A major concern for those of us who work with Race Rocks is the impending disaster that is likely to happen to the Ecological reserve if the Kinder Morgan Trans Mountain Pipeline is built. The Friends of Ecological Reserves is sponsoring the following panel discussion on threats to our Marine environment which has a good chance of happening if this pipeline gets built and the marine transport necessary for it goes within several kilometers of Race Rocks Ecological Reserve. Also see other posts on the Oil Spill Risk Link.
Category Archives: News
Feature Article on Pam Birley,
From: TheThunderbird.ca News, analysis and commentary by UBC Journalism students
B.C. wildlife webcam protects ecosystem, entertains daily British watcher
Visit Pamela Birley in her Leicester, England, home, and you’ll likely see sea lions hauling themselves onto Great Race Rock – an island in B.C., eight time zones away.
Surrounded by tidal races, open to wind and waves, and dwarfed by views of the Olympic Mountains, the treeless rock off the southern tip of Vancouver Island is a magnet for marine life in the area.

A young elephant seal saunters towards the sea.
Photo: Hanne-Marie Barlach Christensen
Birley, 86, has been watching the wildlife on Great Race Rock, the exposed peak of the seamount comprising the Race Rocks marine ecological reserve, for the past 14 years.
The webcams have performed a unique function since they were installed in 2000 by drawing in visitors from around the world and keeping the public from overwhelming the ecosystem. Birley is a daily watcher.
“It’s the variety of wildlife out there,” she said. “You’re never too sure what you’re going to see, and sometimes you see unusual things.”
Hotspot for biodiversity
Home to millions of plankton, thousands of nesting seabirds, and hundreds of sea lions, the reserve in the Strait of Juan de Fuca is rich in marine life. It’s this diversity that motivated Garry Fletcher, a marine biologist, to push for the area’s protection in the 1970s.
“It’s at the confluence of upwelling from deeper ocean and the fresh water spilling out of the Georgia Basin, so it creates a very unique ecosystem,” Fletcher said. “It’s a real hotspot of biodiversity.”

Fletcher’s efforts paid off. In 1980, the B.C. government designated Race Rocks and surrounding seamount as a provincial marine protected area. The federal Department of Fisheries and Oceans subsequently closed the reserve to commercial and ground fishing in 1991 and has designated it an area of interest, slated to become a marine protected area. Spanning 226 hectares, the reserve is managed under lease by the nearby college where Fletcher taught until retirement, Lester B. Pearson United World College of the Pacific.
However, most of those 226 hectares are submerged. Great Race Rock, at merely two hectares, is the only habitable part of the reserve.
Easily crossed on foot in less than 10 minutes, the island has no safe harbour and is cut off from Vancouver Island for days during spells of bad weather. For the island’s resident eco-guardian, Laas Parnell, the island’s size and isolation are impossible to ignore.
Originally from Haida Gwaii, Parnell has lived in isolated, coastal places most of her life. Yet Race Rocks stole her heart when she first visited during a marine-science class in 2011.
“I love it here,” she said of her home of the past year. “I’m not claustrophobic. I keep pretty busy, cooking, cleaning. I spend a lot of time just walking around.”
Still, the island’s tininess can be humbling.
“It reminds me that I’m the only one out there. Alone.” she said.

Light keepers lived on Race Rocks until the beacon was automated in 1997. Their houses, the jetty, and the lighthouse outbuildings remain to house the eco-guardian, researchers, and students. Photo: Hanne-Marie Barlach Christensen
It’s an aspect of the island Birley hadn’t noticed through the webcam.
“It surprised me how compact it was when we actually visited,” she said, reminiscing on the first time she set foot on the island in 2007. “I find it hard to get my bearings on the webcam in relation to what’s near what.”
“Parks end up getting loved to death sometimes”
It was the island’s size that motivated Fletcher to install the webcams. Covered in resting sea lions or seabird nests most of the year, the island can’t handle many visitors. He worried about the impact tourism could have had on the area.
The island is isolated during the winter months by gales and tidal races, but calm seas in the summer make it within easy reach for boats leaving Victoria and other harbours along southern Vancouver Island.
“It’s a bird colony and marine mammal haul-out area,” said Fletcher. “It was just too sensitive to have people coming and going in hordes. You would have every whale-watching boat stop there and disgorge its passengers. Parks end up getting loved to death sometimes.”
To prevent over-visitation, BC Parks mandates that visitors to the island must obtain an education or research permit.

Gulls depend on Great Race Rock as a nesting site and a place to rest.
Photo: Hanne-Marie Barlach Christensen
However, Fletcher wanted to make the reserve’s unique biodiversity and natural beauty publicly available. At the time, webcams offered a novel solution.
Webcams connect wildlife lovers
In 2000, most Canadians relied on dial-up internet, Mark Zuckerberg was 16, and YouTube wouldn’t exist for another five years. Broadcasting online, live from Race Rocks, was a moment Fletcher won’t forget.
“My best memory is when we achieved getting the first video signals off the island, back in 2000,” said Fletcher. “That was quite an accomplishment and represented participation and co-operation from a lot of players.”
For Birley, the introduction of webcams like the ones at Race Rocks were an opportunity to explore the world. She watches four cams daily, including Race Rocks.
“I don’t get out a great deal now,” she said. “But my life is full: I get out in the garden and I do a lot of knitting. I knit birds, just little standing shelf sitters. I can knit while I watch the webcams, so it’s productive.”

Birley’s best-selling knit bird: a peregrine falcon. Photo: Pamela Birley/Etsy
Birley’s knitted birds are popular: she’s sold hundreds in her Etsy shop to buyers far and wide.
Webcams have also fostered international friendships for Birley. Fletcher is one of her regular correspondents, and she’s made friends in Victoria and Seattle through webcams.
It is the animals, however, that keep Birley watching Race Rocks. She documents Race Rocks wildlife extensively through webcam screenshots and turns them into albums on Flickr.
Birley sees some animals regularly, like the gulls and sea lions, but her dedication to the webcam has paid off with an amazing sighting—a snowy owl.
“It was pouring rain, I had the camera on, and I was probably knitting,” she recalls.
“I looked up and thought I saw a funny looking seagull by the rock. I zoomed in and there it was: a snowy owl sitting there, just swivelling its head around from time to time. I’ve only ever seen the one, and that was quite exciting!”

Seeing a snowy owl was a highlight of Birley’s webcam sightings.
Photo: Pamela Birley/Race Rocks
Dr. Anita Brinkmann-Voss…. In Memoriam
 Dr. Anita Brinckmann-Voss passed away on December 12 at her home in Sooke BC. Anita had been a long time friend of Lester B. Pearson College. From 1986, to 2005, Dr. Anita Brinckmann-Voss BC assisted the students and faculty of Lester Pearson College with her understanding of marine invertebrate ecology and her expertise in the taxonomy of hydroids and other invertebrates. Anita was one of the very few remaining taxonomists in the world who worked at such depth with this group of organisms. She assisted many students with their work in biology and marine science and worked closely with several divers at the college who collected specimens for her. Anita also was a regular donor to the Race Rocks program at the college.
Dr. Anita Brinckmann-Voss passed away on December 12 at her home in Sooke BC. Anita had been a long time friend of Lester B. Pearson College. From 1986, to 2005, Dr. Anita Brinckmann-Voss BC assisted the students and faculty of Lester Pearson College with her understanding of marine invertebrate ecology and her expertise in the taxonomy of hydroids and other invertebrates. Anita was one of the very few remaining taxonomists in the world who worked at such depth with this group of organisms. She assisted many students with their work in biology and marine science and worked closely with several divers at the college who collected specimens for her. Anita also was a regular donor to the Race Rocks program at the college.
Dr. Dale Calder, a colleague of Anita who works with the Royal Ontario Museum wrote the following about Anita:
“I knew of Dr. Anita Brinckmann-Voss and her research on hydrozoans from my days as a graduate student in Virginia during the 1960s. Her work at the famous Stazione Zoologica in Naples, Italy, was already widely known and respected.
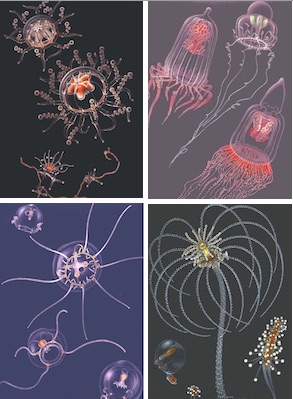 Most noteworthy, however, was a landmark publication to come: her monumental monograph on hydrozoans of the Gulf of Naples, published in 1970. It highlighted studies on hydrozoan life cycles and was accompanied by the most beautiful illustrations of these marine animals that have ever been created. See the complete copy with color plates here: Brinckmann70:
Most noteworthy, however, was a landmark publication to come: her monumental monograph on hydrozoans of the Gulf of Naples, published in 1970. It highlighted studies on hydrozoan life cycles and was accompanied by the most beautiful illustrations of these marine animals that have ever been created. See the complete copy with color plates here: Brinckmann70:
It was not until 1974, and the Third International Conference on Coelenterate Biology in Victoria, British Columbia (BC), Canada, that I met her for the first time. We discovered having common scientific interests and saw absolutely eye-to-eye on most issues. It was the beginning of a scientific collaboration and friendship that would last a lifetime. I always greatly valued her scientific insights, but I also appreciated her humility, good nature, and keen sense of humour.
In having moved from Europe to Canada, first to Winnipeg, Manitoba, and later to Toronto, Ontario, Anita’s research shifted from Mediterranean species to those of Canadian waters and especially British Columbia. Her professional base became the Royal Ontario Museum and the University of Toronto, but it was far from the ocean. She soon acquired a residence in Sooke, BC, conveniently located on the beautiful Pacific coast. Life cycle research was now possible on Canadian species, and at times several hundred cultures of hydrozoans were being maintained by her. One final move was made, from Ontario to permanent residence at her cottage in Sooke. From there she kept marine research underway the rest of her life. A focus became Race Rocks and the rich hydrozoan fauna inhabiting the site.
Anita altered the direction of my career in a most positive way. It was largely thanks to her that I moved from employment as a benthic ecologist in South Carolina to a curatorial position at the Royal Ontario Museum in 1981. It was the best career move of my life. Thank you, Anita!
Over the decades we collaborated in research, shared our libraries, and jointly authored several scientific papers. Outside a professional association, we were close friends. My wife and I often visited Anita at her homes, first in Pickering, Ontario, near Toronto, and later in Sooke. In return, she often visited us in Toronto after moving west. It is an understatement to say she will be sorely missed.”
-(Quote from Dr. Dale Calder, ROM, 2018)
Links to her work with the college:
https://www.racerocks.ca/dr-anita-brinckmann-voss/
Other references: https://www.racerocks.ca/tag/anita-brinckmann-voss/
TC -On the firing line with the navy

The Royal Canadian Navy says it takes great pains to protect whales, so it was a shock in August when skippers of Victoria-based whale-watching boats reported ugly confrontations with sailors during blasting on Bentinck Island.
Navy officials say they try to avoid endangering passing orcas and humpbacks, just as they take care to protect the ecology of Bentinck Island and the nearby land on shore occupied by the Department of National Defence at Rocky Point in Metchosin.
Its sailors and officers make their homes in Greater Victoria. Like any other residents, they say they want nothing to harm the unique elements of living on southern Vancouver Island, whether it’s marine mammals, migrating birds or the other animals and plants.
“We are actually quite proud of the environmental protection we have in place,” said Commodore J.B. (Buck) Zwick in a special media session.
“We take our roles as environmental stewards very seriously,” said Zwick, who commands the Canadian Fleet Pacific and Naval Training System.
In incidents on Aug. 3 and Aug. 31, whale-watching skippers confronted navy sentries posted in small boats off the island during a blasting session. The whale-watching skippers tried to convince the sentries to call off the blast because orcas were nearby.
Instead, the whale-watchers were told it was too late. The fuse was already lit, and safety procedures forbid any attempt to stop it. According to the whale-watching skippers, when the explosions occurred on the beach minutes later, the creatures were obviously distressed.
The incidents were also a shock for whale-watchers, who say they have always enjoyed a positive relationship with the navy.
Dan Kukat, owner of Spring Tide Whale Watching and navy liaison for the Pacific Whale Watching Association, said in the August incidents, whales were spotted approaching the blast zone, the navy was notified but the blasts went ahead regardless.
Whale-watchers worry the acoustic vibrations from the beach blasting interferes with and even harms the whales. The creatures are echo-locators and make their way around underwater obstacles using sound and echoes.
Kukat emphasized several times he and members of his association have nothing but respect for the navy. It’s just sometimes the natural world could use a break.
“In these days now, when it’s not entirely necessary to defend the country, let’s think about defending the environment, too,” he said in an interview.
The navy, however, maintains it was complying with its Marine Mammal Mitigation Procedure. It’s a 15-year-old document that instructs sailors on what to do at Bentinck Island when marine mammals approach during blasting activity.
It requires sentries, posted in boats 1,000 metres offshore from the beach, to look out for whales. When whales approach within two kilometres, the sentries radio the officer in charge of the blast range, who can shut things down.
In the past, the navy has conducted acoustic studies. They show underwater noise from the land-based explosions is negligible compared to the normal ambient noise levels a whale encounters.
Nevertheless, since August, the navy has taken a second look at its demolition training and how it interacts with whales and whale-watchers. It has halved the maximum amount of C4 plastic explosive to 2.5 pounds from five (1.125 kg from 2.25 kg).
The navy says halving the size of the explosive charge will make no difference to the demolition training for sailors and service people. The noise will be slightly less above ground and water.
“The process is the same, the quantity of the charge makes no difference, except for a bigger bang,” said Capt. (N) Martin Drews, commander of Navy Training and Personnel.
“But it’s important to use live ammunition during training because it helps instil a sense of discipline in our sailors,” said Drews.
Its sailors and officers make their homes in Greater Victoria. Like any other residents, they say they want nothing to harm the unique elements of living on southern Vancouver Island, whether it’s marine mammals, migrating birds or the other animals and plants.
“We are actually quite proud of the environmental protection we have in place,” said Commodore J.B. (Buck) Zwick in a special media session.
“We take our roles as environmental stewards very seriously,” said Zwick, who commands the Canadian Fleet Pacific and Naval Training System.
In incidents on Aug. 3 and Aug. 31, whale-watching skippers confronted navy sentries posted in small boats off the island during a blasting session. The whale-watching skippers tried to convince the sentries to call off the blast because orcas were nearby.
Instead, the whale-watchers were told it was too late. The fuse was already lit, and safety procedures forbid any attempt to stop it. According to the whale-watching skippers, when the explosions occurred on the beach minutes later, the creatures were obviously distressed.
The incidents were also a shock for whale-watchers, who say they have always enjoyed a positive relationship with the navy.
Dan Kukat, owner of Spring Tide Whale Watching and navy liaison for the Pacific Whale Watching Association, said in the August incidents, whales were spotted approaching the blast zone, the navy was notified but the blasts went ahead regardless.
Whale-watchers worry the acoustic vibrations from the beach blasting interferes with and even harms the whales. The creatures are echo-locators and make their way around underwater obstacles using sound and echoes.
Kukat emphasized several times he and members of his association have nothing but respect for the navy. It’s just sometimes the natural world could use a break.
“In these days now, when it’s not entirely necessary to defend the country, let’s think about defending the environment, too,” he said in an interview.
The navy, however, maintains it was complying with its Marine Mammal Mitigation Procedure. It’s a 15-year-old document that instructs sailors on what to do at Bentinck Island when marine mammals approach during blasting activity.
It requires sentries, posted in boats 1,000 metres offshore from the beach, to look out for whales. When whales approach within two kilometres, the sentries radio the officer in charge of the blast range, who can shut things down.
In the past, the navy has conducted acoustic studies. They show underwater noise from the land-based explosions is negligible compared to the normal ambient noise levels a whale encounters.
Nevertheless, since August, the navy has taken a second look at its demolition training and how it interacts with whales and whale-watchers. It has halved the maximum amount of C4 plastic explosive to 2.5 pounds from five (1.125 kg from 2.25 kg).
The navy says halving the size of the explosive charge will make no difference to the demolition training for sailors and service people. The noise will be slightly less above ground and water.
“The process is the same, the quantity of the charge makes no difference, except for a bigger bang,” said Capt. (N) Martin Drews, commander of Navy Training and Personnel.
“But it’s important to use live ammunition during training because it helps instil a sense of discipline in our sailors,” said Drews.
Canadian government plans extra protection to critical Island ocean sites TC June 2017
Amy Smart / Times Colonist
June 17, 2017 06:00 AM
A proposed expansion of the federal government’s marine conservation powers could speed protection at Race Rocks and eliminate drilling permits in conservation areas such as Hecate Strait.
Fisheries Minister Dominic LeBlanc introduced amendments to the Oceans Act and Canada Petroleum Resources Act this week.
article continues below
The proposal would create interim protection status for sensitive areas, which could include places such as Race Rocks, the biodiverse ecosystem around nine islets in Juan de Fuca Strait.
The interim status would speed conservation in an area by prohibiting new, potentially disruptive activities such as fishing or drilling while the ecosystem is being assessed.
Once interim protection is granted, the Department of Fisheries and Oceans and the Canadian Coast Guard would have up to five years to recommend that a permanent marine protection area be put in place.
Race Rocks has been suggested as a marine protection area since 1998. While its existing status as an ecological reserve already protects it from dumping, dredging and resource extraction, the new designation would add protection to the sea life in its water column, which is not currently protected.
The amendments would also give the minister power to cancel drilling interests in a marine protection area and provide compensation, should no other option be agreed upon.
That could add extra protection to three sponge-glass reefs north of Vancouver Island and in Hecate Strait near Haida Gwaii, said Alexandra Barron, ocean conservation manager for the Canadian Parks and Wilderness Society’s B.C. chapter.
The Hecate Strait and Queen Charlotte Sound reefs are the largest and most pristine glass-sponge reefs in the world. They are 9,000 years old and cover 1,000 square kilometres, reaching heights of an eight-storey building, according to the society.
The reefs were designated a marine protected area in February.
While there is no active drilling because of a moratorium, several oil and gas companies hold legacy permits in the area, said Candace Newman, senior policy adviser with the petroleum management branch of Natural Resources Canada, during a technical briefing of proposed amendments.
“There are a number of interest owners who hold interests or permits in that area,” Newman said.
“They span from the northern part of Haida Gwaii, between Haida Gwaii and the mainland, south to the northern part of Vancouver Island.”
Barron said it’s a positive move, since drilling could continue if the moratorium were lifted.
She said the society is one of many calling for a blanket ban on oil and gas drilling within marine protected areas — not a case-by-case assessment.
“It’s a good start, they’ve taken some important first steps. We would like to see some of those measures go further,” she said.
Fifteen university marine scientists from Victoria to St. John’s, N.L., also penned a letter to Fisheries Minister Dominic LeBlanc Wednesday, saying the marine protection area designation don’t go far enough.
In 2011, the federal government committed to protect at least 10 per cent of Canadian waters by 2020. The Trudeau government has said it will reach the five per cent mark this year.
But the scientists say only about one per cent is protected.
“Of this, only about 0.1 per cent is strongly protected by restricting resource extraction activities that could harm species of conservation value,” the letter says.
This puts Canada behind other G8 countries in both the quantity and quality of protection, it says.
Science shows that the most effective marine-protection policies ban extractive activities in areas of high biodiversity, said Natalie Ban, an assistant professor at the University of Victoria’s school of environment, who signed the letter.
Ban said there’s a “double standard” in Canada’s protection of land and sea resources.
“We would never stand for having oil and gas extraction in one of our terrestrial parks, so why do we allow it in the ocean?” she said.
asmart@timescolonist.com
Flo Anderson : In Memoriam
 ANDERSON, Florence (Zita) Belle On March 30, 2017 Florence (Zita) Belle Anderson, quietly slipped away at home, while laying next to her beloved husband of seventy-three years, Trevor. Born December 30th, 1924 in Victoria at the family home on Midgard Ave., Flo went to Mount View high school and then onto Victoria College in the historic Craigdarroch Castle. She fondly remembered daydreaming about the formal dances held at the castle. After completion of her college exams, she married Trev (May 20th, 1944, Grace Lutheran Church) on his return from serving in the Canadian Airforce, World War II, North Africa. The newlyweds moved to Boundary Bay where they had their first son Garry. Back and forth across Canada four times, the Anderson family moved to different Airforce stations and radar bases adding Stan, Beth and Adrienne to the family along the way. After Trev left the Airforce in 1960, they lived at Miracle Beach for several years. Then the family moved on to their next adventure – twenty years on five West Coast Lighthouses. Flo’s ingenuity led her to achieve any task that she set her mind to and thrive in new situations. During their last seven years on the lighthouse, she and Trev took on a massive undertaking; building their fifty-six foot sailboat Wawa the Wayward Goose. They launched the two-masted ketch from Race Rocks, February 7th, 1982 and headed off for thirteen years of sailing trips. First they sailed locally amongst the Gulf Islands. Then they circumnavigated Vancouver Island. In July 1985, they headed offshore to Hawaii and onto New Zealand, Tonga, Samoa, Fanning Islands, Pago Pago, returning to Victoria July 1987. Florence had prepared herself by completing a Celestial Navigation course, getting her HAM radio license and joining the Blue Water Cruising Association. They sold Wawa in 1995 settling in Sidney and then in her parents last house in James Bay. Travel has always been a part of Flo’s life. On holidays away from the lighthouse, she and the family travelled on many road trips across North America and an excursion to Portugal and Spain. Flo’s artistic skills started early. She learned to sew, leather work, crochet, tat, spin wool, knit, quilt, draw and paint. While on the lighthouses she taught herself to oil paint and created realistically beautiful wave seascapes. At age seventy, she taught herself to use the computer, wrote a book (Lighthouse Chronicles), found a publisher and went on a book tour around BC. She is predeceased by her parents, Bert and Ida Drader (Victoria), her sisters Nellie Marshall (Niagara Falls, ON) and Eileen Odowichuk (Campbell River) and her brother Bill Drader (Edmonton, AB). She is survived by her husband Trev, sister Julia Guilbault (Victoria), her children Garry Anderson (Phyllis), Stan Anderson (Janet), Beth Cruise, Adrienne Lowden (Jeff); six grandchildren, eight great-grandchildren, one great-great-grandchild and two dear life-long friends Kay Johnson and Arlene Bryan We would like to send a heartfelt thank you to Flo’s Caregivers extraordinaire, Lesley, Joanne, Hughette, Michelle and Wendy. And a special thank you to Dr. Rosenberg and Associates for their compasionate and excellent care. There will be a Celebration of Life June 30th , 1:00 – 3:00 pm at 576 Niagara Street. Flo will be dearly missed by all
ANDERSON, Florence (Zita) Belle On March 30, 2017 Florence (Zita) Belle Anderson, quietly slipped away at home, while laying next to her beloved husband of seventy-three years, Trevor. Born December 30th, 1924 in Victoria at the family home on Midgard Ave., Flo went to Mount View high school and then onto Victoria College in the historic Craigdarroch Castle. She fondly remembered daydreaming about the formal dances held at the castle. After completion of her college exams, she married Trev (May 20th, 1944, Grace Lutheran Church) on his return from serving in the Canadian Airforce, World War II, North Africa. The newlyweds moved to Boundary Bay where they had their first son Garry. Back and forth across Canada four times, the Anderson family moved to different Airforce stations and radar bases adding Stan, Beth and Adrienne to the family along the way. After Trev left the Airforce in 1960, they lived at Miracle Beach for several years. Then the family moved on to their next adventure – twenty years on five West Coast Lighthouses. Flo’s ingenuity led her to achieve any task that she set her mind to and thrive in new situations. During their last seven years on the lighthouse, she and Trev took on a massive undertaking; building their fifty-six foot sailboat Wawa the Wayward Goose. They launched the two-masted ketch from Race Rocks, February 7th, 1982 and headed off for thirteen years of sailing trips. First they sailed locally amongst the Gulf Islands. Then they circumnavigated Vancouver Island. In July 1985, they headed offshore to Hawaii and onto New Zealand, Tonga, Samoa, Fanning Islands, Pago Pago, returning to Victoria July 1987. Florence had prepared herself by completing a Celestial Navigation course, getting her HAM radio license and joining the Blue Water Cruising Association. They sold Wawa in 1995 settling in Sidney and then in her parents last house in James Bay. Travel has always been a part of Flo’s life. On holidays away from the lighthouse, she and the family travelled on many road trips across North America and an excursion to Portugal and Spain. Flo’s artistic skills started early. She learned to sew, leather work, crochet, tat, spin wool, knit, quilt, draw and paint. While on the lighthouses she taught herself to oil paint and created realistically beautiful wave seascapes. At age seventy, she taught herself to use the computer, wrote a book (Lighthouse Chronicles), found a publisher and went on a book tour around BC. She is predeceased by her parents, Bert and Ida Drader (Victoria), her sisters Nellie Marshall (Niagara Falls, ON) and Eileen Odowichuk (Campbell River) and her brother Bill Drader (Edmonton, AB). She is survived by her husband Trev, sister Julia Guilbault (Victoria), her children Garry Anderson (Phyllis), Stan Anderson (Janet), Beth Cruise, Adrienne Lowden (Jeff); six grandchildren, eight great-grandchildren, one great-great-grandchild and two dear life-long friends Kay Johnson and Arlene Bryan We would like to send a heartfelt thank you to Flo’s Caregivers extraordinaire, Lesley, Joanne, Hughette, Michelle and Wendy. And a special thank you to Dr. Rosenberg and Associates for their compasionate and excellent care. There will be a Celebration of Life June 30th , 1:00 – 3:00 pm at 576 Niagara Street. Flo will be dearly missed by all
New hashtag for #racerocks
I have just started a twitter hashtag for our the Race Rocks Ecological Reserve #racerocks You are welcome to use this in your twitter feed to provide links to significant new news-worthy events concerning the Race Rocks Ecological Reserve.
There is also a new one for British Columbia Ecological Reserves: #ecoreserves
GF
Elephant Seal Birth Videos –The delivery
Above, the mother elephant seal is having contractions. The pups nose and head start to become visible at the end of the clip.
The pup is born, steaming in the sun and the mother starts calling to it.
See Elephant Seal Birth part 1- start and end of birth
See Elephant Seal Birth part 2
See Elephant Seal Birth part 3 wide angle
See Elephant Seal Birth part 4
Short-term Eco-guardian Position
Race Rocks needs an Eco-guardian for 3 weeks–( December 2015)
Responsibilities include ecological observations, monitoring of marine activity and maintenance of equipment on the island. If you are interested, and for a complete position description, please call Pearson College and ask for Chris Blondeau.
250-three 91- 2 four 9 zero
Nine divers rescued after boat capsizes near Race Rocks, TC Nov 17, 2015
Also see Ecoguardians report at https://www.racerocks.ca/9-divers-rescued-after-boat-capsized/
Richard Watts / Times Colonist
November 15, 2015 11:18 PM

Rescue in progress off Race Rocks Sunday afternoon. Photograph By Don Macisaac/Pearson College, Race Rocks
See more at: http://www.timescolonist.com/news/local/nine-scuba-divers-rescued-in-rough-seas-off-race-rocks-1.2111723#sthash.37bWnQHs.dpuf
UPDATED: Two volunteer rescue crews, one from Victoria and the other from Sooke, improvised a tag-team-style effort to pluck nine stricken scuba divers off a bouncing, capsized boat Sunday afternoon.
Jason van der Valk, coxswain of the Royal Canadian Marine Search and Rescue craft based in Sooke, said his crew started the rescue by throwing a line to the boat capsized near Race Rocks, and pulling first one, then two divers to safety from the water.
The Sooke boat then moved aside while its crew checked out the medical condition of the two rescued divers. Meanwhile, the Victoria boat moved in and repeated the heaving-line rescue for one more diver. Then, it was the Sooke boat’s turn again.
The strategy was repeated until all nine recreational divers had been pulled to safety. They were taken to Pedder Bay Marina, where ambulances and helicopters were waiting. None suffered anything worse than mild hypothermia and seasickness.
Van der Valk said the dual-team rescue had never been rehearsed or tried before. But after countless hours of drills and hard training, rescue crews learn to put together best procedures on the spur of the moment.
“That’s the first time,” he said in a telephone interview. “But just knowing how everybody is going to operate it just went like clockwork.”
All nine rescued divers are members of a recreational diving club called the Aquarius Dive Club, based at CFB Esquimalt. Eight were wearing cold-water drysuits. One person, the boat driver, was without a dive suit.
Sara Helmeczi, acting spokeswoman for CFB Esquimalt, said the Aquarius Club is for service men and women and associated members from the public. It is not a military body.
Helmeczi said when the divers arrived at Race Rocks on Sunday, they decided it was too rough and tried to head elsewhere, but were swamped by waves.
She said four of the nine divers rescued on Sunday are military personnel, so the Canadian Armed Forces will conduct a safety investigation into the incident.
Van der Valk said the first call came in about 2 p.m. on Sunday, saying there were five people in a capsized boat near Race Rocks.
“We didn’t know much detail at first,” said van der Valk. “But they never like to delay, so it was just ‘Go! Go! Go!’ ”
He said Race Rocks, near the eastern entrance to the Strait of Juan de Fuca, is midway between Sooke and Victoria stations, so both responded in their Zodiac-style jet boats, Sooke with a crew of six and Victoria with five.
Van der Valk said the waves were four to six feet high at Race Rocks. When rescuers arrived at the scene, they could see four people in the water clinging to the boat and five sitting on top of the overturned hull. He estimated they had been in the water for 45 minutes to an hour.
“The waves were breaking over the boat and quite frankly I’m amazed they were able to hang on,” said van der Valk. “I’m surprised one of them hadn’t let go or fallen off and drifted away.
“Given the state of the sea, there is no way they could have swum back to the boat.”
Waiting nearby was a whale-watching boat, the Spring Tide, which had temporarily set its passengers on Race Rocks and stood by to help, if needed. A recreational fishing boat was also standing by.
But van der Valk said the two rescue craft have a special low ramp at the stern, making it easy to pull tired people from the water. As jet boats, they also have no propellors to cut feet treading water.
Don Macisaac, eco-guardian of Race Rocks, said his fellow guardian and fiancée, Nina Yousefpour, noticed the dive boat, which was initially upright, while doing chores. The two live full time on Race Rocks.
A short while later, the two saw the overturned boat with people waving, attempting to attract attention.
Macisaac said Yousefpour helped co-ordinate some of the emergency radio communication, including to fire officials assisting with ambulances at Pedder Bay. Meanwhile, Macisaac helped the Spring Tide unload its passengers and push back off.
Race Rocks, an ecological reserve managed by Pearson College, is normally off limits to the public.
Macisaac said the ocean temperature is about 9.7 C. “If they hadn’t been wearing wetsuits they would have been in a lot of trouble.”
This is the second emergency at Race Rocks in the last few months.
On July 5, Timothy Chu, a 27-year-old British police officer, became separated from his dive master and drowned. His body was recovered on Aug. 27.
rwatts@timescolonist.com
– See more at: http://www.timescolonist.com/news/local/nine-scuba-divers-rescued-in-rough-seas-off-race-rocks-1.2111723#sthash.37bWnQHs.dpuf
Other media covering the event appeared at:
- http://www.komonews.com/news/local/Whale-Watch-Crew-Rescues-9-People-from-Capsized-Boat-350810111.html (improper photo credits given)
- http://www.vancouversun.com/mobile/news/vancouver/dive+club+members+rescued+afer+boat+capsizes/11519240/story.html (improper photo credits given)
- http://www.yyjnews.ca/nine-scuba-divers-rescued-in-rough-seas-off-race-rocks/
- ww.cheknews.ca/race-rocks-divers-rescued-122589-122589/
- http://www.cfax1070.com/News/Top-Stories/Nine-divers-rescued-after-boat-capsizes-at-Race-Ro
- http://www.cknw.com/2015/11/15/nine-rescued-after-dive-club-boat-capsizes-near-victoria/
- http://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/british-columbia/dive-club-rescued-off-coast-of-victoria-b-c-after-boat-capsizes-1.3320261
- http://www.theprovince.com/health/nine+rescued+after+boat+capsizes+near+race+rocks+vancouver+island/11519223/story.html
- http://www.victoriabuzz.com/2015/11/9-photos-from-yesterdays-rescue-off-of-race-rocks-after-vessel-overturns/ (improper photo credits given)



