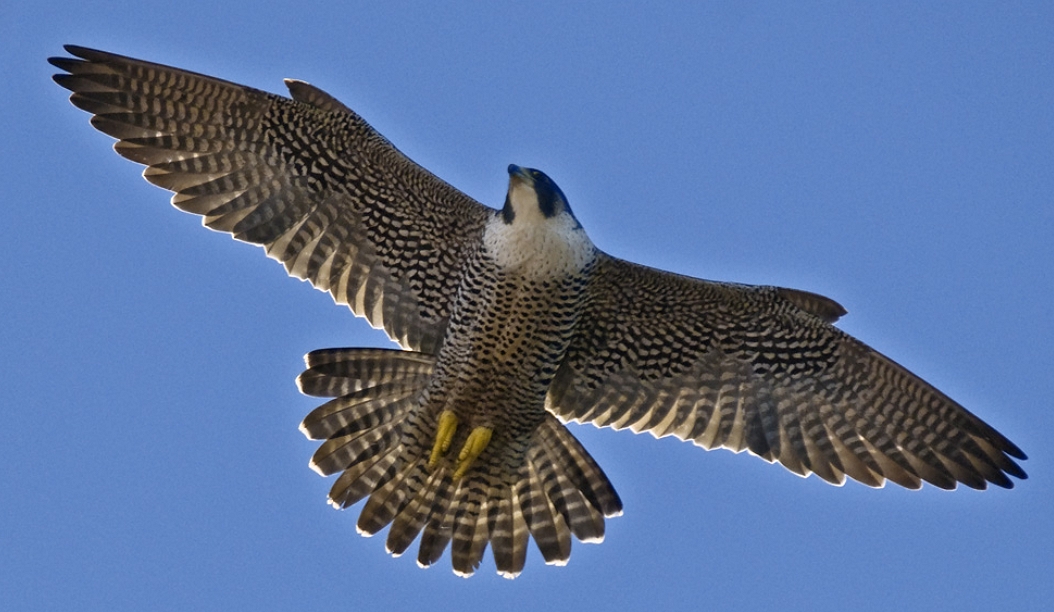
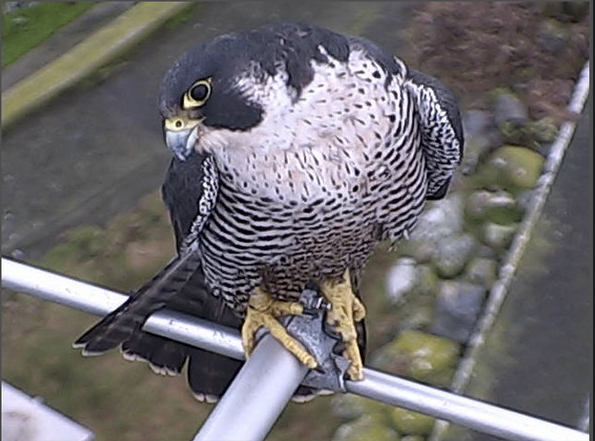
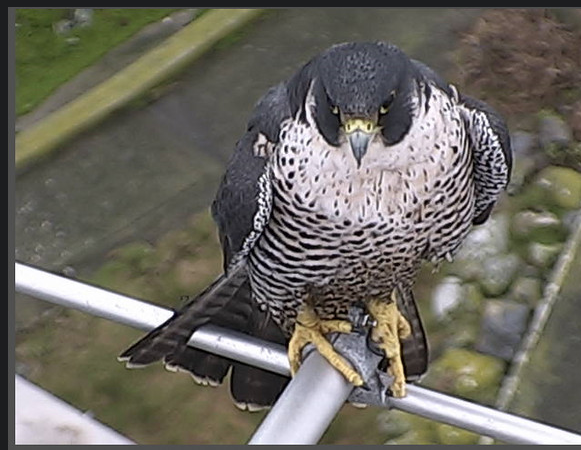
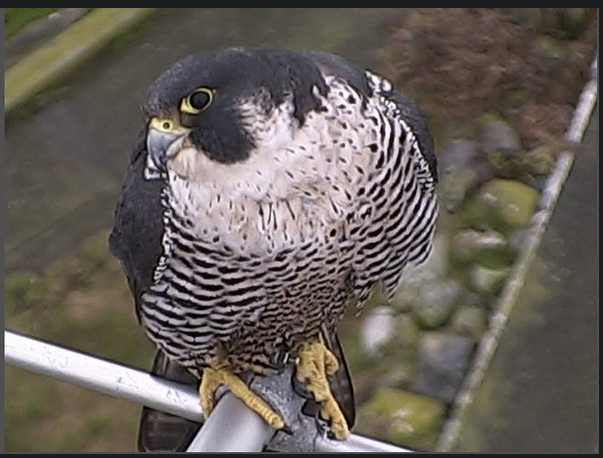
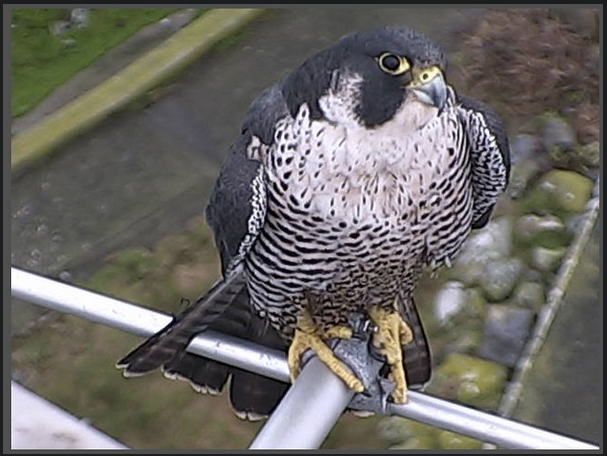
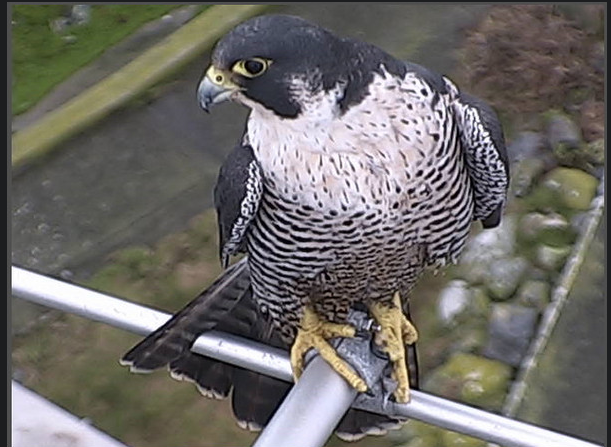
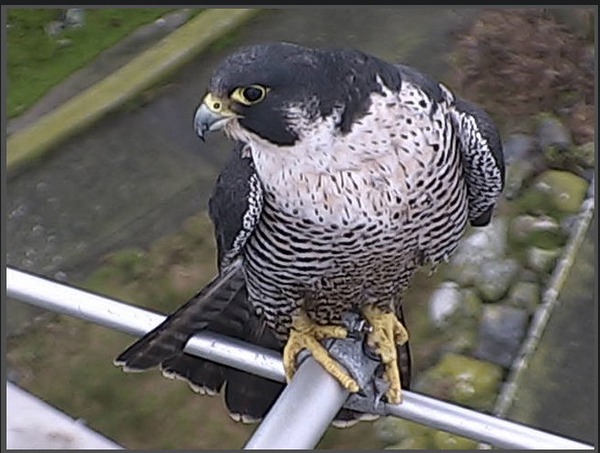
This photo was taken on Race Rocks by Ryan Murphy in December of 2008.
See all the posts on this website with observations of Peregrines
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Class: Aves
Order: Falconiformes
Family: Falconidae
Genus: Falco
Species: peregrinus
Common Name: Peregrine falcon
Unusual footage taken by Pam Birley using the remote camera 5 of a falcon eating a seabird. Also see similar sequence on right below..
The Peregrine falcon, Falco peregrinus, is a bird of prey (or raptor) which has captured the attention and imagination of ornithologists and bird-watchers alike for several thousand years. With a body length of 15-20 inches and a body weight of 1.25-3.75 lbs, the falcon is built specifically for travelling at high speeds (up to 180 m.p.h.) in order to catch its prey. The name Falco peregrinus is derived from the Latin falx, or sickle-shaped, and peregrinus, meaning wandering. It is unclear whether the former is derived from the shape of the bird’s silhouette in the sky or from the shape of its beak, but the latter name comes undoubtedly from its propensity to migrate great distances.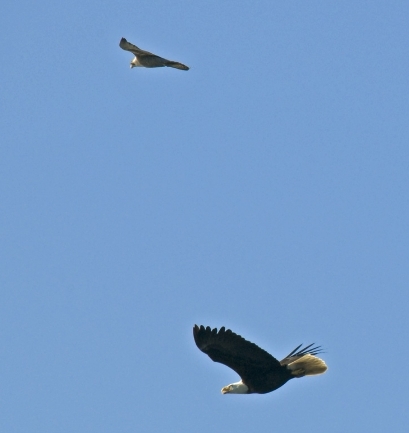 In the picture of a Peregrine Falcon and Bald Eagle from his Flickr site, Ryan Murphy said In the picture of a Peregrine Falcon and Bald Eagle from his Flickr site, Ryan Murphy said“This was amazing to witness in person, I regret not having been able to capture it better than this! Just before this the eagle rolled backwards towards the chasing falcon… awesome aerial battle!” Predation Two sequences of pictures from Race Rocks below have been taken by Pam Birley showing the peregrine eating a shorebird.and a sea gull. Though peregrine falcons, like other birds of prey, are considered to be near the top of the food web, they are not completely free from predators. Great horned owls and golden eagles have been known to attack them. Humans have also been known to take their eggs in hopes to raise the falcons for hunting purposes. As top predators, peregrine falcons play an important ecosystem role in regulating the populations of their prey. Habitat Peregrine Falcons prefer open habitats such as grasslands, tundra, and meadows. They nest on cliff faces and crevices. They have recently begun to colonize urban areas because tall buildings are suitable for nesting in this species, and because of the abundance of pigeons as prey items. Peregrine falcons prey almost exclusively on birds, including mourning doves, pigeons, shorebirds, (see slide shows above) waterfowl, and smaller songbirds. They will also eat small reptiles and mammals. Although peregrine falcons capture their prey with their claws, they generally kill prey with their beak.The photos for this slide show and video were taken on the remote camera 5 at Race Rocks, by Pam Birley operating the camera from Great Britain. Pam had observed the peregrine falcon on various perches around the island in the mornings for several weeks in October and November. Her persistence paid off on November 17, 2005. Pam wrote in her e-mail ….”Today we had just returned home .. I just came up to the computer, switched it on and there was Perry with his breakfast….I really caught him in the act of devouring his prey today! “You may see other pictures that Pam has taken using the remote camera at Race Rocks by clicking here to go to her photo album . CLICK ON THE BLANK SPACE PEREGRINE FALCONS AT RACEROCKS: OCTOBER, 2004
Pam Birley of Leicester England captured some of the pictures remotely on robotic camera 5 and Mike Slater, our reserve guardian took the pictures of the antenna perch on the towerPam was interviewed recently about her wildlife viewing on racerocks.com Conservation Status Jan 25, 2010 Brian Mury sent this link to a set of images he took from Camera 1 on the top of the tower. The falcon is perched on the FM antenna which is used by Environment Canada to transmit anemometer readings from the top of the tower.
|
Other Members of the Class Aves at Race Rocks.
and Image File |
 The Race Rocks taxonomy is a collaborative venture originally started with the Biology and Environmental Systems students of Lester Pearson College UWC. It now also has contributions added by Faculty, Staff, Volunteers and Observers on the remote control webcams. The Race Rocks taxonomy is a collaborative venture originally started with the Biology and Environmental Systems students of Lester Pearson College UWC. It now also has contributions added by Faculty, Staff, Volunteers and Observers on the remote control webcams.
Chiara Ravetti PC yr 31 |