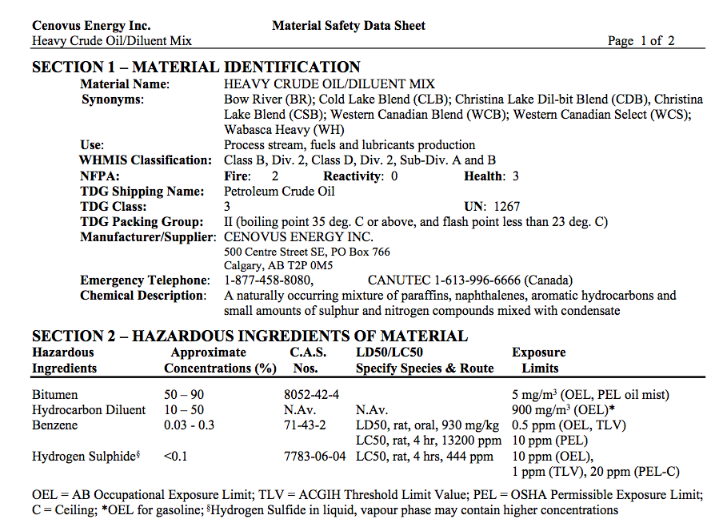
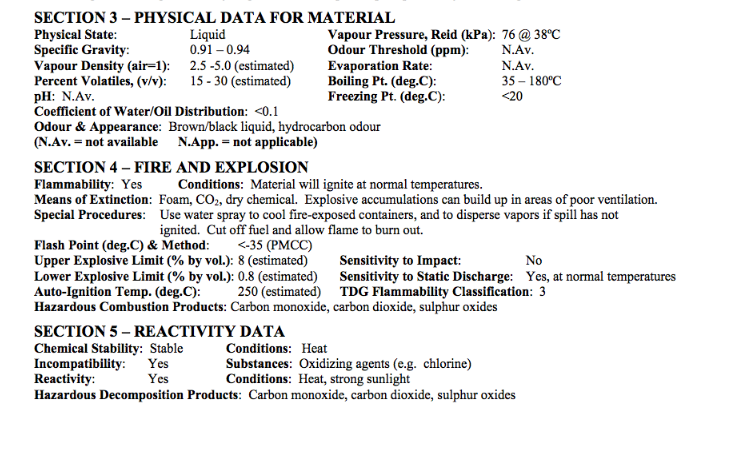
The full pdf of this report is contained in this pdf:
BC EAO Condition 39 Exisitng Shoreline Conditions Report – May 2023 – for engagement
The purpose of this posting is to reference the part of the report referring to Metchosin’s coastline including Race Rocks and to provide comment on it.
===========================================================
 From page 4 of the REPORT:
From page 4 of the REPORT:
1 Introduction
As defined by the amendment to Trans Mountain’s BC Environmental Assessment Certificate (EAC) issued by the Province of British Columbia (the Province) on February 24, 2022, Trans Mountain must prepare an Existing Shorelines Condition Report and submit to the Province within 18 months (August 2023) as Condition No. 39.
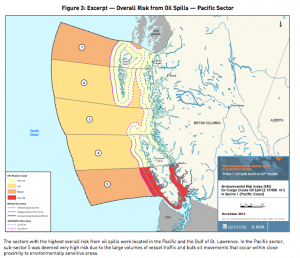
Polaris Applied Sciences was retained to prepare a report containing shoreline baseline data for shoreline areas closest to spill scenario locations modeled along the marine shipping route and submitted in the Project application. The Province listed the specific scenario locations for the purpose of this study (Figure 1) as:
- English Bay (Location B)
- Roberts Bank (Location C)
- Strait of Georgia (Location D)
- Arachne Reef (Location E)
- Strait of Juan de Fuca (south of Race Rocks) (Location G); and
- Buoy J (Location H)
 Page 25
Page 25
Strait of Juan de Fuca (south of Race Rocks) (Location G);
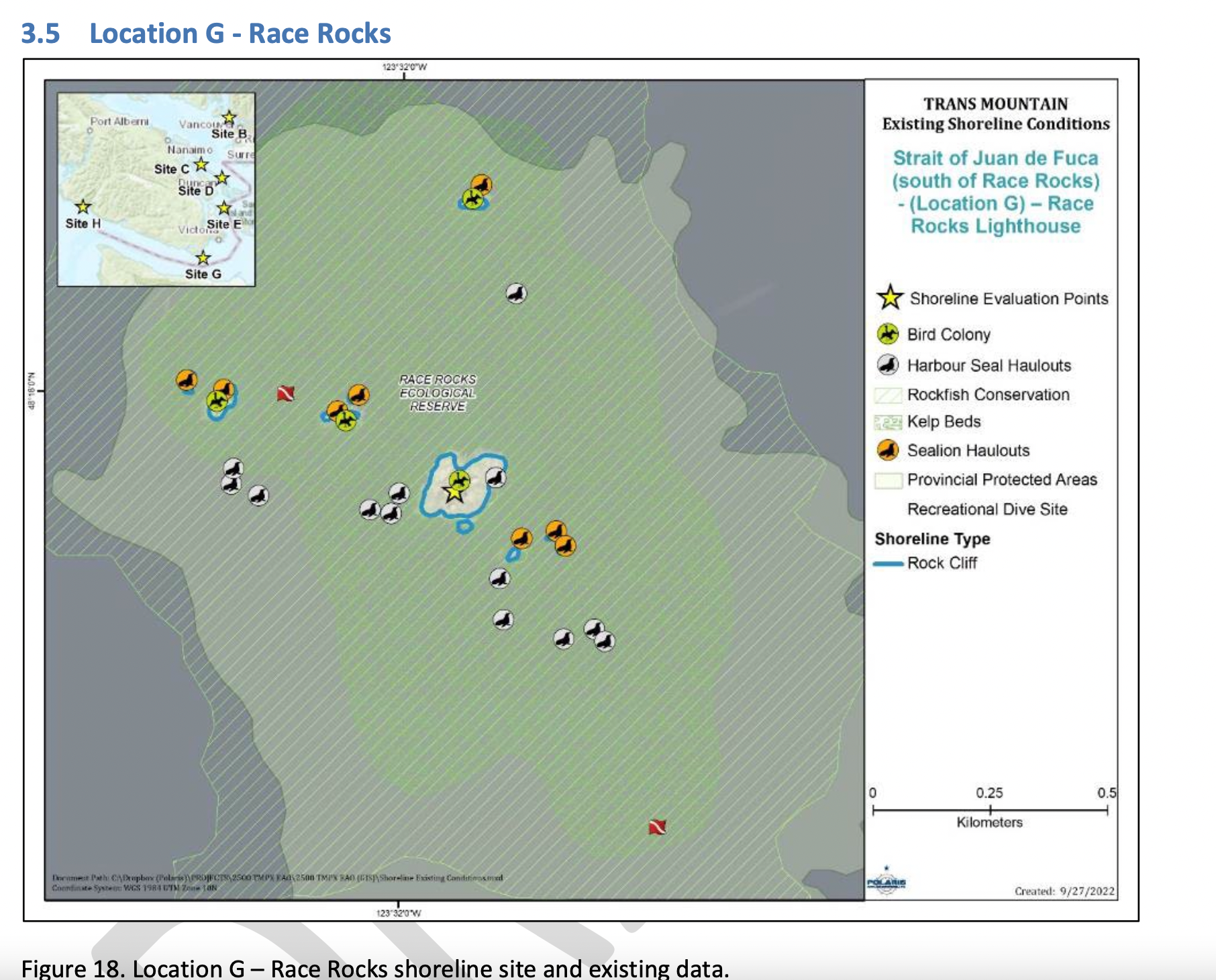
Figure 18 shows the Location G – Race Rocks site with the available existing spatial data. Shoreline data are from the Shorezone mapping effort available from the BC Data Catalogue, which show the shore type consisting of rock cliff. Shore-zone Bioband data indicate the presence of barnacles, dark brown kelps, fucus, bull kelp, red algae, surf grass, and Verrucaria. Other data sources indicate offshore kelp beds and multiple seal and sealion haulouts. The Race Rocks Ecological Reserve (RRER) website (https://racerocks.ca/home/) provides more details on ecological resources documented and studied at the site, but not in a spatial format for mapping.
COMMENTS : The exceptionally high Biodiversity of the area and high level of protection since 1980 as a Provincial Ecological Reserve are not reflected at all in the map presented. If one were to look at the Race Rocks Taxonomy presented at https://racerocks.ca/race-rocks-animals-plants/taxonomy-image-gallery/ there may be a better appreciation of the natural capital of this area
- Rock Cliff Beach designation is inaccurate.. there is a pebble beach and Intertidal areas with tidepools on much of the shorelines of the 9 islandfsd in the Archipelago. Also several surge channels are located around the main island.
- Bird Colonies :
–no mentions is made of four species of nesting seabirds.
–no mention is made of the fact this is a winter roosting area for thousands of seabirds.
— no mention of the fact that the archipelago of islands are an important migratory stopover for marine and terrestrial migratory birds. - Marine Mammals:
–no mention is made of the fact this is the most northerly haul-out and pupping colony for Elephant seals — no mention of the fact that California and Northern sealions haul out in numbers over 1000 in the fall of the year.
—no mention that the haul-out locations for harbour seals are also pupping colonies.
— no mention of the ocurrence of river otters and sea otters on and within the islands.
– no mention of the fact that it is an important feeding area for Biggs killer whales. https://racerocks.ca/humpback-and-orca-sightings-race-rocks/
–no mention of the fact that the surrounding waters have had a rapid increase in the past few years of Humpback whales - Invertebrates:
–The extremely high biodiversity of invertebrate species both inter-tidally and sub-tidally is not mentioned.
–Several rare species of invertebrates are found here and are not acknowledged - Fish :
–This is a rockfish protection area and all species of BC Rockfish are represented.– a high diversity of other fish are also represented here, with even sitings of Sturgeon occurring. - Marine Algae :
–There is a much higher species diversity of Marine Algae found in the ecological reserve than is n surrounding areas.
— the indication of kelp beds on the map presented here is totally inaccurate and insufficient. Given the decline of kelp beds in our coastal water , this is highly relevant. - Indigenous and Historical Significance:
— the presence of archaeological sites and the significance of the historic structures cannot be minimized . All are sprayed with seawater and therefore subject to immersion in pollutants during intense winds which occur regularly.
===============================================================
Page 26
Comments:
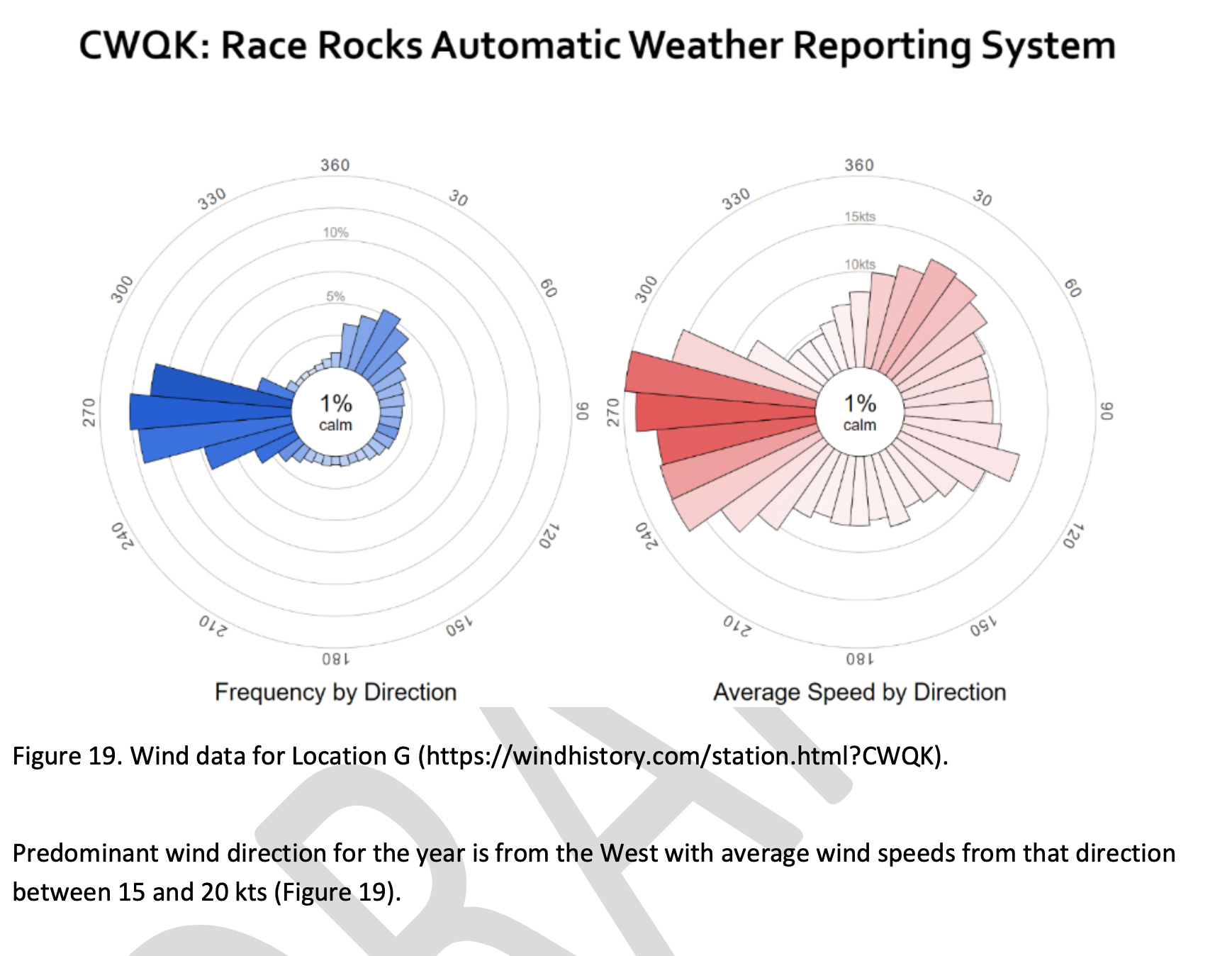
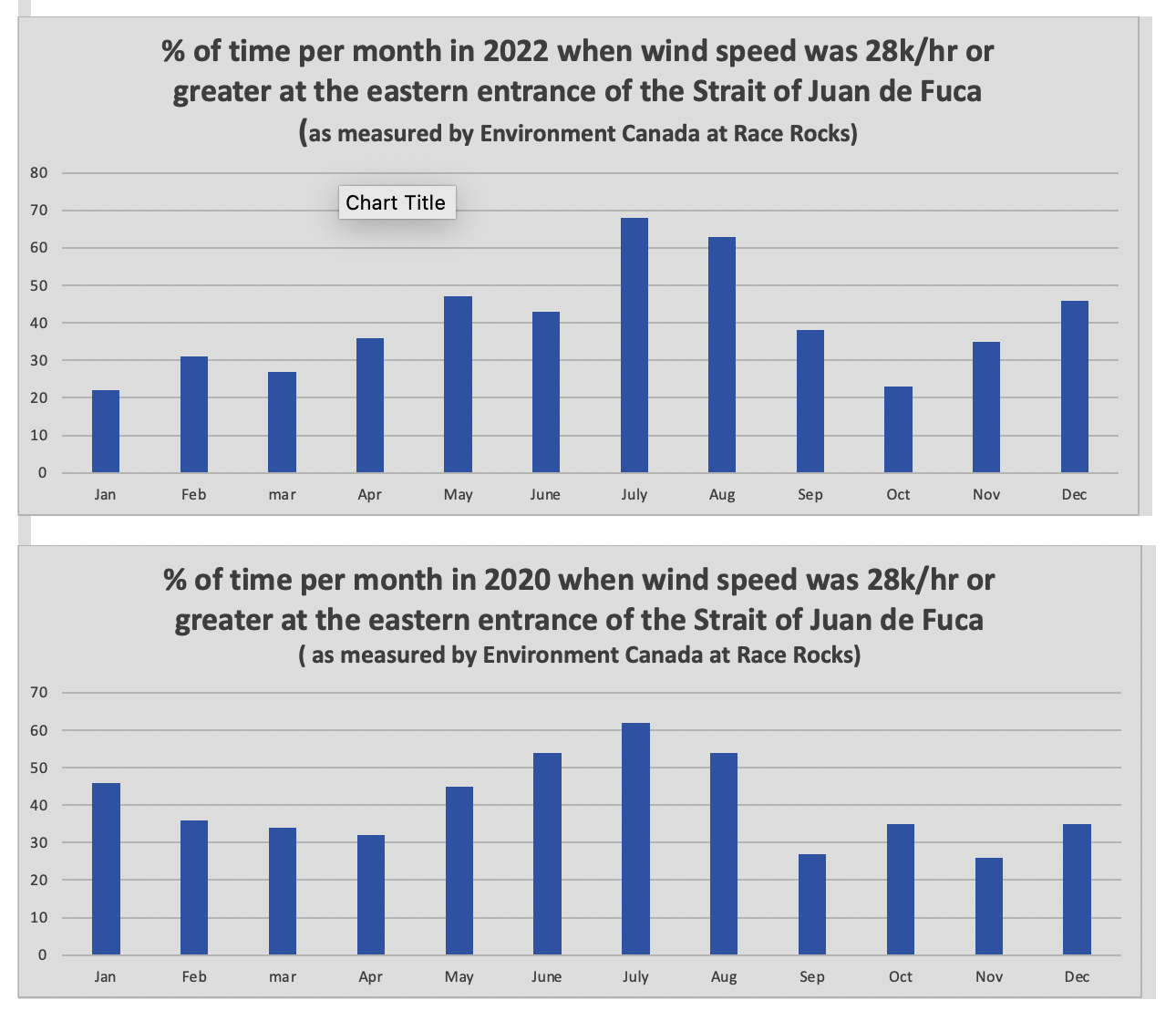
The reference at the Race Rocks website from racerocks.ca which analyzes the Wind speed from observations of the hourly data provided by Environment Canada show a completely different picture . https://racerocks.ca/race-rocks-lightstation-weather-conditions-environment-canada-problems-for-oil-spill-cleanup/
Some facts from the Environment Canada data:
1. In July of 2022 there were 11 days when the wind speed every hour was 28 km/hr or greater. and 69.5% of the hours in the month, clean up equipment could not be deployed due to high velocity wind conditions.
2. In March of 2023, the wind speed was 28 km/hr or greater 37% of the time.
3. In Februarry of 2023 , the wind speed was 28 km/hr or greater 43 % of the time
4. In January of 2023 , the wind speed was 28 km/hr or greater 36% of the time
============================================================
================================================
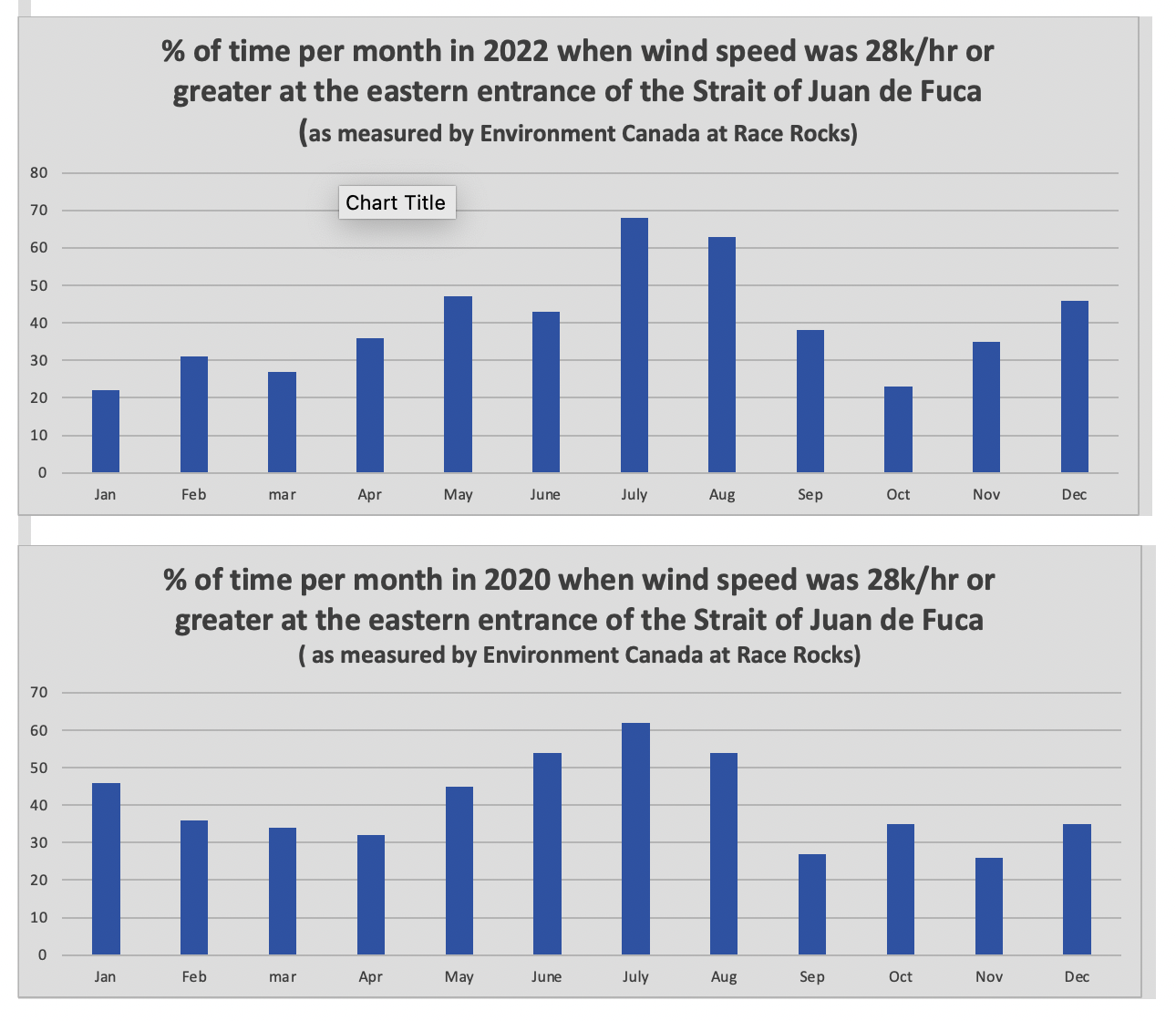
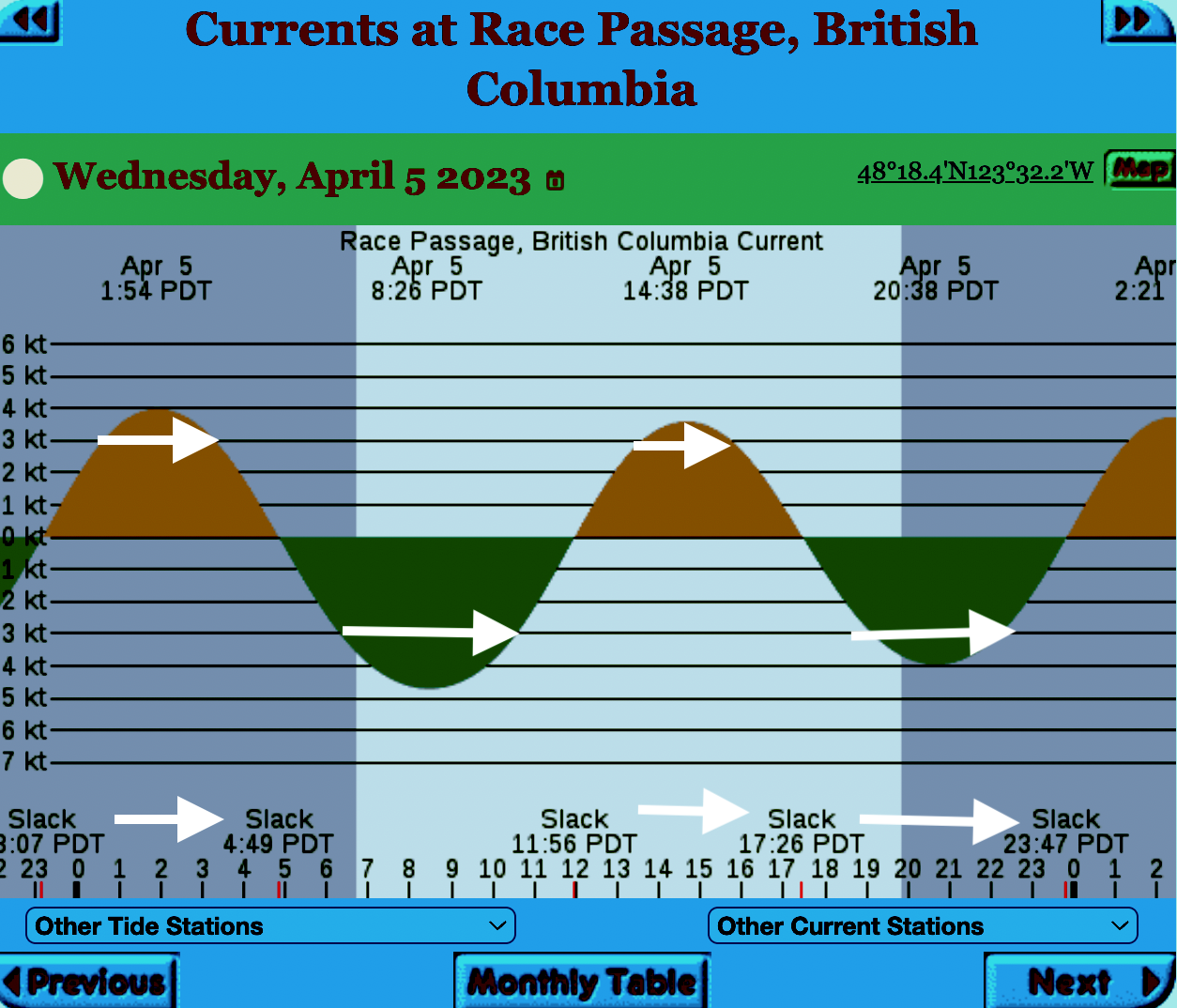
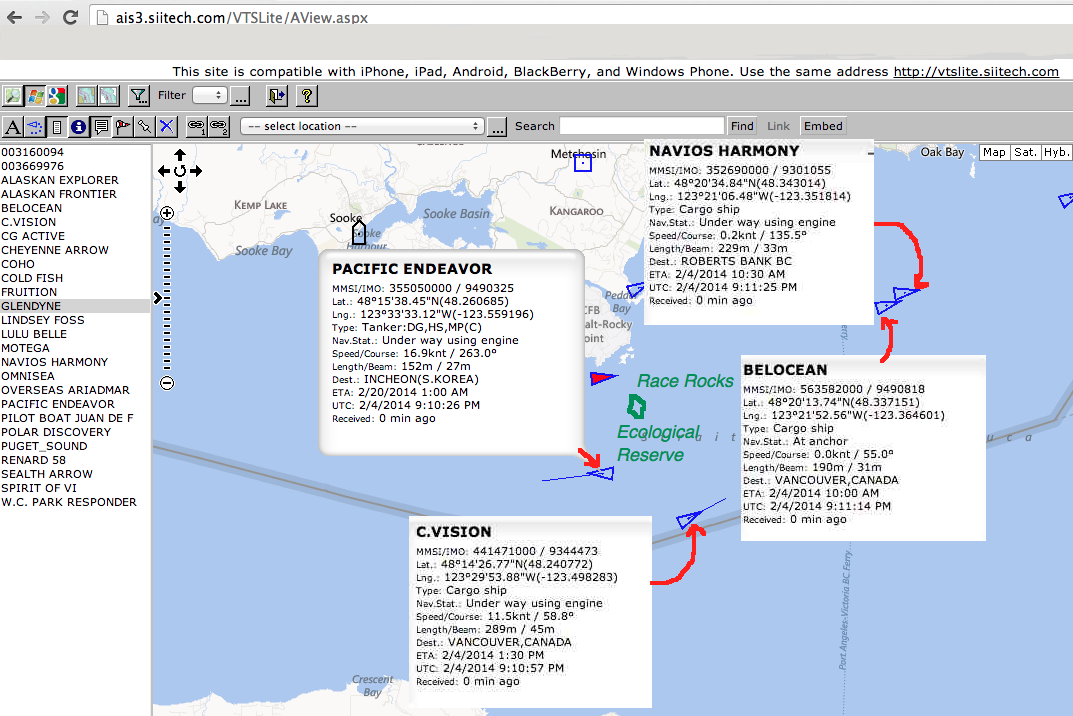
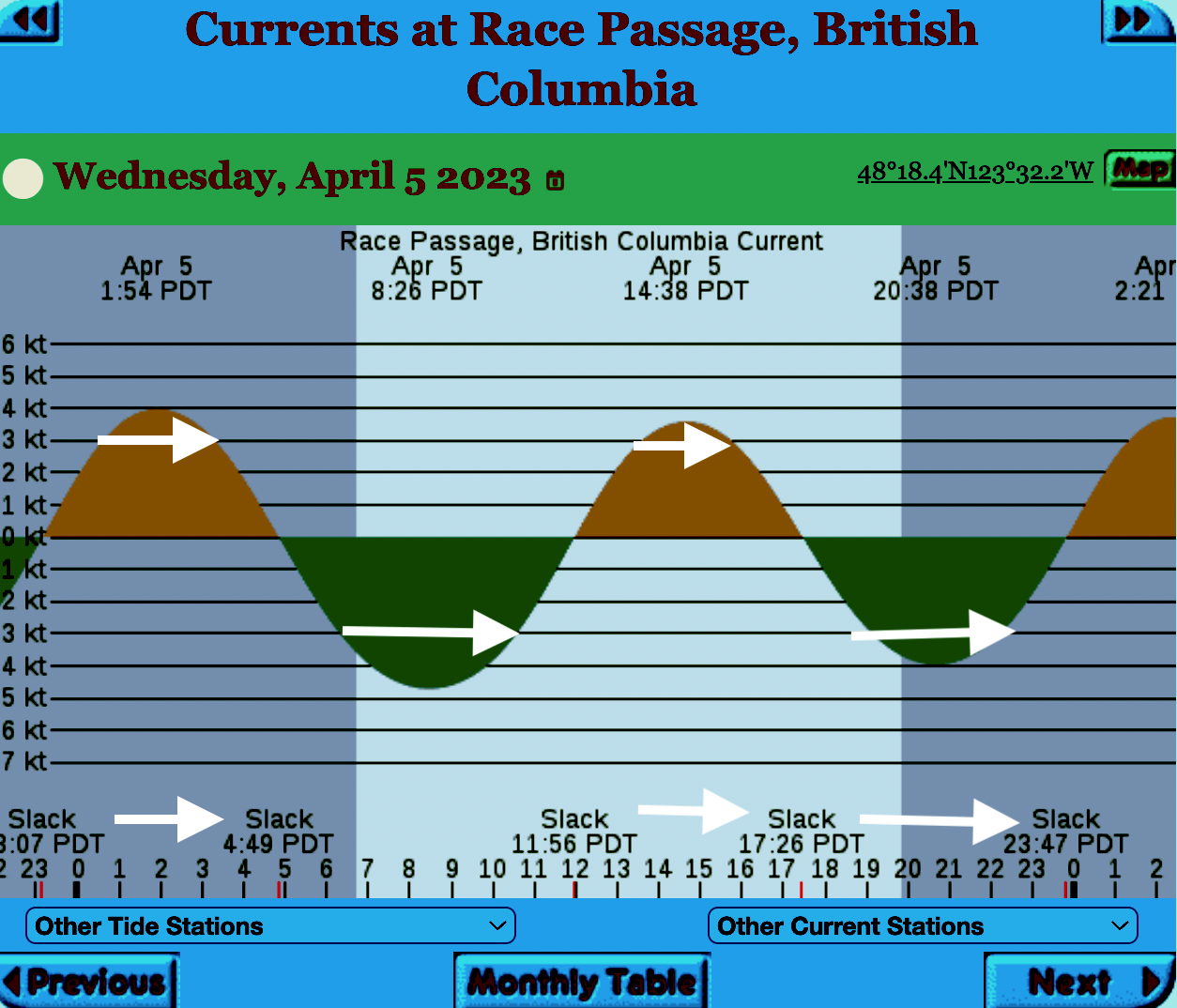
The reality of current speed is that there is a very small window of time during the day that the waters around Race Rocks are not over three knots. In the graph below only in the few hours a day not covered by the white arrows could any boom placement be established. WHen looked at from this perspective, added onto the small windows of time when the wind speed is under 28 km per hour could spilled oil containment even be possible.
=============================================================
 From page 28 of the Polaris report
From page 28 of the Polaris report
Field surveys were not conducted at Race Rocks due to the long lead time in acquiring a “research” permit from BC Parks to access the Ecological Reserve. Information detailed below comes from reviewing the existing data available, Google Earth, the RRER website, and a First Nations representative.
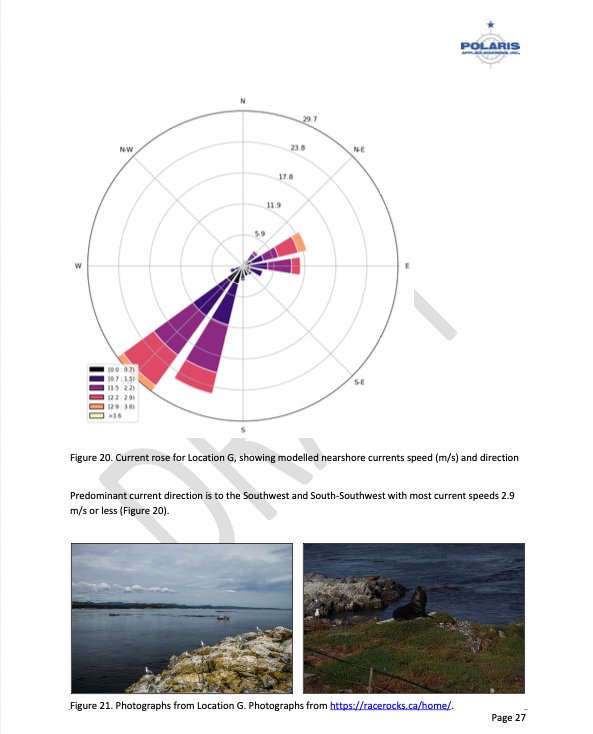
The shoreline at Race Rocks, specifically Great Race Rock, appears to be mostly bedrock cliff, ramp, and platform, possibly with some small pocket pebble/cobble beaches. Bedrock cliffs and ramps are observable in Figure 21 which show some example photographs from the Race Rocks Ecological Reserve website. The backshore appears to be mostly bedrock with some vegetation.
An active lighthouse along with several other buildings are present. Pearson College UWC conducts research and teaches classes at the site. Whale and sightseeing boats frequent the waters around Great Race Rock and are visible from photographs on the Race Rocks website and on Google Earth.
As mentioned before, Race Rocks is a BC Parks Ecological Reserve which are “areas selected to preserve representative and special natural ecosystems, plant and animal species, features and phenomena. Scientific research and educational purposes are the principal uses of ecological reserves”7. A wide variety of ecological resources are documented, tracked, and studied at the site. This documentation includes a weekly animal census, annual bird counts, and an entire list of species ever documented with photos/videos since 2000 (https://racerocks.ca/race-rocks-animals-plants/taxonomy-image-gallery/). Additional research conducted at the site can also be found on the RRER website. The extensive use of the site as a haulout location by pinnipeds is documented on the website and visible on Google Earth.
This area has historically been used by First Nations for harvesting food, as documented on the Race Rocks website, and a First Nations representative indicated that fishing is common in the waters around the site. Burial mounds/cairns have been researched and documented on Great Race Rock.
A helicopter pad is located near the lighthouse.
Based on the available data, and without visiting Race Rocks, the Shorezone mapping appears to be relatively accurate. The detailed observation of the flora and fauna on the Race Rocks website and other research conducted by Pearson College provides the most thorough documentation of the ecological resources present compared to any of the other sites visited.
7 https://bcparks.ca/eco_reserve/
================================================================
================================================================