Predation of a Psolus chitinoides by a sea star is examined and discussed by Laura and Nadege. The stomach of the sea star surrounds the sea cucumber and the soft neck and mouth of Psolus is well inside the cavity of the sea
Sea cucumbers have inhabited the world’ s oceans for about 400 million years. Psolus chitonoides is an unusual species of these marine invertebrates. Its diverse characteristics have given it 4 common names: Armoured sea cucumber, Creeping armoured sea cucumber, Slipper sea cucumber and Creeping pedal sea cucumber.
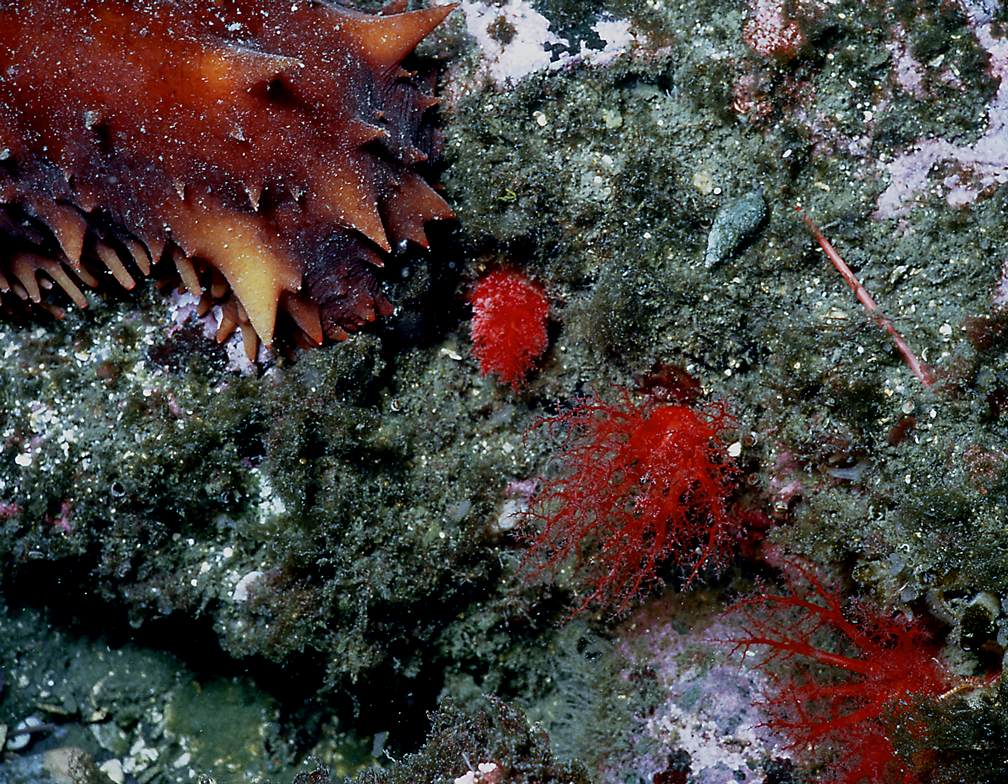

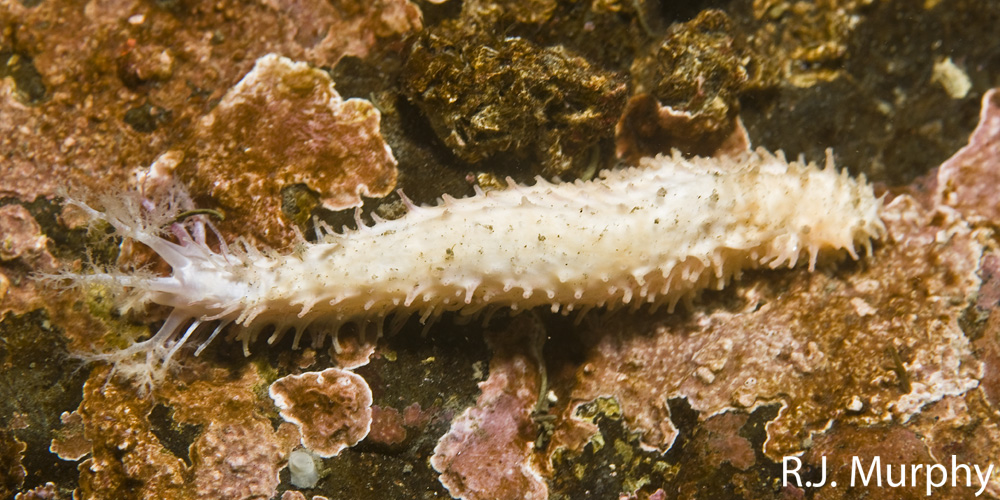
Compare the tentaclesof Psolus with the end of the California Sea Cucumber to the left. Photo by Dr.A.Svoboda
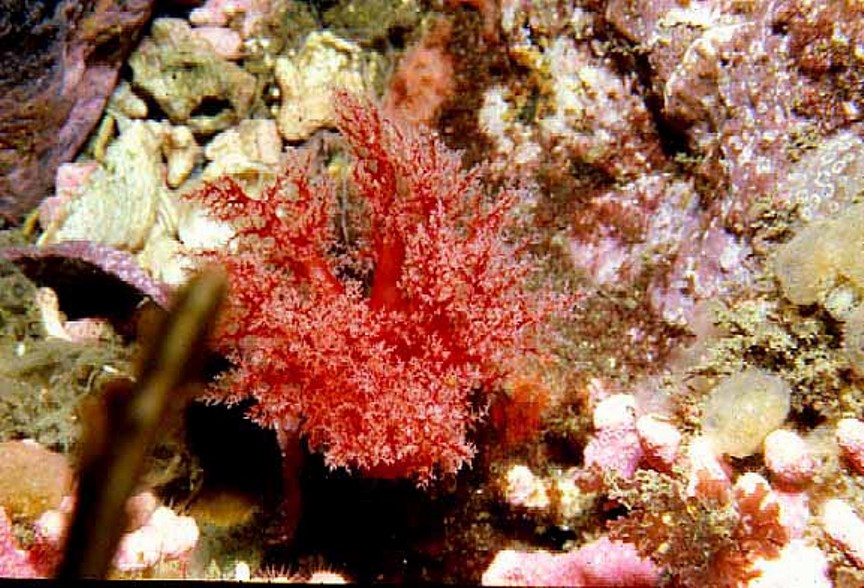

Tentacles of P.chitinoides
A-Description
As all echinoderms, the creeping pedal cucumber has a spiny skin. Also, its appearance is closer to a chiton than to a sea cucumber (here is the origin of its name “chitonoides“).
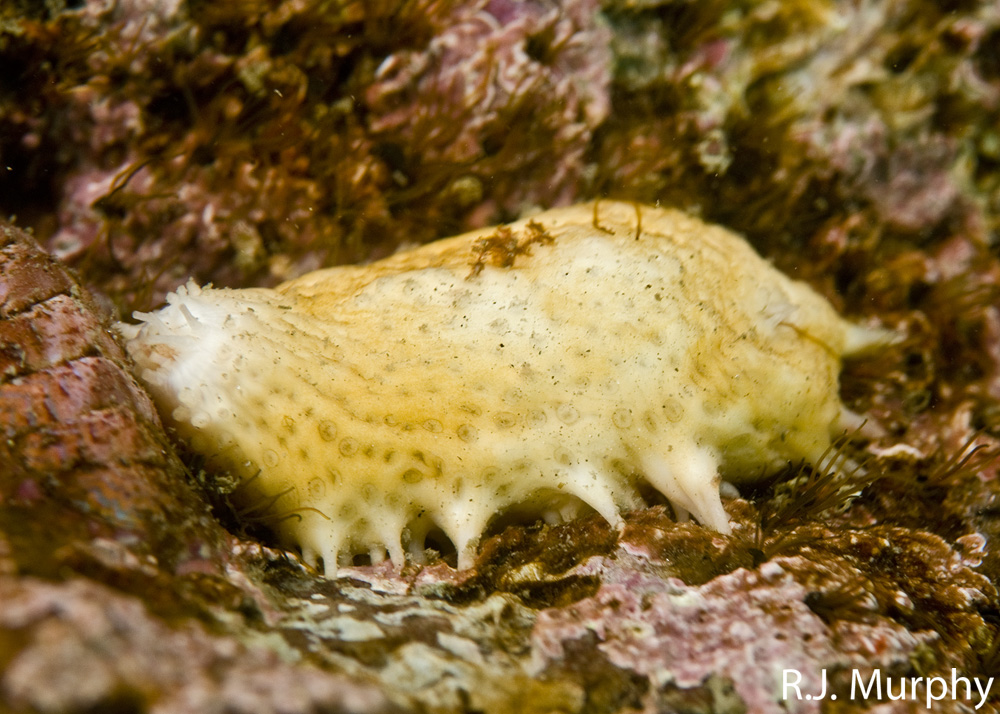
1-External features:an oval body (7cm long to 5.8 cm wide) domed dorsally with stiff, shingle-like scales, flat, flexible sole ventrally. Its tentacles(8-10) are dendritic, equal in size, or 8 large and 2 small. Also observing the body, it could be compared to an elongate cylinder lying on its side with the mouth at one end and the anus at the other. The rows of tube feet run the length of the body
2-Internal features: the tentacle ampullae, the rete mirable and cuverian organs are absent . On the other hand, we can observe the presence of retractor muscles. Respiratory trees are “y shaped”. Note that its madreporic body is attached to a dorsal mesentery. Its internal calcareous skeleton is composed as following:calcareous ring with anterior processes only. Psolus chitonoides is characterized by typical skin ossicles, where one type of circular perforated plate (some with knobs coalesced into a raised network) occur only in the ventral sole.
Domain Eukarya
Kingdom Animalia
Phylum Echinodermata
Class Holothuroidea
SubclassAspidochirotacea
Order Dendrochirotida
Family Psolidae
Genus Psolus
Species chitonoides
Common Name: Creeping pedal sea cucumber
B-Physiology and Biology
1-Suspension feeder: tentacles trap larger particles (larger than 2mm) by bending inwards to form a cagelike enclosure. The mouth lips extend toward the particle as the nearest tentacle pushes it into the mouth .
2-Reproduction : the reproductive organs of a sea cucumber generally consist of 1 or 2 tufts of elongated tubules in the forepart of the body cavity.Spawning occurs annually, from mid March ot late May, commonly in the early morning. A spawning male will swab its genital papilla with its tentacles, then lift the tentacles to disperse the sperm . Females release long ropes of brick red eggs; fertilized eggs develop into pelagic lecithotrophic vitellaria larvae. Late larvae and early juveniles are negatively phototatic and settle gregariously.
3- Respiratory system: its water vascular system is a hydraulic system made up of tubes and valves that operate rows of extendible tube feet . As other sea cucumbers, Slipper sea cucumbers respire through their tube feet, body wall and respiratory trees.
4-Chemicals: there are toxic chemicals (saponins) on its tentacles, discouraging predators from nipping the tentacles. For example, even the Kelp Greenling (Hexagrammos decagrammus), which feeds on sea cucumbers, avoids this species.
C-Predators, parasites and commensals
1-Sea stars and fish are the main predators of the Psolus chitonoides.
2-Parasitic forms of flatworms and snails can live inside the sea cucumber
3-Commensal organisms are mostly scales that mimic the colour of sea cucumbers, and crawl on their skin.
D-Habitat
From exposed coast to sheltered inlets; although it seems to prefer clean, vertical rock that is free of sediment. Its soft, flat sole enables it to attach firmly to rock.
E-Range
Aleutian Islands to Baja California ; intertidal to 247m ; common in shallow subtidal areas.
References:
Kozloff, E.N. Keys to the Marine Invertebrates of Puget Sound , the San Juan Archipelago, and Adjacent Regions.
Lambert, P. 1997. Sea cucumbers of British Columbia, Southeast Alaska, and Puget Sound. UBC Press,
 by Ryan Murphy, April, 2010 See Ryan’s underwater set on Flickr with a range of invertebrates:
by Ryan Murphy, April, 2010 See Ryan’s underwater set on Flickr with a range of invertebrates: