Debates of the Senate (Hansard)
1st Session, 39th Parliament,
Volume 143, Issue 44
Wednesday, November 1, 2006
The Honourable Noël A. Kinsella, Speaker
Heritage Lighthouse Protection Bill
 Second Reading—Debate Adjourned
Second Reading—Debate Adjourned
Hon. Pat Carney moved second reading of Bill S-220, to protect heritage lighthouses.
She said: Honourable senators, this bill represents the sixth attempt in as many years to grant protection to heritage lighthouses of Canada. It was introduced five times previously, including during the Second Session of the Thirty-sixth Parliament, the First, Second and Third Sessions of the Thirty-seventh Parliament, and the First Session of the Thirty-eighth Parliament, and it has proceeded to committee stage in the other place. It never received Royal Assent before those parliaments rose.
While this bill was co-authored by me and the late Senator Forrestall, it was introduced five times by him, and it is in his memory that I speak today.
Despite the broad support in Parliament for this bill from all parties, the fact that we have not been able to enact it thus far represents a legislative embarrassment. It should be noted that this bill is supported in principle by the Departments of the Environment, Heritage and Fisheries and Oceans. Aside from the obvious negative political optics of such failure, even more regrettable is the practical damage being sustained by the lighthouses no longer in operation and the loss to the communities they have served, and where they stand as a proud pillar of heritage. Each day that goes by without the kind of legal protection afforded by the heritage lighthouse protection bill is a day that lighthouses are left exposed to neglect.
This bill addresses the problem that lighthouses, once deemed to be surplus to operational requirements, have no mechanism for their preservation. In the past they have been blown up, burned down, jack-hammered or left prey to vandalism, because the operational departments have no means of transferring them to interested community groups that are prepared to take on their maintenance. The present heritage designations are too restrictive to apply to most and do not provide a public consultation process.
The main feature of this bill is to facilitate the designation and preservation of heritage lighthouses as part of Canada’s culture and history, and to protect them from being altered or disposed of without public consultation. The bill defines heritage lighthouses as any lighthouse, together with all buildings and other works belonging thereto and in connection with which, as designated by the minister on the recommendation of the board as a heritage lighthouse.
The board referred to is the National Historic Sites and Monuments Board.
It defines “alter” as “to change in any manner” and includes “to restore or renovate” but does not include the performance of routine maintenance and repairs.
Honourable senators, I could take the time of the Senate to read the other main purposes of this short bill, but it would serve the interests of the Senate better to move this bill into committee where these aspects can be addressed.
The key to this bill is that the Canadian public will be consulted before any lighthouse is disposed of or destroyed, because currently there is no method by which to protect those structures.
The substantive provisions of this bill remain the same as they were the past five times it was introduced, and each time it received unanimous support in this chamber. I have been in communication with the government and believe that there may be minor amendments made to the bill at committee stage to align it with other legislation that was passed since this bill was first proposed.
I hope this bill can be referred to committee today.
Hon. Jim Munson: Honourable senators, I agree that this bill should be sent to the appropriate committee today. I have a keen interest in this bill. My great-great-uncle, James Munson, was the first lighthouse keeper in Cape Enrage, New Brunswick. It is a wonderful place just outside of Fundy National Park. It is the home of regulation-sized Munsons. I somehow got short shrift.
It is a great historical story which must be put on the record. I would like to speak to this bill at report stage when it returns from committee.
The Hon. the Speaker: Are honourable senators ready for the question?
Some Hon. Senators: Question!
Hon. Gerald J. Comeau (Deputy Leader of the Government): I move the adjournment of the debate.
Senator Carney: Honourable senators, it was my understanding from my house leader that this bill would go to committee today. Can I be told why the deputy leader has moved the adjournment of the debate when it has been agreed with the opposition and the committee that it be sent to committee?
Senator Comeau: There is no agreement that it would be sent to committee today.
On motion of Senator Comeau, debate adjourned.
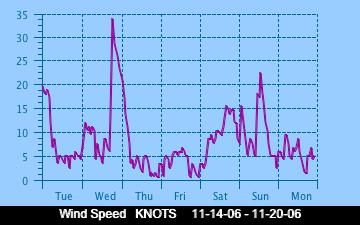
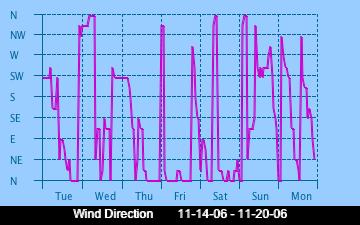
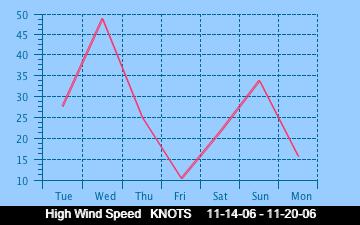
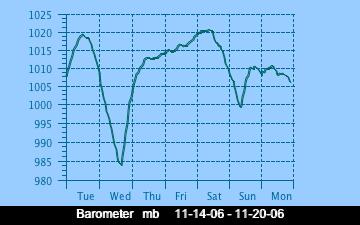
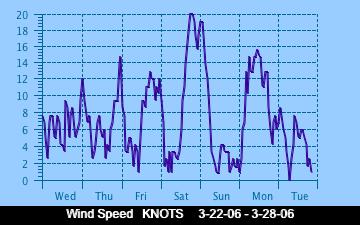
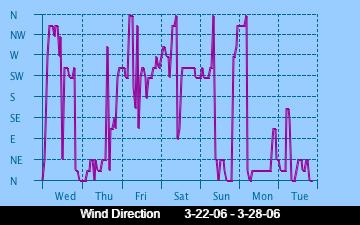
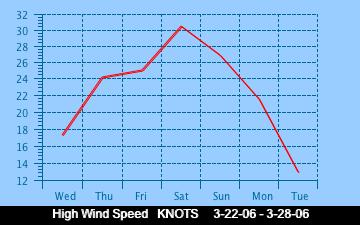
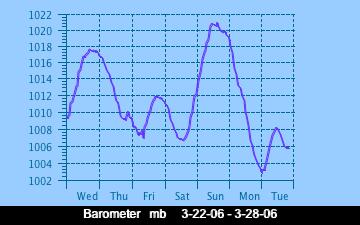
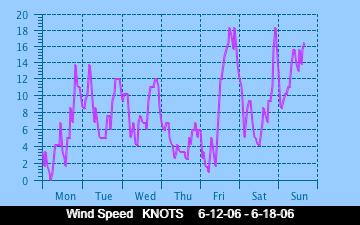
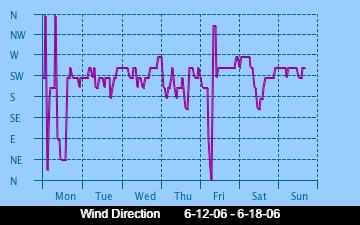
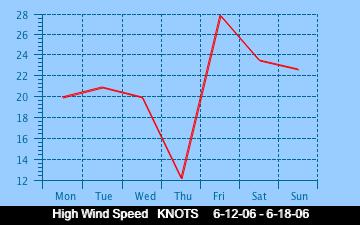
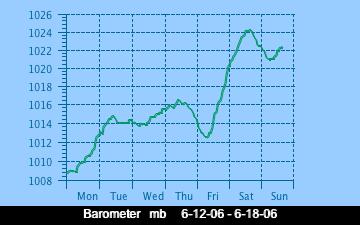
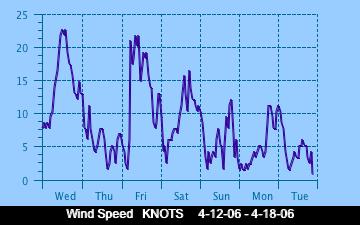
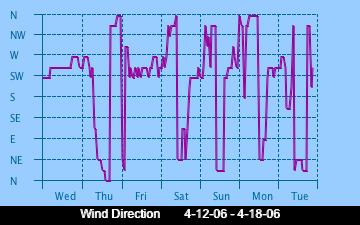
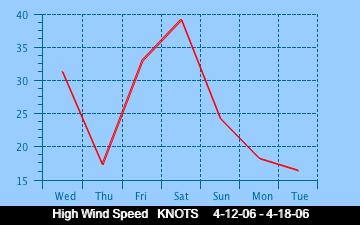
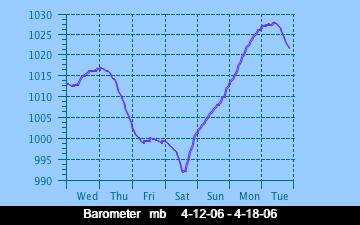
 The current Humidity, measured by a sensor 1.5 metres above the rock surface at Race Rocks. Humidity in concert with Temperature, Sunlight and Wind is an important factor which all organisms have to tolerate or adjust to at Race Rocks. The humidity changes widely in a number of micro ecosystems, even in the intertidal area, such as in crevices and under vegetation.
The current Humidity, measured by a sensor 1.5 metres above the rock surface at Race Rocks. Humidity in concert with Temperature, Sunlight and Wind is an important factor which all organisms have to tolerate or adjust to at Race Rocks. The humidity changes widely in a number of micro ecosystems, even in the intertidal area, such as in crevices and under vegetation.