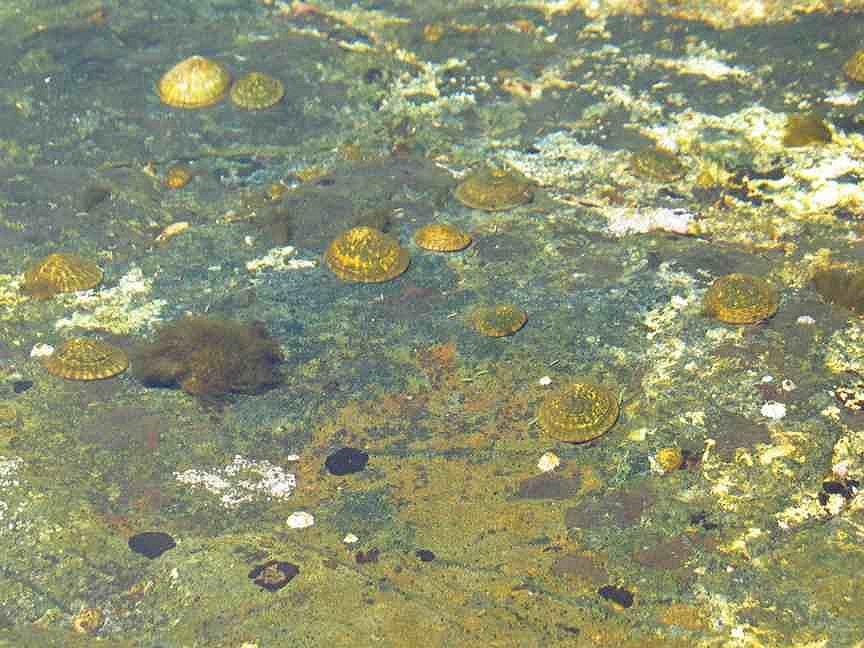
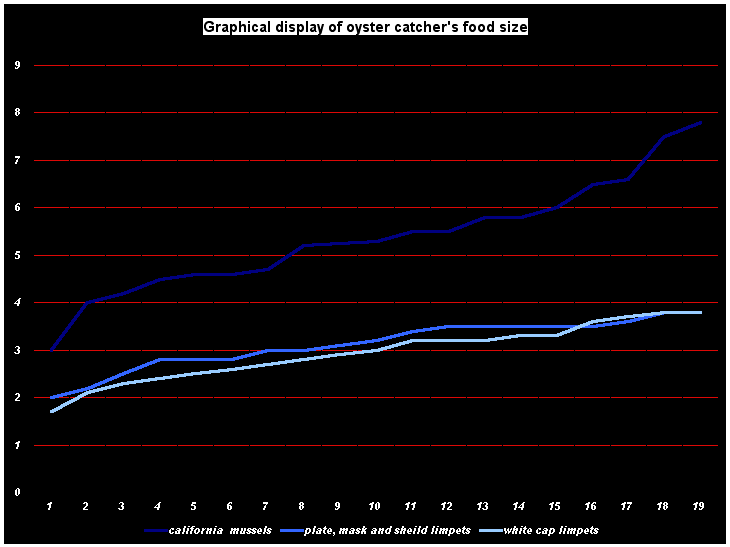
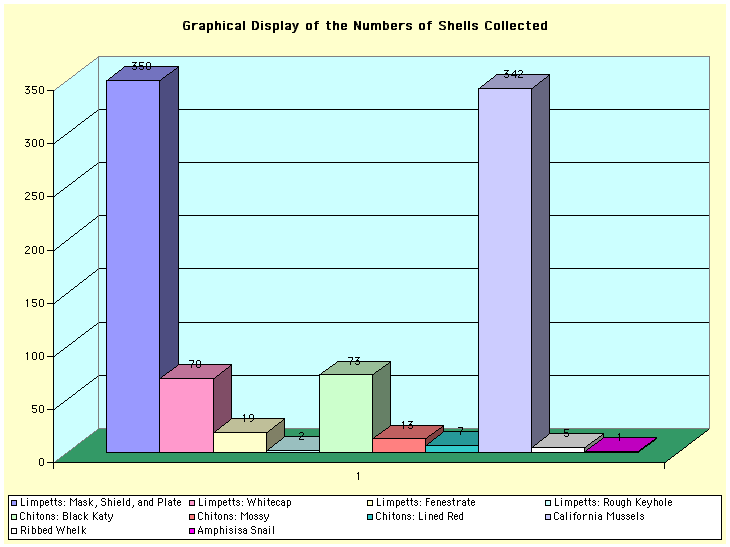
The low tide of 1.1m at 13:52, exposed lots of species from the low tide zone into the air. The shore and tidal pools were full of life: mussels, barnacles, limpets and lots of other flora and fauna of the sea. The oystercatchers and shore birds were having a feast.
There were no small birds perching birds seen today. There are usually a few fox, sparrows, savannah sparrows and occasionally juncos and robins zipping around the island.
Here are the results from today’s Megafauna Census:
Elephant Seal: 1
Steller Sea Lion: 54
California Sea Lion: 43
Harbour Seal: 52
Bald Eagle: 9
Great Blue Heron: 1
Crow: 1
Oystercatcher: 4
Double Crested Cormorant: 12
Brandt’s Cormorant: 21
Gull: 247
Canada Goose: 14
Pigeon Guillemot: 9
Harlequin Duck: 13
Surfbird: 3
Black Turnstone: 10
Rock Sandpiper: 2
- A california sea lion gets ready to take the plunge. More sea lions float in the background.
- An oystercatcher takes flight after feasting in the intertidal zone.
- Chunk’s usual spot below the helicopter pad.
- Chunk takes a break on the way to the water.
- Hanne and Martin help shrink the wood pile, wheelbarrowing it to summer storage spots around the island.
- Karen and Sunny after sweeping all 99 steps of the lighthouse.
- An eco tour boat gets very close to sea lions in the water and on the rock.