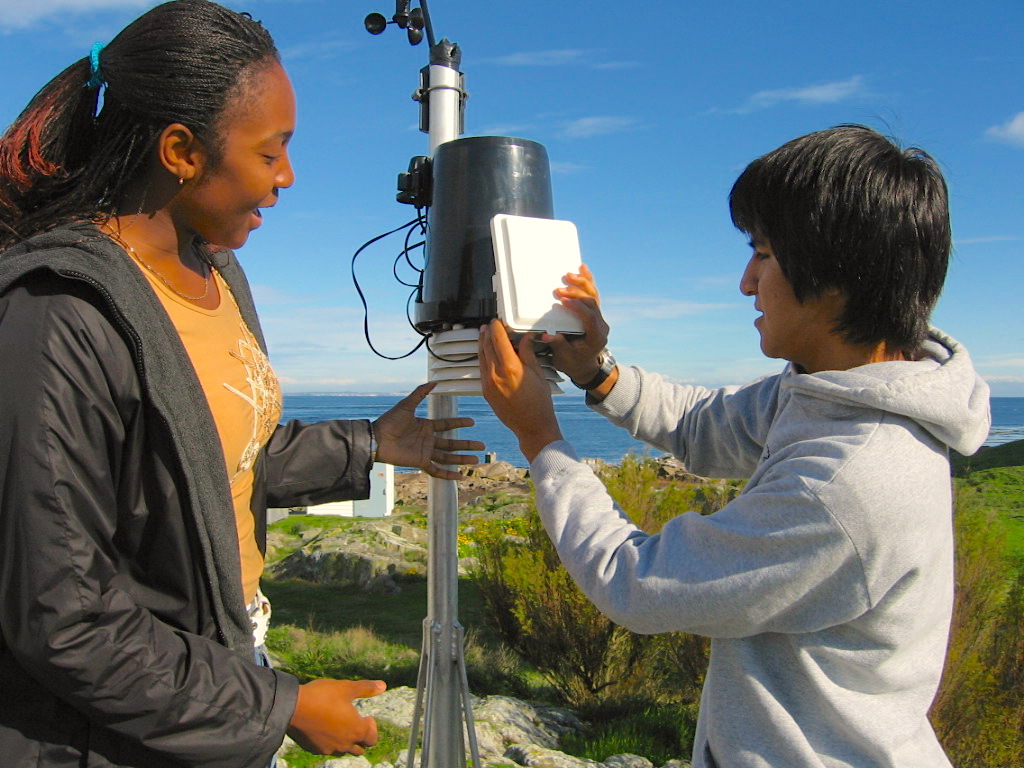
Complete Video Coverage of the Announcement at Pearson College
 TV and Print Media Coverage of the event.
TV and Print Media Coverage of the event.
Press Release : CANA PARTNERS TO ENABLE PEARSON COLLEGE – ENCANA – CLEAN CURRENT TIDAL POWER DEMONSTRATION PROJECT AT RACE ROCKS, BC Victoria
– Thanks to an innovative partnership between Lester B. Pearson College of the Pacific, EnCana Corporation and Clean Current Power Systems Incorporated, Canada’s first free-stream tidal power project will be built at the Race Rocks Ecological Reserve, offshore of Vancouver Island in British Columbia. The project will enable the world famous marine park to tap into surrounding ocean currents and convert tidal energy to electric power for its needs beginning in early 2006. Making the announcement were:
Gwyn Morgan, President and CEO of EnCana,
Glen Darou, President and CEO of Clean Current,
Richard Neufeld, British Columbia Minister of Energy and Mines,
and Stuart Walker, Director of Pearson College.

Gwyn Morgan
Officially known as the “Pearson College – EnCana – Clean Current Tidal Power Demonstration Project at Race Rocks,” the project is enabled by a $3-million investment from the EnCana Environmental Innovation Fund. “EnCana is pleased to be a partner in this first-class, alternative energy project,” said Morgan. “Our investment in this B.C.-based unconventional environmental and power technology reflectsour desire to tangibly encourage innovative energy solutions.” EnCana’s Environmental Innovation Fund was established to advance new technologies and solutions that improve environmental performance associated with consuming and producing energy. Commercial proceeds from financed projects will be re-invested into the fund to ensure their sustainability.

Richard Neufeld
“The commitment by Premier Campbell in promoting alternative energy sources has helped British Columbia become a world leader in sustainable environmental management,” said Neufeld. “The province commends projects like this one, as they show our commitment to developing clean energy solutions that will benefit all British Columbians.” The multi-year demonstration project will involve the installation, operation and monitoring of a 65kW free-stream tidal turbine generator in the water near Race Rocks, a provincial ecological reserve located 10 nautical miles southwest of Victoria.

Glen Darou
Clean Current is a private British Columbia-based company that designs and licenses technology that efficiently converts the energy of tidal currents into electricity. Clean Current’s proprietary technology consists of a horizontal-axis ducted turbine with a direct-drive variable speed permanent magnet generator. The turbine generator is equally efficient in both directions as the tidal currents reverse twice each day. “This Canadian technology is simple, efficient and environmentally friendly,” said Darou. “We believe it is highly exportable technology, with strong potential to succeed in international settings. Our company is delighted to have the support of EnCana, Pearson College, and technical partners AMEC, Powertech Labs Inc. and Triton Consultants Ltd.”
Pearson College, one of ten United World Colleges worldwide, is the custodian of the Race Rocks Ecological Reserve, located three nautical miles from campus. Diesel-powered generators currently provide electricity requirements at the reserve. Students and staff will work elements of the tidal power demonstration project into their studies. “This is a terrific project for Pearson College, in that it supports our goal of making the ecological reserve a showcase for alternative, low-impact technologies such as tidal power,” said Walker. “We would like to thank Clean Current for their commitment to developing the technology and EnCana for the financial support that is making this demonstration project possible.”
 Second Year Pearson College student Alyssa Holland (year 30) concluded the presentation , by thanking the speakers. As a student involved in Environmental Systems and the diving program, she shared the enthusiasm she has for the resources of the area and emphasized the great importance she and other students attach to the effort of those involved in this project in the ongoing goal of producing energy sustainably.
Second Year Pearson College student Alyssa Holland (year 30) concluded the presentation , by thanking the speakers. As a student involved in Environmental Systems and the diving program, she shared the enthusiasm she has for the resources of the area and emphasized the great importance she and other students attach to the effort of those involved in this project in the ongoing goal of producing energy sustainably.
Dave Skilling
Communications Coordinator
Lester B. Pearson College
250-391-2479
www.pearsoncollege.ca
www.racerocks.ca
 Tidal Current Predictions for Race Passage
Tidal Current Predictions for Race Passage Race Passage Current tables, 2021
Race Passage Current tables, 2021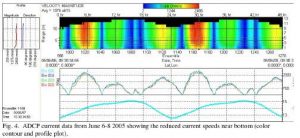 Along with the installation of the Tidal Current turbine, an ADCP was installed to give real time profiles of the Currents at Race Rocks. See the attached file for the type of profile that was generated:Sample of the result of the data analysis at Site 1:
Along with the installation of the Tidal Current turbine, an ADCP was installed to give real time profiles of the Currents at Race Rocks. See the attached file for the type of profile that was generated:Sample of the result of the data analysis at Site 1: The Creation of the Race Passage Current Tables
The Creation of the Race Passage Current Tables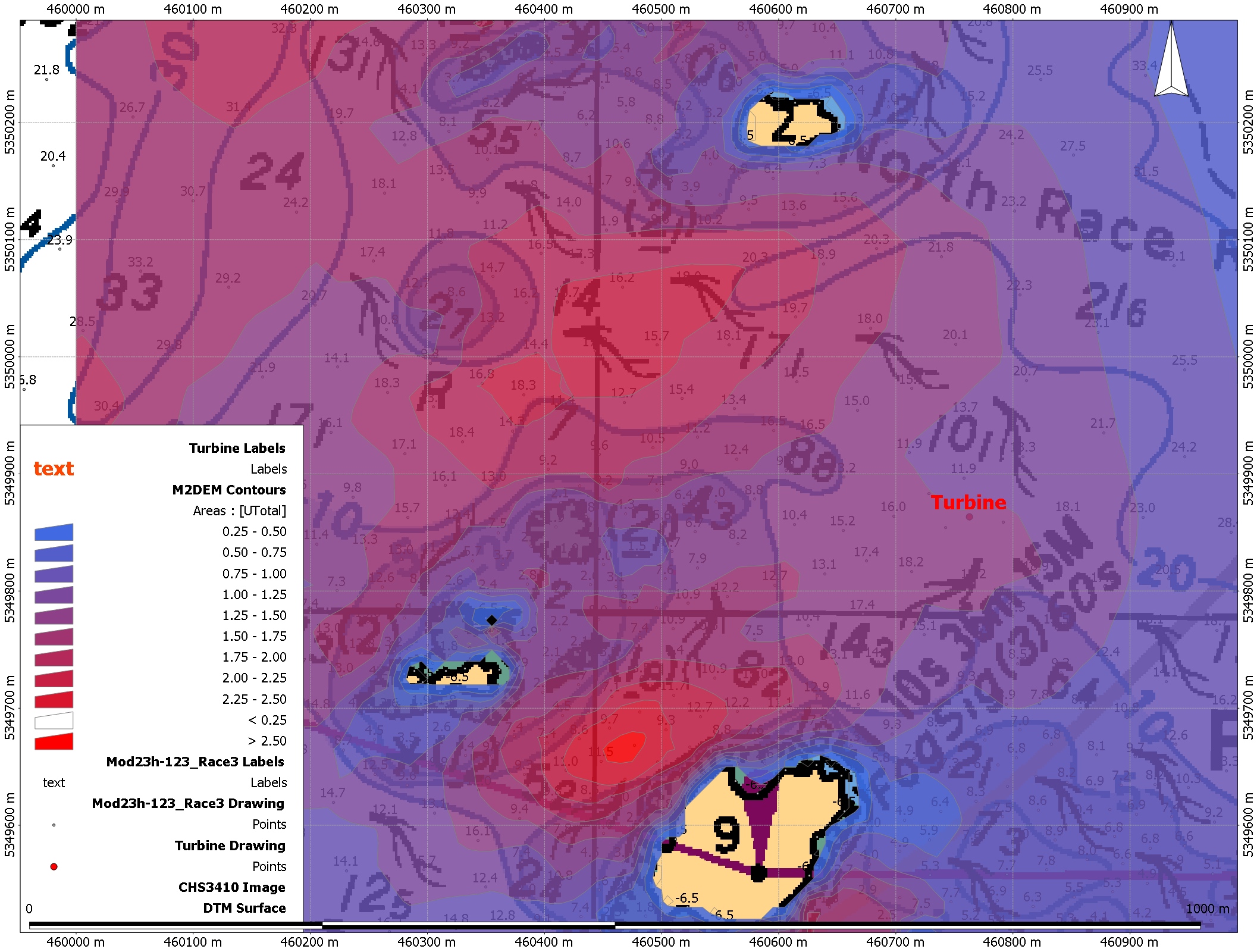 Map of Currents at Race Rocks from ADCP tests
Map of Currents at Race Rocks from ADCP tests See the video on wave and current measurement using the Acoustic Wave and Current instrument.
See the video on wave and current measurement using the Acoustic Wave and Current instrument. Water Properties in Juan de Fuca
Water Properties in Juan de Fuca Field Lab on Current Studies using Drogues.
Field Lab on Current Studies using Drogues. Oceanographic
Oceanographic Kalle Kallestrom’s essay on The biotic associations on the Current meter Block
Kalle Kallestrom’s essay on The biotic associations on the Current meter Block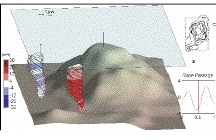 Stratified Tidal Flow over a Bump
Stratified Tidal Flow over a Bump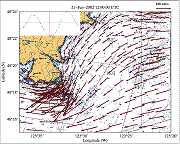 MATLAB charts of barotropic currents to the east of Race Rocks.
MATLAB charts of barotropic currents to the east of Race Rocks. Link to the Tidal Current Power Project
Link to the Tidal Current Power Project