Former Pearson College student Marc-Fawcett-Atkinson and Annie Rueter have published the following article in about our most consistent contributer to the website , Pam Birley of Leicester England.
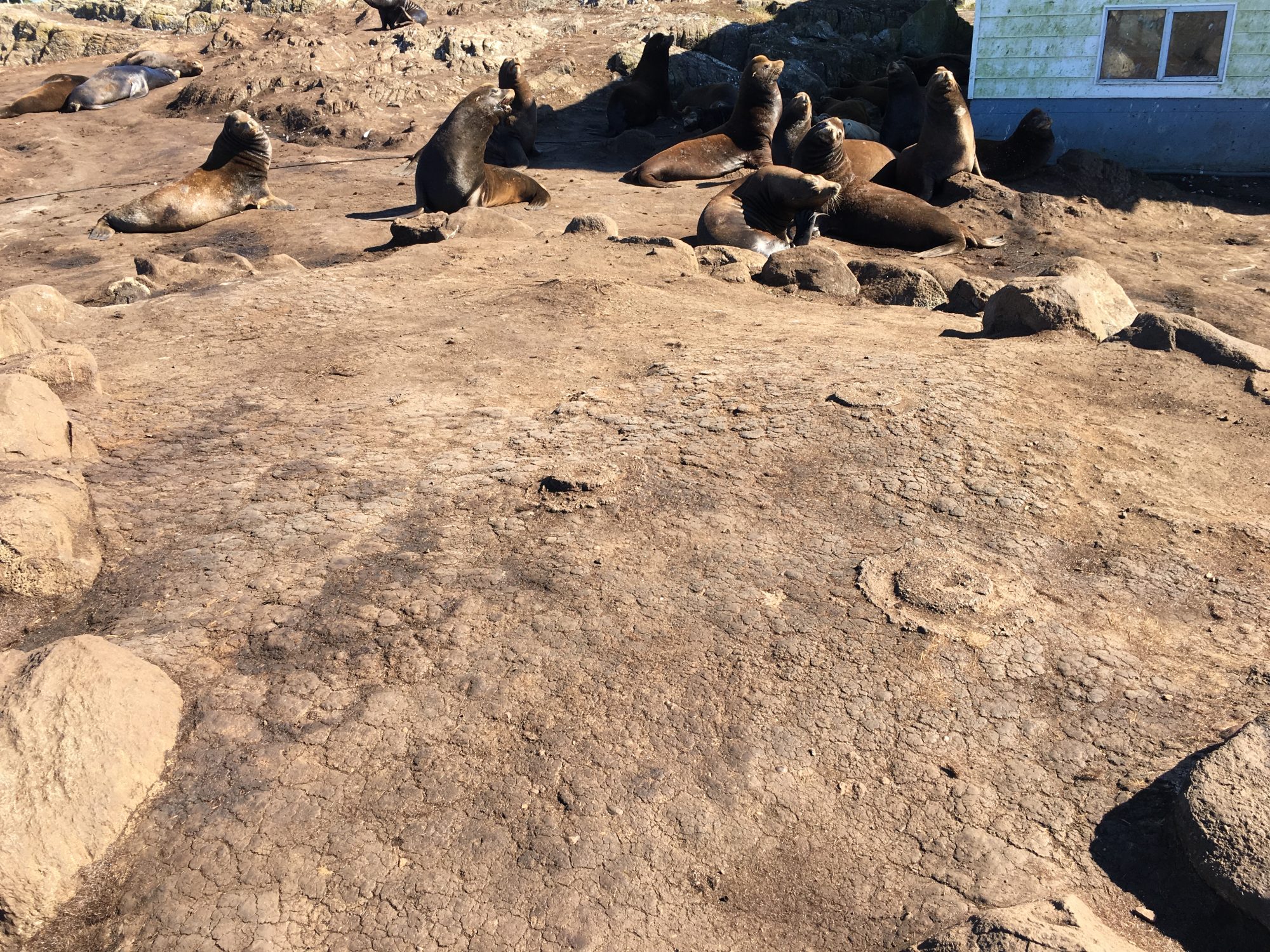
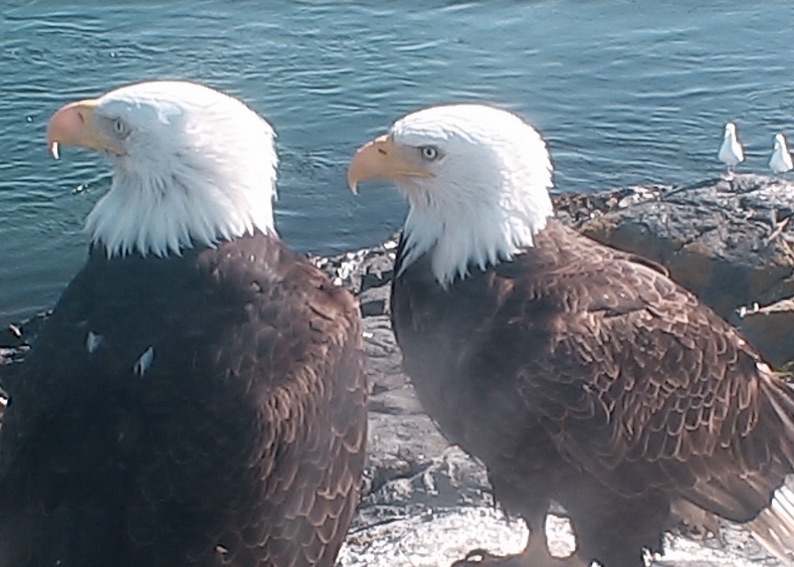
Visit Pamela Birley in her Leicester, England, home, and you’ll likely see sea lions hauling themselves onto Great Race Rock – an island in B.C., eight time zones away.
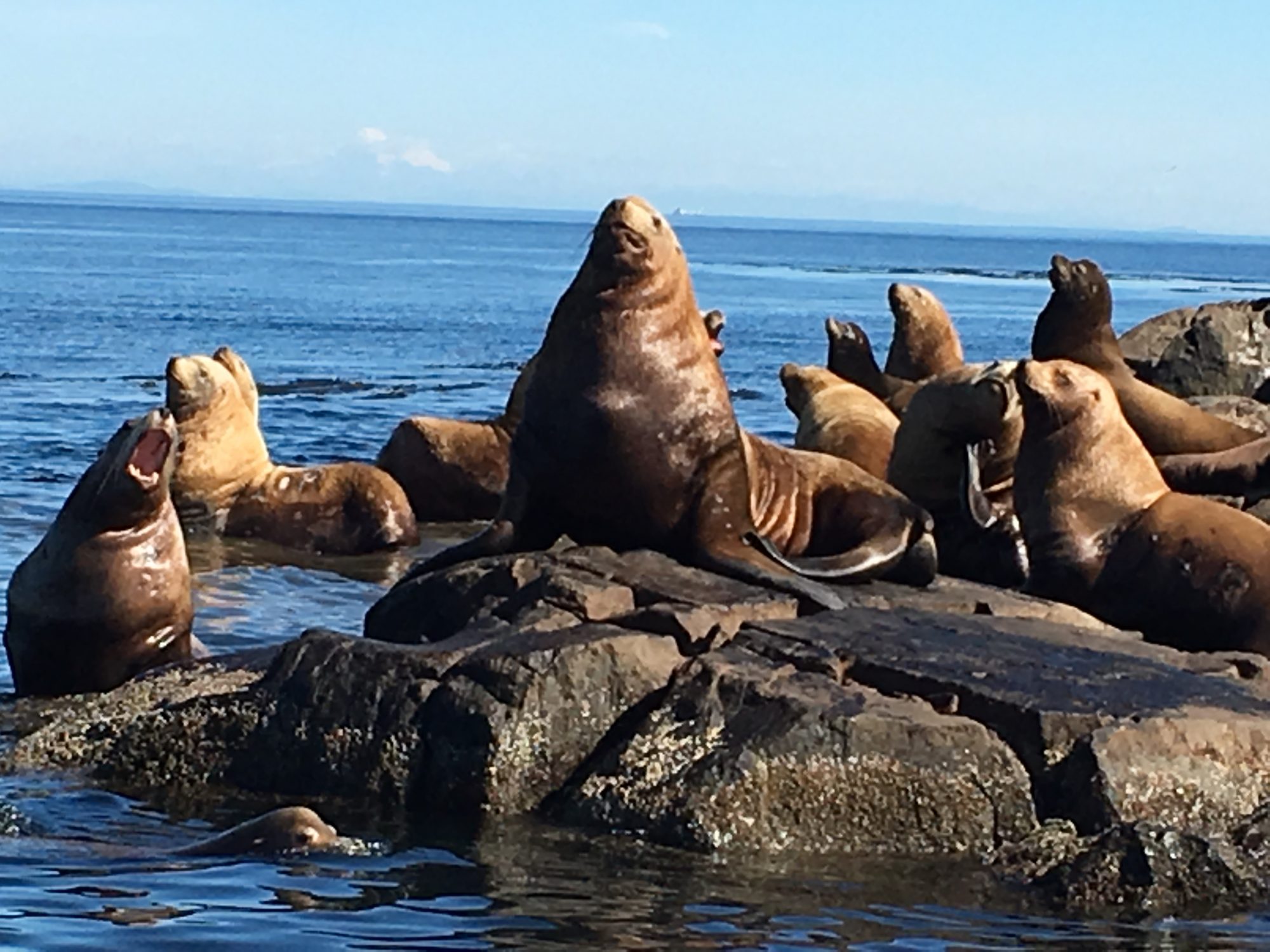
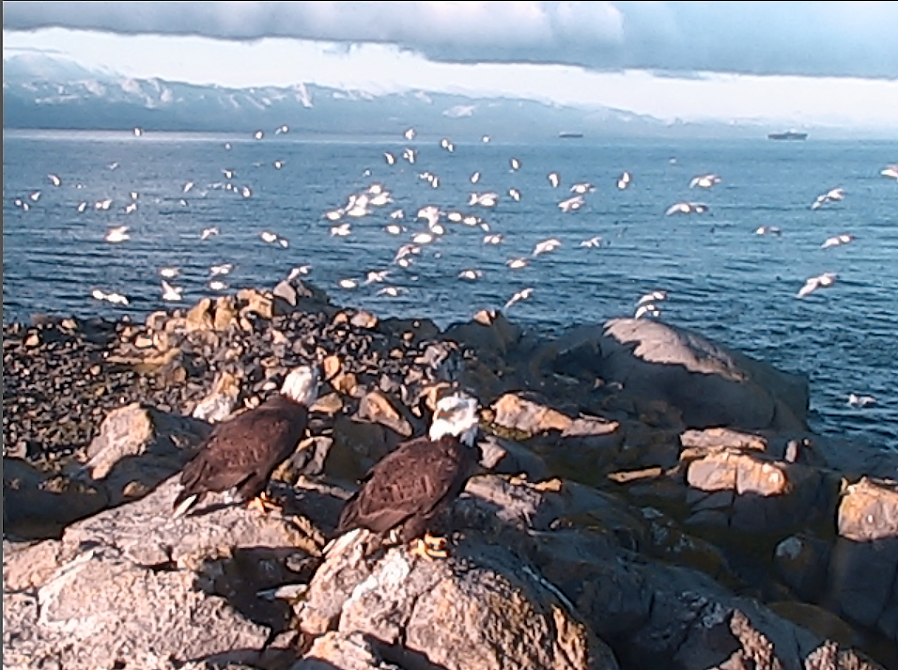
Surrounded by tidal races, open to wind and waves, and dwarfed by views of the Olympic Mountains, the treeless rock off the southern tip of Vancouver Island is a magnet for marine life in the area.

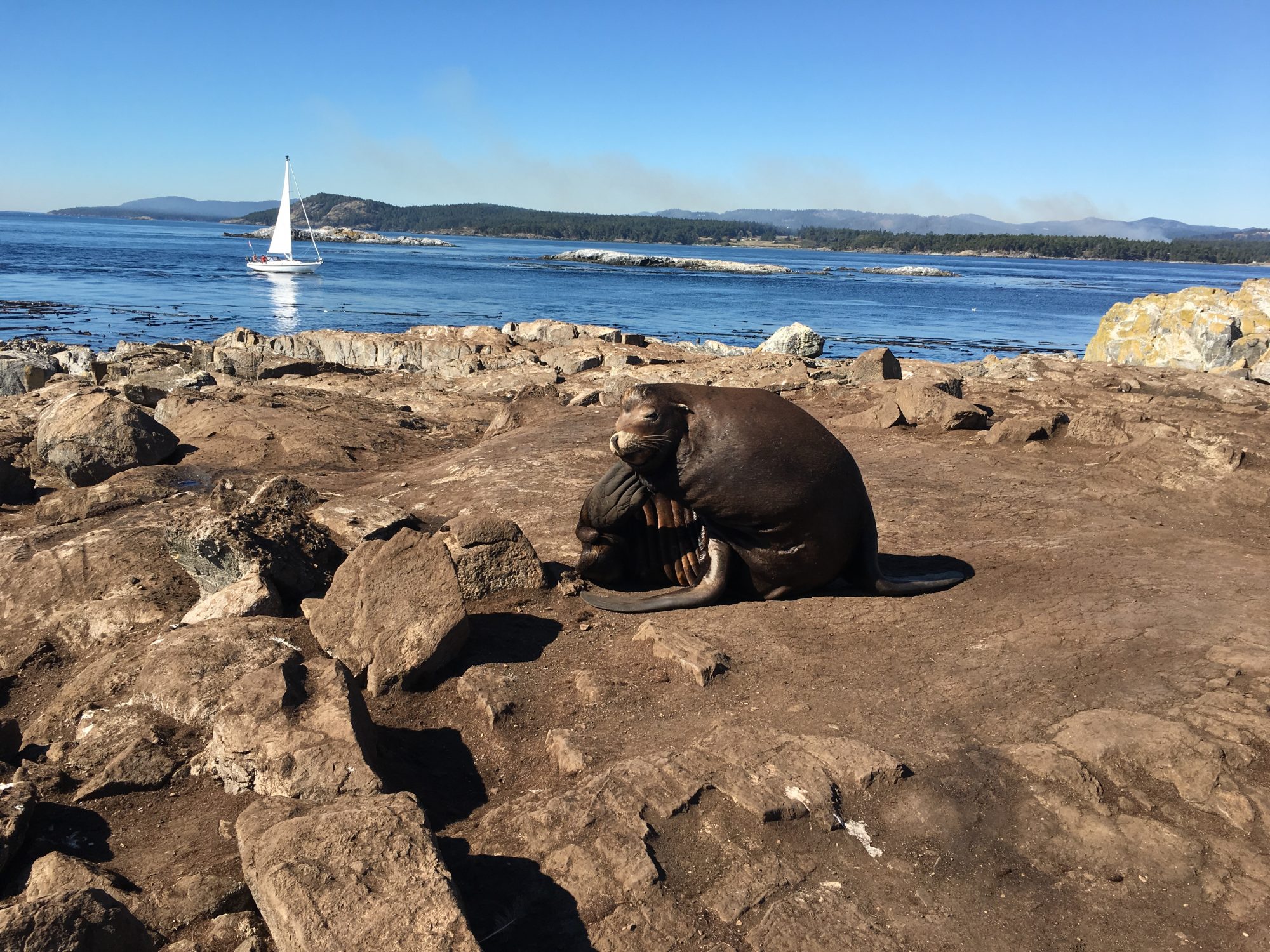
A young elephant seal saunters towards the sea.
Photo: Hanne-Marie Barlach Christensen
Birley, 86, has been watching the wildlife on Great Race Rock, the exposed peak of the seamount comprising the Race Rocks marine ecological reserve, for the past 14 years.
The webcams have performed a unique function since they were installed in 2000 by drawing in visitors from around the world and keeping the public from overwhelming the ecosystem. Birley is a daily watcher.
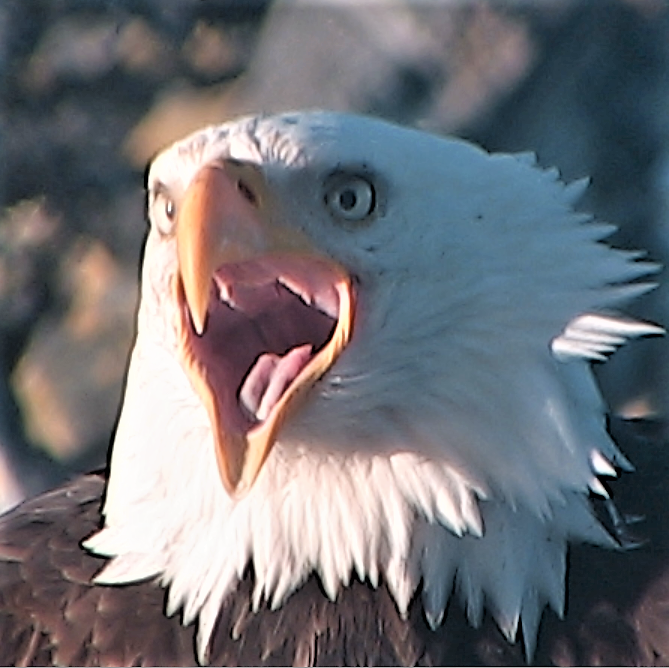
“It’s the variety of wildlife out there,” she said. “You’re never too sure what you’re going to see, and sometimes you see unusual things.”
Hotspot for biodiversity
Home to millions of plankton, thousands of nesting seabirds, and hundreds of sea lions, the reserve in the Strait of Juan de Fuca is rich in marine life. It’s this diversity that motivated Garry Fletcher, a marine biologist, to push for the area’s protection in the 1970s.
“It’s at the confluence of upwelling from deeper ocean and the fresh water spilling out of the Georgia Basin, so it creates a very unique ecosystem,” Fletcher said. “It’s a real hotspot of biodiversity.”

Fletcher’s efforts paid off. In 1980, the B.C. government designated Race Rocks and surrounding seamount as a provincial marine protected area. The federal Department of Fisheries and Oceans subsequently closed the reserve to commercial and ground fishing in 1991 and has designated it an area of interest, slated to become a marine protected area. Spanning 226 hectares, the reserve is managed under lease by the nearby college where Fletcher taught until retirement, Lester B. Pearson United World College of the Pacific.
However, most of those 226 hectares are submerged. Great Race Rock, at merely two hectares, is the only habitable part of the reserve.
Easily crossed on foot in less than 10 minutes, the island has no safe harbour and is cut off from Vancouver Island for days during spells of bad weather. For the island’s resident eco-guardian, Laas Parnell, the island’s size and isolation are impossible to ignore.
Originally from Haida Gwaii, Parnell has lived in isolated, coastal places most of her life. Yet Race Rocks stole her heart when she first visited during a marine-science class in 2011.
“I love it here,” she said of her home of the past year. “I’m not claustrophobic. I keep pretty busy, cooking, cleaning. I spend a lot of time just walking around.”
Still, the island’s tininess can be humbling.
“It reminds me that I’m the only one out there. Alone.” she said.

Light keepers lived on Race Rocks until the beacon was automated in 1997. Their houses, the jetty, and the lighthouse outbuildings remain to house the eco-guardian, researchers, and students. Photo: Hanne-Marie Barlach Christensen
It’s an aspect of the island Birley hadn’t noticed through the webcam.
“It surprised me how compact it was when we actually visited,” she said, reminiscing on the first time she set foot on the island in 2007. “I find it hard to get my bearings on the webcam in relation to what’s near what.”
“Parks end up getting loved to death sometimes”
It was the island’s size that motivated Fletcher to install the webcams. Covered in resting sea lions or seabird nests most of the year, the island can’t handle many visitors. He worried about the impact tourism could have had on the area.
The island is isolated during the winter months by gales and tidal races, but calm seas in the summer make it within easy reach for boats leaving Victoria and other harbours along southern Vancouver Island.
“It’s a bird colony and marine mammal haul-out area,” said Fletcher. “It was just too sensitive to have people coming and going in hordes. You would have every whale-watching boat stop there and disgorge its passengers. Parks end up getting loved to death sometimes.”
To prevent over-visitation, BC Parks mandates that visitors to the island must obtain an education or research permit.

Gulls depend on Great Race Rock as a nesting site and a place to rest.
Photo: Hanne-Marie Barlach Christensen
However, Fletcher wanted to make the reserve’s unique biodiversity and natural beauty publicly available. At the time, webcams offered a novel solution.
Webcams connect wildlife lovers
In 2000, most Canadians relied on dial-up internet, Mark Zuckerberg was 16, and YouTube wouldn’t exist for another five years. Broadcasting online, live from Race Rocks, was a moment Fletcher won’t forget.
“My best memory is when we achieved getting the first video signals off the island, back in 2000,” said Fletcher. “That was quite an accomplishment and represented participation and co-operation from a lot of players.”
For Birley, the introduction of webcams like the ones at Race Rocks were an opportunity to explore the world. She watches four cams daily, including Race Rocks.
“I don’t get out a great deal now,” she said. “But my life is full: I get out in the garden and I do a lot of knitting. I knit birds, just little standing shelf sitters. I can knit while I watch the webcams, so it’s productive.”

Birley’s best-selling knit bird: a peregrine falcon. Photo: Pamela Birley/Etsy
Birley’s knitted birds are popular: she’s sold hundreds in her Etsy shop to buyers far and wide.
Webcams have also fostered international friendships for Birley. Fletcher is one of her regular correspondents, and she’s made friends in Victoria and Seattle through webcams.
It is the animals, however, that keep Birley watching Race Rocks. She documents Race Rocks wildlife extensively through webcam screenshots and turns them into albums on Flickr.
Birley sees some animals regularly, like the gulls and sea lions, but her dedication to the webcam has paid off with an amazing sighting—a snowy owl.
“It was pouring rain, I had the camera on, and I was probably knitting,” she recalls.
“I looked up and thought I saw a funny looking seagull by the rock. I zoomed in and there it was: a snowy owl sitting there, just swivelling its head around from time to time. I’ve only ever seen the one, and that was quite exciting!”

Seeing a snowy owl was a highlight of Birley’s webcam sightings.
Photo: Pamela Birley/Race Rocks